 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 How to deal with sparse matrices? Python implementation of sparse matrix tutorial
How to deal with sparse matrices? Python implementation of sparse matrix tutorial
How to deal with sparse matrices? Python implementation of sparse matrix tutorial
This article mainly introduces the example code for implementing sparse matrix in python. The editor thinks it is quite good. Now I will share it with you and give it as a reference. Let’s follow the editor to take a look
In engineering practice, in most cases, large matrices are generally sparse matrices, so how to deal with sparse matrices is very important in practice. This article takes the implementation in Python as an example. First, let's explore how sparse matrices are stored and represented.
1. A preliminary study on the sparse module
In the scipy module in python, there is a module called the sparse module, which is specifically designed to solve sparse matrices. Most of the content of this article is actually based on the sparse module.
The first step is to import the sparse module
>>> from scipy import sparse
Then help, let’s take a look first
>>> help(sparse)
Find directly the part we are most concerned about:
Usage information
=================
There are seven available sparse matrix types:
1. csc_matrix: Compressed Sparse Column format
2. csr_matrix: Compressed Sparse Row format
3. bsr_matrix: Block Sparse Row format
4. lil_matrix: List of Lists format
5. dok_matrix: Dictionary of Keys format
6. coo_matrix: COOrdinate format (aka IJV, triplet format)
7. dia_matrix: DIAgonal format
To construct a matrix efficiently, use either dok_matrix or lil_matrix.
The lil_matrix class supports basic slicing and fancy
indexing with a similar syntax to NumPy arrays. As illustrated below,
the COO format may also be used to efficiently construct matrices.
To perform manipulations such as multiplication or inversion, first
convert the matrix to either CSC or CSR format. The lil_matrix format is
row-based, so conversion to CSR is efficient, whereas conversion to CSC
is less so.
All conversions among the CSR, CSC, and COO formats are efficient,
linear-time operations.Through this description, we have a general understanding of the sparse module. There are 7 ways to store sparse matrices in the sparse module. Next, we will introduce these 7 methods one by one.
2.coo_matrix
coo_matrix is the simplest storage method. Use three arrays row, col and data to store the information of non-zero elements. The three arrays have the same length, row holds the row of elements, col holds the column of elements, and data holds the value of the element. Generally speaking, coo_matrix is mainly used to create matrices, because coo_matrix cannot add, delete, or modify elements of the matrix. Once the matrix is successfully created, it will be converted into other forms of matrices.
>>> row = [2,2,3,2] >>> col = [3,4,2,3] >>> c = sparse.coo_matrix((data,(row,col)),shape=(5,6)) >>> print c.toarray() [[0 0 0 0 0 0] [0 0 0 0 0 0] [0 0 0 5 2 0] [0 0 3 0 0 0] [0 0 0 0 0 0]]
One thing to note is that when using coo_matrix to create a matrix, the same row and column coordinates can appear multiple times. After the matrix is actually created, the corresponding coordinate values will be added up to get the final result.
3.dok_matrix and lil_matrix
The scenario where dok_matrix and lil_matrix are applicable is to gradually add elements of the matrix. The strategy of doc_matrix is to use a dictionary to record the elements in the matrix that are not 0. Naturally, the key of the dictionary stores the ancestor of the position information of the recorded element, and the value is the specific value of the recorded element.
>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy.sparse import dok_matrix >>> S = dok_matrix((5, 5), dtype=np.float32) >>> for i in range(5): ... for j in range(5): ... S[i, j] = i + j ... >>> print S.toarray() [[ 0. 1. 2. 3. 4.] [ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.] [ 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.] [ 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.] [ 4. 5. 6. 7. 8.]]
lil_matrix uses two lists to store non-0 elements. data stores the non-zero elements in each row, and rows stores the columns in which the non-zero elements are located. This format is also great for adding elements one at a time and getting row-related data quickly.
