 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Summary of the most common python interview questions and answers
Summary of the most common python interview questions and answers
Summary of the most common python interview questions and answers

This article brings you a summary of the most common python interview questions and answers. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be useful to you. Helps.
Python Newbies must be familiar with the basics of Python before seeking a Python programming job. The technical team of the programming website DataFlair has shared a collection of the most common Python interview questions in 2018. There are both basic Python interview questions and advanced version questions to guide you in preparing for the interview. The questions are all accompanied by answers. Interview questions include coding, data structures, scripting and other topics. This article is the previous one.
Recommended related articles: "2020 python interview questions summary (latest)"
Q 1: What are the features and advantages of Python?
As an introductory programming language, Python mainly has the following features and advantages:
Interpretable
Has dynamic characteristics
Object-oriented
Concise and simple
Open source
Has strong community support
Of course, in fact, the advantages of Python go beyond that.
Q 2: What is the difference between deep copy and shallow copy?
Answer: Deep copy is to copy one object to another object, which means that if you make changes to the copy of an object, it will not affect the original object. In Python, we use the function deepcopy() to perform deep copy and import the module copy, as shown below:
>>> import copy >>> b=copy.deepcopy(a)
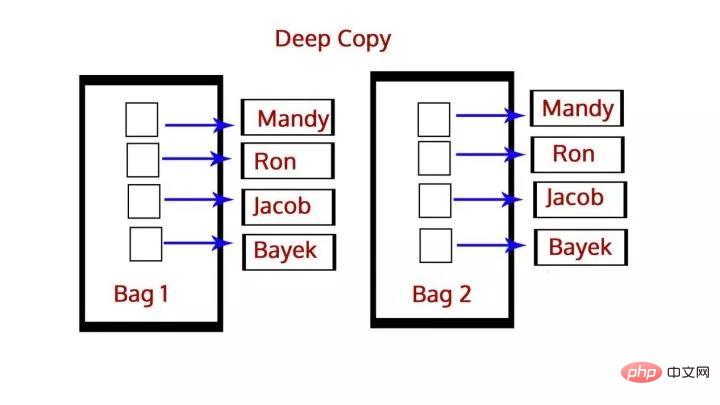
And shallow copy copies the reference of an object to on another object, so if we make changes in the copy, it will affect the original object. We use the function function() to perform a shallow copy, using the following:
>>> b=copy.copy(a)
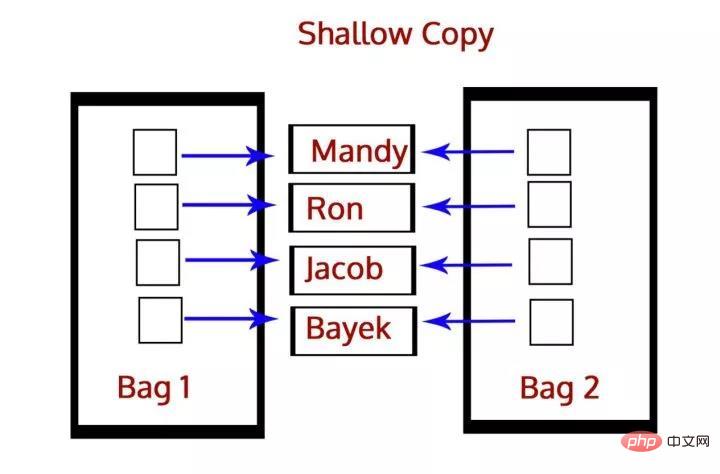
Q 3. What is the difference between a list and a tuple?
Answer: The main difference between the two is that lists are mutable, while tuples are immutable. For example, as shown below:
>>> mylist=[1,3,3] >>> mylist[1]=2 >>> mytuple=(1,3,3) >>> mytuple[1]=2 Traceback (most recent call last): File "<pyshell#97>", line 1, in <module> mytuple[1]=2
The following error will appear:
TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment
For more information about lists and tuples, you can check here:
https://data-flair.training/blogs/python-tuples-vs-lists/
Q4 to Q20 are basic Python interview questions for novices, but experienced people can also do it Check out these questions to review basic concepts.
Q 4. Explain the ternary operator in Python
Unlike C, we don’t have ?: in Python, but we have this:
[on true] if [expression] else [on false]
If the expression is True, execute the statement in [on true]. Otherwise, execute the statement in [on false].
