Detailed introduction to Python operators
Python Arithmetic Operator
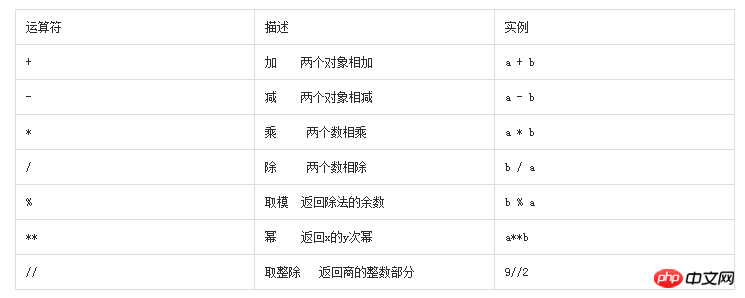
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
a = 21
b = 10
c = 0
c = a + b
print ("1.c的值为:",c)
c = a - b
print ("2.c的值为:",c)
c = a * b
print ("3.c的值为:",c)
c = a / b
print ("4.c的值为:",c)
c = a % b
print ("5.c的值为:",c)
# 修改变量 a 、b 、c
a = 2
b = 3
c = a**b
print ("6.c的值为:",c)
a = 10
b = 5
c = a//b
print ("7.c的值为:",c)The above example output result:
1.c的值为: 31 2.c的值为: 11 3.c的值为: 210 4.c的值为: 2.1 5.c的值为: 1 6.c的值为: 8 7.c的值为: 2
Python Comparison Operator
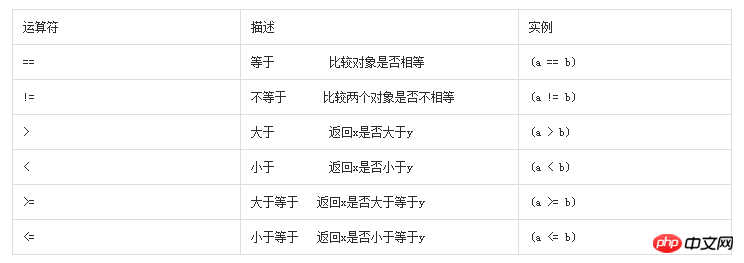
The following examples demonstrate the operation of all comparison operators in Python:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
a = 21
b = 10
c = 0
if (a == b):
print ("1. a 等于 b")
else:
print ("1. a 不等于 b")
if ( a != b):
print ("2. a 不等于 b")
else:
print ("2. a 等于 b")
if ( a < b ):
print ("4. a 小于 b")
else:
print ("4. a 大于 b")
if ( a > b ):
print ("5. a 大于 b")
else:
print ("6. a 小于 b")
if ( a >= b ):
print ("7. a 大于等于 b")
else:
print ("7. a 小于 b ")
if ( a <= b):
print ("8. a 小于等于 b")
else:
print ("8. a 大于 b")The output results of the above examples:
1. a 不等于 b 2. a 不等于 b 4. a 大于 b 5. a 大于 b 7. a 大于等于 b 8. a 大于 b
Python assignment operators
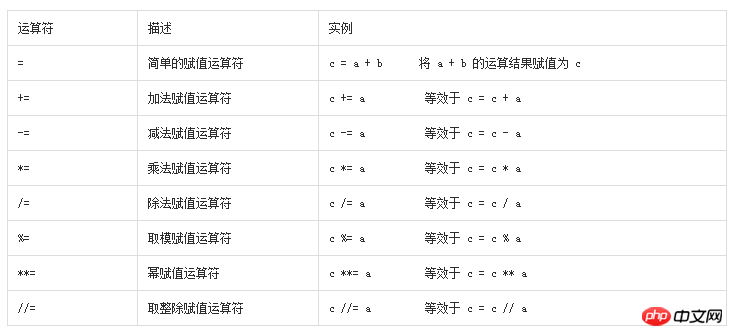
The following examples demonstrate the operation of all assignment operators in Python:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
a = 21
b = 10
c = 0
c = a + b
print ("1 - c 的值为:", c)
c += a
print ("2 - c 的值为:", c)
c *= a
print ("3 - c 的值为:", c)
c /= a
print ("4 - c 的值为:", c)
c = 2
c %= a
print ("5 - c 的值为:", c)
c **= a
print ("6 - c 的值为:", c)
c //= a
print ("7 - c 的值为:", c)The output results of the above examples:
1 - c 的值为: 31 2 - c 的值为: 52 3 - c 的值为: 1092 4 - c 的值为: 52.0 5 - c 的值为: 2 6 - c 的值为: 2097152 7 - c 的值为: 99864
Python logical operators
The following examples demonstrate Python Operations of all logical operators:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
a = 21
b = 10
if ( a and b ):
print ("1 - 变量 a 和 b 都为 true")
else:
print ("1 - 变量 a 和 b 有一个不为 true")
if ( a or b ):
print ("2 - 变量 a 和 b 都为 true,或其中一个变量为 true")
else:
print ("2 - 变量 a 和 b 都不为 true")
# 修改变量 a 的值
a = 0
if ( a and b ):
print ("3 - 变量 a 和 b 都为 true")
else:
print ("3 - 变量 a 和 b 有一个不为 true")
if ( a or b ):
print ("4 - 变量 a 和 b 都为 true,或其中一个变量为 true")
else:
print ("4 - 变量 a 和 b 都不为 true")
if not( a and b ):
print ("5 - 变量 a 和 b 都为 false,或其中一个变量为 false")
else:
print ("5 - 变量 a 和 b 都为 true")Output results of the above examples:
