 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Example of how flask_sqlalchemy operates the database in python
Example of how flask_sqlalchemy operates the database in python
Example of how flask_sqlalchemy operates the database in python
This article brings you an example of how flask_sqlalchemy operates the database in Python. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
flask_sqlalchemy
Uses the Object-Relational Mapper (ORM) framework, which abstracts low-level database operation instructions into high-level object-oriented operations. In other words, if we use the database engine directly, we have to write SQL operation statements, but if we use the ORM framework, we can simplify the operation of database entities such as tables and documents into Python object operations
SQLAlchemy has become the standard for ORM in the Python world. Flask is a lightweight web framework that can be freely used with ORM. Flask-sqlalchemy is a plug-in specifically designed for Flask.
In Flask-SQLAlchemy, the database is specified using a URL.
MySQL --> mysql://username:password@hostname/database
Installation
pip install flask-sqlalchemy
Database operation
##1. How to create a database operation connection
from flask import Flask from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy app = Flask(__name__) db = SQLAlchemy(app) app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'mysql+pymysql://root:sheen@localhost/zaj_sql' app.config['SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS'] = True class User(db.Model): id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True) username = db.Column(db.String(80), unique=True) email = db.Column(db.String(120), unique=True)
db.create_all()
admin = User('admin', 'admin@example.com')
guest = User('guest', 'guest@example.com')db.session.add(admin) db.session.add(guest) db.session.commit()
2. Create relationships Type database table
SQLAlchemy is connected to a relational database. The best thing about relational data is relationships. Therefore, we will create an application that uses two related tables as an example.The most common relationship is the one-to-many relationship. Because relationships are declared before they are created, you can use strings to refer to classes that have not yet been created
Relationships are represented using the relationship() function. However, foreign keys must be declared separately using the class sqlalchemy.schema.ForeignKey.
from datetime import datetime
from flask_bootstrap import Bootstrap
from flask_wtf import FlaskForm
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
from flask import Flask
import pymysql
from sqlalchemy import desc
app = Flask(__name__)
db = SQLAlchemy(app)
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'mysql+pymysql://root:sheen@localhost/zaj_sql'
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS'] = True
bootstrap = Bootstrap(app)
class User(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.Integer,autoincrement=True,primary_key=True)
name = db.Column(db.String(50),unique=True)