Here’s how to use it:
>>> a,b=2,3 >>> min=a if a<b else b >>> min
Run result:
2
>>> print("Hi") if a<b else print("Bye")Run result:
Hi
Q 5. In How to implement multithreading in Python?
A thread is a lightweight process. Multi-threading allows us to execute multiple threads at a time. We all know that Python is a multi-threaded language with a built-in multi-threading toolkit.
The GIL (Global Interpreter Lock) in Python ensures execution of a single thread at a time. One thread saves the GIL and performs some operations before passing it to the next thread, which gives us the illusion of running in parallel. But in reality, it's just threads taking turns running on the CPU. Of course, all passing increases the memory pressure on program execution.
Q 6. Explain inheritance in Python
When a class inherits from another class, it is called a subclass/derived class, which inherits from Parent class/base class/super class. It inherits/gets all class members (properties and methods).
Inheritance allows us to reuse code and make it easier to create and maintain applications. Python supports the following types of inheritance:
Single inheritance: A class inherits from a single base class
Multiple inheritance: A class inherits from multiple base classes
Multi-level inheritance: One class inherits from a single base class, which in turn inherits from another base class
Hierarchical inheritance: multiple classes inherit from a single base class
Mixed inheritance: two or more types Mixing inheritance
For more information about inheritance, see:
https://data-flair.training/blogs/python-inheritance/
Q 7. What is Flask?
Flask is a lightweight web application framework written in Python. Its WSGI toolbox uses Werkzeug and its template engine uses Jinja2. Flask is licensed under BSD. Two of the environment dependencies are Werkzeug and jinja2, which means it does not need to rely on external libraries. Because of this, we call it a lightweight framework.
Flask sessions use signed cookies to allow users to view and modify session content. It logs information from one request to another. However, to modify the session, the user must have the secret Flask.secret_key.
Q 8. How is memory managed in Python?
Python 有一个私有堆空间来保存所有的对象和数据结构。作为开发者,我们无法访问它,是解释器在管理它。但是有了核心 API 后,我们可以访问一些工具。Python 内存管理器控制内存分配。
另外,内置垃圾回收器会回收使用所有的未使用内存,所以使其适用于堆空间。
Q 9. 解释 Python 中的 help() 和 dir() 函数
Help() 函数是一个内置函数,用于查看函数或模块用途的详细说明:
>>> import copy >>> help(copy.copy)
运行结果为:
Help on function copy in module copy: copy(x) Shallow copy operation on arbitrary Python objects. See the module’s __doc__ string for more info.
Dir() 函数也是 Python 内置函数,dir() 函数不带参数时,返回当前范围内的变量、方法和定义的类型列表;带参数时,返回参数的属性、方法列表。
以下实例展示了 dir 的使用方法:
>>> dir(copy.copy)
运行结果为:
[‘__annotations__’, ‘__call__’, ‘__class__’, ‘__closure__’, ‘__code__’, ‘__defaults__’, ‘__delattr__’, ‘__dict__’, ‘__dir__’, ‘__doc__’, ‘__eq__’, ‘__format__’, ‘__ge__’, ‘__get__’, ‘__getattribute__’, ‘__globals__’, ‘__gt__’, ‘__hash__’, ‘__init__’, ‘__init_subclass__’, ‘__kwdefaults__’, ‘__le__’, ‘__lt__’, ‘__module__’, ‘__name__’, ‘__ne__’, ‘__new__’, ‘__qualname__’, ‘__reduce__’, ‘__reduce_ex__’, ‘__repr__’, ‘__setattr__’, ‘__sizeof__’, ‘__str__’, ‘__subclasshook__’]
Q 10. 当退出 Python 时,是否释放全部内存?
答案是 No。循环引用其它对象或引用自全局命名空间的对象的模块,在 Python 退出时并非完全释放。
另外,也不会释放 C 库保留的内存部分。
Q 11. 什么是猴子补丁?
在运行期间动态修改一个类或模块。
>>> class A:
def func(self):
print("Hi")
>>> def monkey(self):
print "Hi, monkey"
>>> m.A.func = monkey
>>> a = m.A()
>>> a.func()运行结果为:
Hi, Monkey
Q 12. Python 中的字典是什么?