>>> from scipy.sparse import lil_matrix >>> l = lil_matrix((6,5)) >>> l[2,3] = 1 >>> l[3,4] = 2 >>> l[3,2] = 3 >>> print l.toarray() [[ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] [ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] [ 0. 0. 0. 1. 0.] [ 0. 0. 3. 0. 2.] [ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.] [ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]] >>> print l.data [[] [] [1.0] [3.0, 2.0] [] []] >>> print l.rows [[] [] [3] [2, 4] [] []]
It can be easily seen from the above analysis that the above two methods of constructing sparse matrices are generally used to construct matrices by gradually adding non-zero elements, and then convert them into other methods that can be quickly calculated. Matrix storage method.
4.dia_matrix
This is a diagonal storage method. Where columns represent diagonals and rows represent rows. If the elements on the diagonal are all 0, they are omitted.
If the original matrix is a diagonal matrix, the compression rate will be very high.
If I find a picture on the Internet, everyone can easily understand the principle.

5.csr_matrix and csc_matrix
csr_matrix, the full name is Compressed Sparse Row, is a row-based processing of matrices compressed. CSR requires three types of data: numerical values, column numbers, and row offsets. CSR is a coding method in which the meanings of numerical values and column numbers are consistent with those in coo. The row offset indicates the starting offset position of the first element of a row in values.
I also found a picture on the Internet that can better reflect the principle.
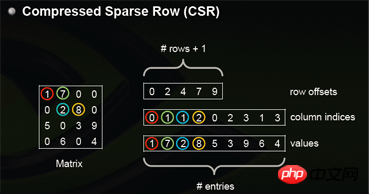
Let’s see how to use it in python: How about
>>> from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
>>> indptr = np.array([0, 2, 3, 6])
>>> indices = np.array([0, 2, 2, 0, 1, 2])
>>> data = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
>>> csr_matrix((data, indices, indptr), shape=(3, 3)).toarray()
array([[1, 0, 2],
[0, 0, 3],
[4, 5, 6]]), is it not difficult to understand?
Let’s take a look at what the document says
Notes | ----- | | Sparse matrices can be used in arithmetic operations: they support | addition, subtraction, multiplication, pision, and matrix power. | | Advantages of the CSR format | - efficient arithmetic operations CSR + CSR, CSR * CSR, etc. | - efficient row slicing | - fast matrix vector products | | Disadvantages of the CSR format | - slow column slicing operations (consider CSC) | - changes to the sparsity structure are expensive (consider LIL or DOK)
It is not difficult to see that csr_matrix is more suitable for real matrix operations.
As for csc_matrix, it is similar to csr_matrix, but it is compressed based on columns and will not be introduced separately.
6.bsr_matrix
Block Sparse Row format, as the name suggests, compresses the matrix based on the idea of blocking.

The above is the detailed content of How to deal with sparse matrices? Python implementation of sparse matrix tutorial. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1677
1677
 14
14
 1431
1431
 52
52
 1334
1334
 25
25
 1279
1279
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang is better than Python in terms of performance and scalability. 1) Golang's compilation-type characteristics and efficient concurrency model make it perform well in high concurrency scenarios. 2) Python, as an interpreted language, executes slowly, but can optimize performance through tools such as Cython.
 How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Running Python code in Notepad requires the Python executable and NppExec plug-in to be installed. After installing Python and adding PATH to it, configure the command "python" and the parameter "{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}" in the NppExec plug-in to run Python code in Notepad through the shortcut key "F6".
 Golang vs. Python: Key Differences and Similarities
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Golang vs. Python: Key Differences and Similarities
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Golang and Python each have their own advantages: Golang is suitable for high performance and concurrent programming, while Python is suitable for data science and web development. Golang is known for its concurrency model and efficient performance, while Python is known for its concise syntax and rich library ecosystem.
 Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python is easier to learn and use, while C is more powerful but complex. 1. Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners. Dynamic typing and automatic memory management make it easy to use, but may cause runtime errors. 2.C provides low-level control and advanced features, suitable for high-performance applications, but has a high learning threshold and requires manual memory and type safety management.