1 - 变量 a 和 b 都为 true 2 - 变量 a 和 b 都为 true,或其中一个变量为 true 3 - 变量 a 和 b 有一个不为 true 4 - 变量 a 和 b 都为 true,或其中一个变量为 true 5 - 变量 a 和 b 都为 false,或其中一个变量为 false
Python member operators

The following examples demonstrate Python Operations of all member operators
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
a = 10
b = 20
list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ];
if ( a in list ):
print ("1 - 变量 a 在给定的列表中 list 中")
else:
print ("1 - 变量 a 不在给定的列表中 list 中")
if ( b not in list ):
print ("2 - 变量 b 不在给定的列表中 list 中")
else:
print ("2 - 变量 b 在给定的列表中 list 中")
# 修改变量 a 的值
a = 2
if ( a in list ):
print ("3 - 变量 a 在给定的列表中 list 中")
else:
print ("3 - 变量 a 不在给定的列表中 list 中")The above example output results:
1 - 变量 a 不在给定的列表中 list 中 2 - 变量 b 不在给定的列表中 list 中 3 - 变量 a 在给定的列表中 list 中
Python operator priority
The following table lists all operations from the highest to the lowest priority Symbols:
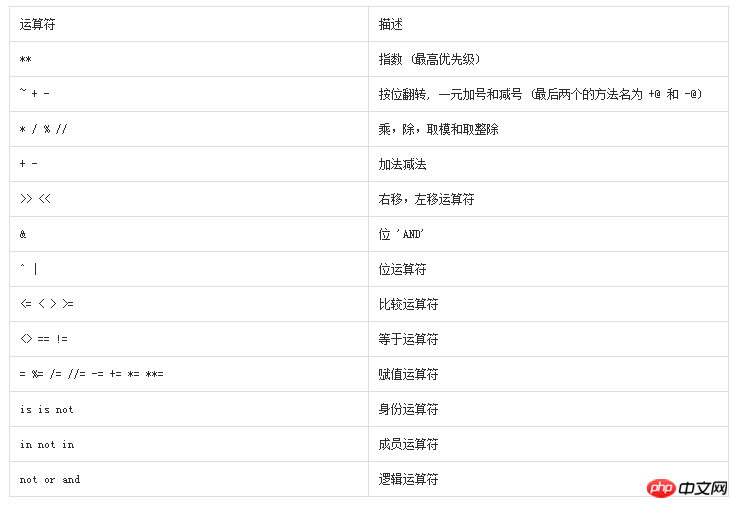
The following example demonstrates the operation of the precedence of all operators in Python:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
a = 20
b = 10
c = 15
d = 5
e = 0
e = (a + b) * c / d #( 30 * 15 ) / 5
print ("(a + b) * c / d 运算结果为:", e)
e = ((a + b) * c) / d # (30 * 15 ) / 5
print ("((a + b) * c) / d 运算结果为:", e)
e = (a + b) * (c / d); # (30) * (15/5)
print ("(a + b) * (c / d) 运算结果为:", e)
e = a + (b * c) / d; # 20 + (150/5)
print ("a + (b * c) / d 运算结果为:", e)The output result of the above example:
(a + b) * c / d 运算结果为: 90.0 ((a + b) * c) / d 运算结果为: 90.0 (a + b) * (c / d) 运算结果为: 90.0 a + (b * c) / d 运算结果为: 50.0
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to Python operators. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1421
1421
 52
52
 1315
1315
 25
25
 1266
1266
 29
29
 1239
1239
 24
24
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang is better than Python in terms of performance and scalability. 1) Golang's compilation-type characteristics and efficient concurrency model make it perform well in high concurrency scenarios. 2) Python, as an interpreted language, executes slowly, but can optimize performance through tools such as Cython.
 How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Running Python code in Notepad requires the Python executable and NppExec plug-in to be installed. After installing Python and adding PATH to it, configure the command "python" and the parameter "{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}" in the NppExec plug-in to run Python code in Notepad through the shortcut key "F6".