字典是 C++ 和 Java 等编程语言中所没有的东西,它具有键值对。
>>> roots={25:5,16:4,9:3,4:2,1:1}
>>> type(roots)
<class 'dict'>
>>> roots[9]运行结果为:
3
字典是不可变的,我们也能用一个推导式来创建它。
>>> roots={x**2:x for x in range(5,0,-1)}
>>> roots运行结果:
{25: 5, 16: 4, 9: 3, 4: 2, 1: 1}Q 13. 请解释使用 *args 和 **kwargs 的含义
当我们不知道向函数传递多少参数时,比如我们向传递一个列表或元组,我们就使用*args。
>>> def func(*args):
for i in args:
print(i)
>>> func(3,2,1,4,7)运行结果为:
3 2 1 4 7
在我们不知道该传递多少关键字参数时,使用**kwargs来收集关键字参数。
>>> def func(**kwargs):
for i in kwargs:
print(i,kwargs[i])
>>> func(a=1,b=2,c=7)运行结果为:
a.1 b.2 c.7
Q 14. 请写一个Python逻辑,计算一个文件中的大写字母数量
>>> import os
>>> os.chdir('C:\Users\lifei\Desktop')
>>> with open('Today.txt') as today:
count=0
for i in today.read():
if i.isupper():
count+=1运行结果:
26
Q 15. 什么是负索引?
我们先创建这样一个列表:
>>> mylist=[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]
负索引和正索引不同,它是从右边开始检索。
>>> mylist[-3]
运行结果:
6
它也能用于列表中的切片:
>>> mylist[-6:-1]
结果:
[3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
Q 16. 如何以就地操作方式打乱一个列表的元素?
为了达到这个目的,我们从random模块中导入shuffle()函数。
>>> from random import shuffle >>> shuffle(mylist) >>> mylist
运行结果:
[3, 4, 8, 0, 5, 7, 6, 2, 1]
Q 17. 解释Python中的join()和split()函数
Join()能让我们将指定字符添加至字符串中。 >>> ','.join('12345')
运行结果:
‘1,2,3,4,5’
Split()能让我们用指定字符分割字符串。
>>> '1,2,3,4,5'.split(',')
运行结果:
[‘1’, ‘2’, ‘3’, ‘4’, ‘5’]
Q 18. Python区分大小写吗?
如果能区分像myname和Myname这样的标识符,那么它就是区分大小写的。也就是说它很在乎大写和小写。我们可以用Python试一试:
>>> myname='Ayushi' >>> Myname Traceback (most recent call last): File "<pyshell#3>", line 1, in <module>
运行结果:
Myname NameError: name ‘Myname’ is not defined
可以看到,这里出现了NameError,所以Python是区分大小写的。
Q 19. Python中的标识符长度能有多长?
在Python中,标识符可以是任意长度。此外,我们在命名标识符时还必须遵守以下规则:
只能以下划线或者 A-Z/a-z 中的字母开头
其余部分可以使用 A-Z/a-z/0-9
区分大小写
关键字不能作为标识符,Python中共有如下关键字:
Q 20. 怎么移除一个字符串中的前导空格?
字符串中的前导空格就是出现在字符串中第一个非空格字符前的空格。我们使用方法Istrip()可以将它从字符串中移除。
>>> ' Ayushi '.lstrip()
结果:
‘Ayushi ‘
可以看到,该字符串既有前导字符,也有后缀字符,调用Istrip()去除了前导空格。如果我们想去除后缀空格,就用rstrip()方法。
>>> ' Ayushi '.rstrip()
结果:
‘ Ayushi’
从Q 21到Q 35是为有Python经验者准备的进阶版Python面试题。
Q 21. 怎样将字符串转换为小写?
我们使用lower()方法。
>>> 'AyuShi'.lower()
结果:
‘ayushi’
使用upper()方法可以将其转换为大写。
>>> 'AyuShi'.upper()
结果:
‘ayushi’
另外,使用isupper()和islower()方法检查字符串是否全为大写或小写。
>>> 'AyuShi'.isupper() False >>> 'AYUSHI'.isupper() True >>> 'ayushi'.islower() True >>> '@yu$hi'.islower() True >>> '@YU$HI'.isupper() True
那么,像@和$这样的字符既满足大写也满足小写。
Istitle()能告诉我们一个字符串是否为标题格式。
>>> 'The Corpse Bride'.istitle() True
Q 22. Python中的pass语句是什么?
