 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 One article to understand the problem of large file sorting/external memory sorting
One article to understand the problem of large file sorting/external memory sorting
One article to understand the problem of large file sorting/external memory sorting
Question 1: A file contains 500 million lines, each line is a random integer, and all integers in the file need to be sorted.
Divide&Conquer (pide&Conquer), ReferenceBig data algorithm: Sorting 500 million data
For this one Total.txt with 500000000 lines is sorted, and the file size is 4.6G.
Every time 10,000 lines are read, sort and write them into a new subfile (quick sort is used here).
1. Split & Sort
#!/usr/bin/python2.7
import time
def readline_by_yield(bfile):
with open(bfile, 'r') as rf:
for line in rf:
yield line
def quick_sort(lst):
if len(lst) < 2:
return lst
pivot = lst[0]
left = [ ele for ele in lst[1:] if ele < pivot ]
right = [ ele for ele in lst[1:] if ele >= pivot ]
return quick_sort(left) + [pivot,] + quick_sort(right)
def split_bfile(bfile):
count = 0
nums = []
for line in readline_by_yield(bfile):
num = int(line)
if num not in nums:
nums.append(num)
if 10000 == len(nums):
nums = quick_sort(nums)
with open('subfile/subfile{}.txt'.format(count+1),'w') as wf:
wf.write('\n'.join([ str(i) for i in nums ]))
nums[:] = []
count += 1
print count
now = time.time()
split_bfile('total.txt')
run_t = time.time()-now
print 'Runtime : {}'.format(run_t)will generate 50,000 small files, each small file is about 96K in size.
During the execution of the program, the memory usage has been around 5424kB

It takes 94146 seconds to split the entire file.
2. Merge
#!/usr/bin/python2.7
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import time
testdir = '/ssd/subfile'
now = time.time()
# Step 1 : 获取全部文件描述符
fds = []
for f in os.listdir(testdir):
ff = os.path.join(testdir,f)
fds.append(open(ff,'r'))
# Step 2 : 每个文件获取第一行,即当前文件最小值
nums = []
tmp_nums = []
for fd in fds:
num = int(fd.readline())
tmp_nums.append(num)
# Step 3 : 获取当前最小值放入暂存区,并读取对应文件的下一行;循环遍历。
count = 0
while 1:
val = min(tmp_nums)
nums.append(val)
idx = tmp_nums.index(val)
next = fds[idx].readline()
# 文件读完了
if not next:
del fds[idx]
del tmp_nums[idx]
else:
tmp_nums[idx] = int(next)
# 暂存区保存1000个数,一次性写入硬盘,然后清空继续读。
if 1000 == len(nums):
with open('final_sorted.txt','a') as wf:
wf.write('\n'.join([ str(i) for i in nums ]) + '\n')
nums[:] = []
if 499999999 == count:
break
count += 1
with open('runtime.txt','w') as wf:
wf.write('Runtime : {}'.format(time.time()-now))During the execution of the program, the memory usage has been around 240M
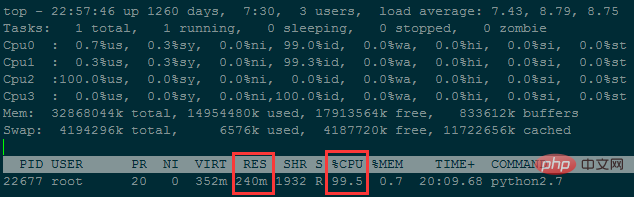

It took about 38 hours to merge less than 50 million rows of data...
Although the memory usage is reduced, the time is complicated The degree is too high; You can further reduce memory usage by reducing the number of files (increasing the number of rows stored in each small file).
Question 2: A file has 100 billion lines of data, each line is an IP address, and the IP addresses need to be sorted.