passwd = db.Column(db.String(100))
add_time = db.Column(db.DATETIME,default=datetime.now())
gender = db.Column(db.BOOLEAN,default=True)
role_id = db.Column(db.INTEGER,db.ForeignKey('role.id'))
def __repr__(self):
return '<user:>' %(self.name)
class Role(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.INTEGER,autoincrement=True,primary_key=True)
name = db.Column(db.String(50),unique=True)
users = db.relationship('User',backref='role')
# 给Role模型添加users属性
# backref 是定义反向引用
def __repr__(self):
return '<role:>' % (self.name)
if __name__ =='__main__':
# 1. 创建数据库表
# db.drop_all()
# db.create_all()
# # 2. 创建role数据库表数据
role_1 = Role(name='超级会员')
role_2 = Role(name='普通会员')
db.session.add(role_1)
db.session.add(role_2)
db.session.commit()
# # # 3. 添加user表内数据,100个用户,50个为超级会员,50个为普通会员
for i in range(1,13):
if i%2 == 0:
u = User(name='sheen'+str(i),passwd='sheen',role_id=1)
db.session.add(u)
else:
u = User(name='star'+str(i),passwd='star',role_id=2)
db.session.add(u)
db.session.commit()</role:></user:>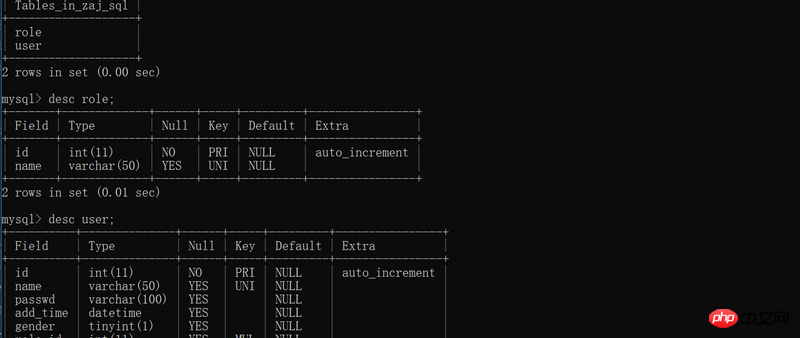
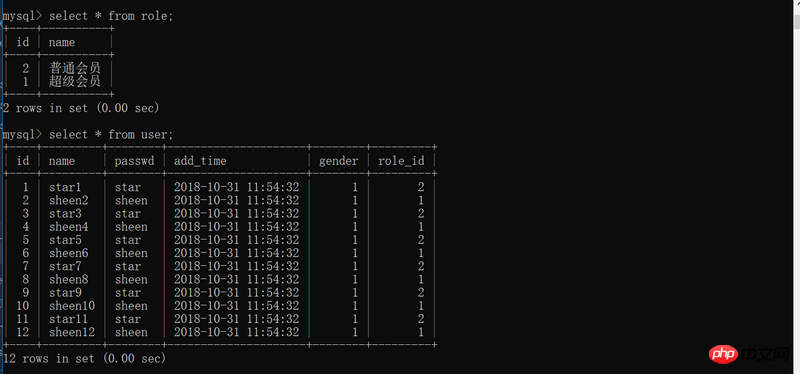
print('角色',Role.query.all())
print('用户',User.query.all())# select * from tablename where xxx=xxxxx print(User.query.filter_by(role_id=1).all()) print(Role.query.filter_by().all()) print(User.query.filter_by(role_id=2).all())
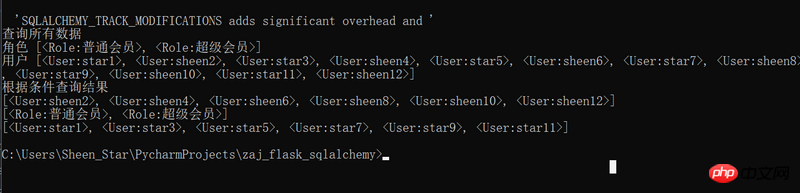
print('进行数据更新',end='\n')
u =User.query.filter_by(name='sheen2').first()
print(u)
u.passwd = '123'
db.session.add(u)
db.session.commit()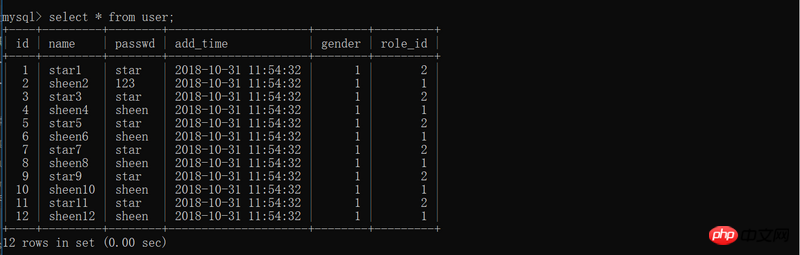
print('数据筛选', end='\n')
user = User.query.filter(User.role_id==1)
print(user) 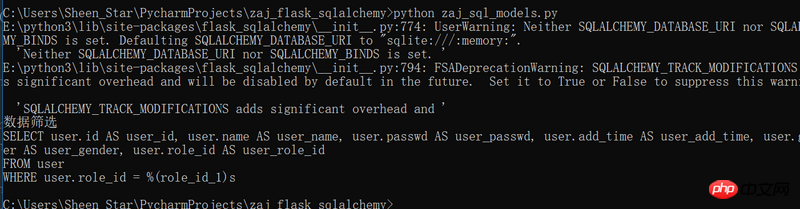
print('限制查询数据的显示', end='\n')
users = User.query.filter_by(role_id=1).limit(3).all()
print(users) print('数据再处理', end='\n')
users = User.query.filter_by(role_id=1).order_by(desc(User.name)).all()
print(users)print('多个过滤函数', end='\n')
users = User.query.filter_by(role_id=1).order_by(desc(User.name)).limit(3).offset(1).all()
print(users)
users = User.query.filter_by(role_id=1).order_by(desc(User.name)).slice(1,4).all()
print(users)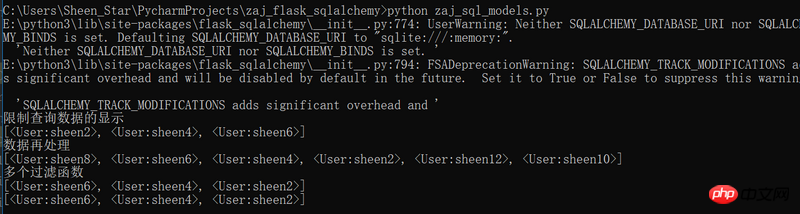
print('分页显示', end='\n')
users = User.query.paginate(1,5)
print(users.items)
users = User.query.paginate(2, 5)
print(users.items)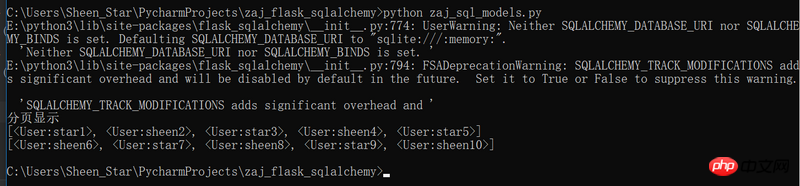
The above is the detailed content of Example of how flask_sqlalchemy operates the database in python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1662
1662
 14
14
 1419
1419
 52
52
 1313
1313
 25
25
 1262
1262
 29
29
 1235
1235
 24
24
 Explain the purpose of foreign keys in MySQL.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Explain the purpose of foreign keys in MySQL.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:17 AM
In MySQL, the function of foreign keys is to establish the relationship between tables and ensure the consistency and integrity of the data. Foreign keys maintain the effectiveness of data through reference integrity checks and cascading operations. Pay attention to performance optimization and avoid common errors when using them.