在用Python写代码时,有时可能还没想好函数怎么写,只写了函数声明,但为了保证语法正确,必须输入一些东西,在这种情况下,我们会使用pass语句。
>>> def func(*args):
pass
>>>同样,break语句能让我们跳出循环。
>>> for i in range(7):
if i==3: break
print(i)结果:
0 1 2
最后,continue语句能让我们跳到下个循环。
>>> for i in range(7):
if i==3: continue
print(i)结果:
0 1 2 4 5 6
Q 23. Python中的闭包是什么?
当一个嵌套函数在其外部区域引用了一个值时,该嵌套函数就是一个闭包。其意义就是会记录这个值。
>>> def A(x):
def B():
print(x)
return B
>>> A(7)()结果:
17
更多关于闭包的知识,请参看这里:
https://data-flair.training/blogs/python-closure/
**Q 24. 解释一下Python中的//,%和 ** 运算符**
//运算符执行地板除法(向下取整除),它会返回整除结果的整数部分。 >>> 7//2 3
这里整除后会返回3.5。
同样地,执行取幂运算。ab会返回a的b次方。
>>> 2**10 1024
最后,%执行取模运算,返回除法的余数。
>>> 13%7 6 >>> 3.5%1.5 0.5
Q 24. 在Python中有多少种运算符?解释一下算数运算符。
在Python中,我们有7种运算符:算术运算符、关系运算符、赋值运算符、逻辑运算符、位运算符、成员运算符、身份运算符。
我们有7个算术运算符,能让我们对数值进行算术运算:
1.加号(+),将两个值相加
>>> 7+8 15
2.减号(-),将第一个值减去第二个值
>>> 7-8 -1
3.乘号(*),将两个值相乘
>>> 7*8 56
4.除号(/),用第二个值除以第一个值
>>> 7/8 0.875 >>> 1/1 1.0
5.向下取整除、取模和取幂运算,参见上个问题。
Q 25. 解释一下Python中的关系运算符
关系运算符用于比较两个值。
1.小于号(<),如果左边的值较小,则返回True。
>>> 'hi'<'Hi' False
2.大于号(>),如果左边的值较大,则返回True。
>>> 1.1+2.2>3.3 True
3.小于等于号(<=),如果左边的值小于或等于右边的值,则返回Ture。
>>> 3.0<=3 True
4.大于等于号(>=),如果左边的值大于或等于右边的值,则返回True。
>>> True>=False True
等于号(==),如果符号两边的值相等,则返回True。
>>> {1,3,2,2}=={1,2,3}
True不等于号(!=),如果符号两边的值不相等,则返回True。
>>> True!=0.1 True >>> False!=0.1 True
Q 26. 解释一下Python中的赋值运算符
这在Python面试中是个重要的面试问题。
我们将所有的算术运算符和赋值符号放在一起展示:
>>> a=7 >>> a+=1 >>> a 8 >>> a-=1 >>> a 7 >>> a*=2 >>> a 14 >>> a/=2 >>> a 7.0 >>> a**=2 >>> a 49 >>> a//=3 >>> a 16.0 >>> a%=4 >>> a 0.0
Q 27. 解释一下Python中的逻辑运算符
Python中有3个逻辑运算符:and,or,not。
>>> False and True False >>> 7<7 or True True >>> not 2==2 False
Q 28. 解释一下Python中的成员运算符
通过成员运算符‘in’和‘not in’,我们可以确认一个值是否是另一个值的成员。
>>> 'me' in 'disappointment' True >>> 'us' not in 'disappointment' True
Q 29. 解释一下Python中的身份运算符
这也是一个在Python面试中常问的问题。
通过身份运算符‘is’和‘is not’,我们可以确认两个值是否相同。
>>> 10 is '10' False >>> True is not False True
Q 30. 讲讲Python中的位运算符
该运算符按二进制位对值进行操作。
与(&),按位与运算符:参与运算的两个值,如果两个相应位都为1,则该位的结果为1,否则为0
>>> 0b110 & 0b010 2
2.或(|),按位或运算符:只要对应的二个二进位有一个为1时,结果位就为1。
>>> 3|2 3
3.异或(^),按位异或运算符:当两对应的二进位相异时,结果为1
>>> 3^2 1
4.取反(~),按位取反运算符:对数据的每个二进制位取反,即把1变为0,把0变为1
>>> ~2 -3
5.左位移(<<),运算数的各二进位全部左移若干位,由 << 右边的数字指定了移动的位数,高位丢弃,低位补0
>>> 1<<2 4
6.右位移(>>),把">>"左边的运算数的各二进位全部右移若干位,>> 右边的数字指定了移动的位数
>>> 4>>2 1
更多关于运算符的知识,参考这里:
https://data-flair.training/blogs/python-operators/
Q 31. 在Python中如何使用多进制数字?