Convert IP address to numbers
# 方法一:手动计算
In [62]: ip
Out[62]: '10.3.81.150'
In [63]: ip.split('.')[::-1]
Out[63]: ['150', '81', '3', '10']
In [64]: [ '{}-{}'.format(idx,num) for idx,num in enumerate(ip.split('.')[::-1]) ]
Out[64]: ['0-150', '1-81', '2-3', '3-10']
In [65]: [256**idx*int(num) for idx,num in enumerate(ip.split('.')[::-1])]
Out[65]: [150, 20736, 196608, 167772160]
In [66]: sum([256**idx*int(num) for idx,num in enumerate(ip.split('.')[::-1])])
Out[66]: 167989654
In [67]:
# 方法二:使用C扩展库来计算
In [71]: import socket,struct
In [72]: socket.inet_aton(ip)
Out[72]: b'\n\x03Q\x96'
In [73]: struct.unpack("!I", socket.inet_aton(ip))
# !表示使用网络字节顺序解析, 后面的I表示unsigned int, 对应Python里的integer or long
Out[73]: (167989654,)
In [74]: struct.unpack("!I", socket.inet_aton(ip))[0]
Out[74]: 167989654
In [75]: socket.inet_ntoa(struct.pack("!I", 167989654))
Out[75]: '10.3.81.150'
In [76]:Question 3: There is a 1.3GB file (a total of 100 million lines). Each line in it is a string. Please find duplicates in the file. The most frequent string.
Basic idea: Read large files iteratively, split the large files into multiple small files; and finally merge these small files.
Splitting rules:
Read large files iteratively, maintain a dictionary in memory, the key is a string, and the value is the number of times the string appears;
When the number of string types maintained by the dictionary reaches 10,000 (customizable), the dictionary is sorted from small to large by key , and then written into a small file, each line is key\tvalue;
Then clear the dictionary and continue reading until the large file is finished.
Merge rules:
First get the file descriptors of all small files, and then read out the first line (that is, each small file The string with the smallest ascii value of the file string) is compared.
Find the string with the smallest ascii value. If there are duplicates, add up the number of occurrences, and then store the current string and the total number of times into a list in memory.
Then move the read pointer of the file where the smallest string is located downward, that is, read another line from the corresponding small file for the next round of comparison.
When the number of lists in the memory reaches 10,000, the contents of the list are written to a final file at once and stored on the hard disk. At the same time, clear the list for subsequent comparisons.
Until all the small files have been read, the final file is a large file sorted in ascending order according to the string ascii value. The content of each line is the string\trepetition times,
The last iteration is to read the final file and find the one with the most repetitions.
1. Split
def readline_by_yield(bfile):
with open(bfile, 'r') as rf:
for line in rf:
yield line
def split_bfile(bfile):
count = 0
d = {}
for line in readline_by_yield(bfile):
line = line.strip()
if line not in d:
d[line] = 0
d[line] += 1
if 10000 == len(d):
text = ''
for string in sorted(d):
text += '{}\t{}\n'.format(string,d[string])
with open('subfile/subfile{}.txt'.format(count+1),'w') as wf:
wf.write(text.strip())
d.clear()
count += 1
text = ''
for string in sorted(d):
text += '{}\t{}\n'.format(string,d[string])
with open('subfile/subfile_end.txt','w') as wf:
wf.write(text.strip())
split_bfile('bigfile.txt')2. Merge
import os
import json
import time
import traceback
testdir = '/ssd/subfile'
now = time.time()
# Step 1 : 获取全部文件描述符
fds = []
for f in os.listdir(testdir):
ff = os.path.join(testdir,f)
fds.append(open(ff,'r'))
# Step 2 : 每个文件获取第一行
tmp_strings = []
tmp_count = []
for fd in fds:
line = fd.readline()
string,count = line.strip().split('\t')
tmp_strings.append(string)
tmp_count.append(int(count))
# Step 3 : 获取当前最小值放入暂存区,并读取对应文件的下一行;循环遍历。
result = []
need2del = []
while True:
min_str = min(tmp_strings)
str_idx = [i for i,v in enumerate(tmp_strings) if v==min_str]
str_count = sum([ int(tmp_count[idx]) for idx in str_idx ])
result.append('{}\t{}\n'.format(min_str,str_count))
for idx in str_idx:
next = fds[idx].readline() # IndexError: list index out of range
# 文件读完了
if not next:
need2del.append(idx)
else:
next_string,next_count = next.strip().split('\t')
tmp_strings[idx] = next_string
tmp_count[idx] = next_count
# 暂存区保存10000个记录,一次性写入硬盘,然后清空继续读。
if 10000 == len(result):
with open('merged.txt','a') as wf:
wf.write(''.join(result))
result[:] = []
# 注意: 文件读完需要删除文件描述符的时候, 需要逆序删除
need2del.reverse()
for idx in need2del:
del fds[idx]
del tmp_strings[idx]
del tmp_count[idx]
need2del[:] = []
if 0 == len(fds):
break
with open('merged.txt','a') as wf:
wf.write(''.join(result))