 Compare and contrast MySQL and MariaDB.
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Compare and contrast MySQL and MariaDB.
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:08 AM
The main difference between MySQL and MariaDB is performance, functionality and license: 1. MySQL is developed by Oracle, and MariaDB is its fork. 2. MariaDB may perform better in high load environments. 3.MariaDB provides more storage engines and functions. 4.MySQL adopts a dual license, and MariaDB is completely open source. The existing infrastructure, performance requirements, functional requirements and license costs should be taken into account when choosing.
 SQL vs. MySQL: Clarifying the Relationship Between the Two
Apr 24, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL vs. MySQL: Clarifying the Relationship Between the Two
Apr 24, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL is a standard language for managing relational databases, while MySQL is a database management system that uses SQL. SQL defines ways to interact with a database, including CRUD operations, while MySQL implements the SQL standard and provides additional features such as stored procedures and triggers.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Development Environments and Tools
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Development Environments and Tools
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Both Python and JavaScript's choices in development environments are important. 1) Python's development environment includes PyCharm, JupyterNotebook and Anaconda, which are suitable for data science and rapid prototyping. 2) The development environment of JavaScript includes Node.js, VSCode and Webpack, which are suitable for front-end and back-end development. Choosing the right tools according to project needs can improve development efficiency and project success rate.
 The Future of Python and JavaScript: Trends and Predictions
Apr 27, 2025 am 12:21 AM
The Future of Python and JavaScript: Trends and Predictions
Apr 27, 2025 am 12:21 AM
The future trends of Python and JavaScript include: 1. Python will consolidate its position in the fields of scientific computing and AI, 2. JavaScript will promote the development of web technology, 3. Cross-platform development will become a hot topic, and 4. Performance optimization will be the focus. Both will continue to expand application scenarios in their respective fields and make more breakthroughs in performance.
 How to handle high DPI display in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 09:57 PM
How to handle high DPI display in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 09:57 PM
Handling high DPI display in C can be achieved through the following steps: 1) Understand DPI and scaling, use the operating system API to obtain DPI information and adjust the graphics output; 2) Handle cross-platform compatibility, use cross-platform graphics libraries such as SDL or Qt; 3) Perform performance optimization, improve performance through cache, hardware acceleration, and dynamic adjustment of the details level; 4) Solve common problems, such as blurred text and interface elements are too small, and solve by correctly applying DPI scaling.
 An efficient way to batch insert data in MySQL
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:18 PM
An efficient way to batch insert data in MySQL
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:18 PM
Efficient methods for batch inserting data in MySQL include: 1. Using INSERTINTO...VALUES syntax, 2. Using LOADDATAINFILE command, 3. Using transaction processing, 4. Adjust batch size, 5. Disable indexing, 6. Using INSERTIGNORE or INSERT...ONDUPLICATEKEYUPDATE, these methods can significantly improve database operation efficiency.
 How to uninstall MySQL and clean residual files
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:03 PM
How to uninstall MySQL and clean residual files
Apr 29, 2025 pm 04:03 PM
To safely and thoroughly uninstall MySQL and clean all residual files, follow the following steps: 1. Stop MySQL service; 2. Uninstall MySQL packages; 3. Clean configuration files and data directories; 4. Verify that the uninstallation is thorough.