我们在Python中,除十进制外还可以使用二进制、八进制和十六进制。
二进制数字由0和1组成,我们使用 0b 或 0B 前缀表示二进制数。
>>> int(0b1010) 10
2.使用bin()函数将一个数字转换为它的二进制形式。
>>> bin(0xf) ‘0b1111’
3.八进制数由数字 0-7 组成,用前缀 0o 或 0O 表示 8 进制数。
>>> oct(8) ‘0o10’
4.十六进数由数字 0-15 组成,用前缀 0x 或者 0X 表示 16 进制数。
>>> hex(16) ‘0x10’ >>> hex(15) ‘0xf’
Q 32. 怎样获取字典中所有键的列表?
使用 keys() 获取字典中的所有键
>>> mydict={'a':1,'b':2,'c':3,'e':5}
>>> mydict.keys()
dict_keys(['a', 'b', 'c', 'e'])Q 33. 为何不建议以下划线作为标识符的开头
因为Python并没有私有变量的概念,所以约定速成以下划线为开头来声明一个变量为私有。所以如果你不想让变量私有,就不要使用下划线开头。
Q 34. 怎样声明多个变量并赋值?
一共有两种方式:
>>> a,b,c=3,4,5 #This assigns 3, 4, and 5 to a, b, and c respectively >>> a=b=c=3 #This assigns 3 to a, b, and c
Q 35. 元组的解封装是什么?
首先我们来看解封装:
>>> mytuple=3,4,5 >>> mytuple (3, 4, 5)
这将 3,4,5 封装到元组 mytuple 中。
现在我们将这些值解封装到变量 x,y,z 中:
>>> x,y,z=mytuple >>> x+y+z
得到结果12.
相关学习推荐:python视频教程
The above is the detailed content of Summary of the most common python interview questions and answers. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1666
1666
 14
14
 1425
1425
 52
52
 1327
1327
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1252
1252
 24
24
 Python vs. C : Applications and Use Cases Compared
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. C : Applications and Use Cases Compared
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python is suitable for data science, web development and automation tasks, while C is suitable for system programming, game development and embedded systems. Python is known for its simplicity and powerful ecosystem, while C is known for its high performance and underlying control capabilities.
 Python: Games, GUIs, and More
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Games, GUIs, and More
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in gaming and GUI development. 1) Game development uses Pygame, providing drawing, audio and other functions, which are suitable for creating 2D games. 2) GUI development can choose Tkinter or PyQt. Tkinter is simple and easy to use, PyQt has rich functions and is suitable for professional development.
 Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python is easier to learn and use, while C is more powerful but complex. 1. Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners. Dynamic typing and automatic memory management make it easy to use, but may cause runtime errors. 2.C provides low-level control and advanced features, suitable for high-performance applications, but has a high learning threshold and requires manual memory and type safety management.
 Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
To maximize the efficiency of learning Python in a limited time, you can use Python's datetime, time, and schedule modules. 1. The datetime module is used to record and plan learning time. 2. The time module helps to set study and rest time. 3. The schedule module automatically arranges weekly learning tasks.
 Python vs. C : Exploring Performance and Efficiency
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Exploring Performance and Efficiency
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python is better than C in development efficiency, but C is higher in execution performance. 1. Python's concise syntax and rich libraries improve development efficiency. 2.C's compilation-type characteristics and hardware control improve execution performance. When making a choice, you need to weigh the development speed and execution efficiency based on project needs.
 Which is part of the Python standard library: lists or arrays?
Apr 27, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Which is part of the Python standard library: lists or arrays?
Apr 27, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Pythonlistsarepartofthestandardlibrary,whilearraysarenot.Listsarebuilt-in,versatile,andusedforstoringcollections,whereasarraysareprovidedbythearraymoduleandlesscommonlyusedduetolimitedfunctionality.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.
 Learning Python: Is 2 Hours of Daily Study Sufficient?
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Learning Python: Is 2 Hours of Daily Study Sufficient?
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Is it enough to learn Python for two hours a day? It depends on your goals and learning methods. 1) Develop a clear learning plan, 2) Select appropriate learning resources and methods, 3) Practice and review and consolidate hands-on practice and review and consolidate, and you can gradually master the basic knowledge and advanced functions of Python during this period.