result[:] = []Merge result analysis:
| Dictionary size maintained in memory during splitting | Number of small files to be split | Number of file descriptors to be maintained during merging | Memory usage during merging | Merge takes time | |
| First time | 10000 | 9000 | 9000 ~ 0 | 200M | The merge speed is slow and the completion time has not yet been calculated |
| Second time | 100000 | 900 | 900 ~ 0 | 27M | The merge speed is fast, only 2572 seconds |
3. Find the most frequent occurrences Strings and their times
import time
def read_line(filepath):
with open(filepath,'r') as rf:
for line in rf:
yield line
start_ts = time.time()
max_str = None
max_count = 0
for line in read_line('merged.txt'):
string,count = line.strip().split('\t')
if int(count) > max_count:
max_count = int(count)
max_str = string
print(max_str,max_count)
print('Runtime {}'.format(time.time()-start_ts))The merged file has a total of 9999788 lines and a size of 256M; it takes 27 seconds to perform the search and occupies 6480KB of memory.
The above is the detailed content of One article to understand the problem of large file sorting/external memory sorting. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1662
1662
 14
14
 1419
1419
 52
52
 1313
1313
 25
25
 1262
1262
 29
29
 1235
1235
 24
24
 Python vs. C : Applications and Use Cases Compared
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. C : Applications and Use Cases Compared
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python is suitable for data science, web development and automation tasks, while C is suitable for system programming, game development and embedded systems. Python is known for its simplicity and powerful ecosystem, while C is known for its high performance and underlying control capabilities.
 The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
You can learn basic programming concepts and skills of Python within 2 hours. 1. Learn variables and data types, 2. Master control flow (conditional statements and loops), 3. Understand the definition and use of functions, 4. Quickly get started with Python programming through simple examples and code snippets.
 Python: Games, GUIs, and More
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Games, GUIs, and More
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in gaming and GUI development. 1) Game development uses Pygame, providing drawing, audio and other functions, which are suitable for creating 2D games. 2) GUI development can choose Tkinter or PyQt. Tkinter is simple and easy to use, PyQt has rich functions and is suitable for professional development.
 How Much Python Can You Learn in 2 Hours?
Apr 09, 2025 pm 04:33 PM
How Much Python Can You Learn in 2 Hours?
Apr 09, 2025 pm 04:33 PM
You can learn the basics of Python within two hours. 1. Learn variables and data types, 2. Master control structures such as if statements and loops, 3. Understand the definition and use of functions. These will help you start writing simple Python programs.
 Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python is easier to learn and use, while C is more powerful but complex. 1. Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners. Dynamic typing and automatic memory management make it easy to use, but may cause runtime errors. 2.C provides low-level control and advanced features, suitable for high-performance applications, but has a high learning threshold and requires manual memory and type safety management.
 Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
To maximize the efficiency of learning Python in a limited time, you can use Python's datetime, time, and schedule modules. 1. The datetime module is used to record and plan learning time. 2. The time module helps to set study and rest time. 3. The schedule module automatically arranges weekly learning tasks.
 Python: Exploring Its Primary Applications
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AM
Python: Exploring Its Primary Applications
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AM
Python is widely used in the fields of web development, data science, machine learning, automation and scripting. 1) In web development, Django and Flask frameworks simplify the development process. 2) In the fields of data science and machine learning, NumPy, Pandas, Scikit-learn and TensorFlow libraries provide strong support. 3) In terms of automation and scripting, Python is suitable for tasks such as automated testing and system management.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.



