
Introduction: Redis is an open source log-type, Key-Value database written in ANSI C language, complying with the BSD protocol, supporting the network, and can be based on memory or persistence, and provides Non-relational database with APIs in multiple languages.
Special recommendation: 2020 redis interview questions collection (latest)
Traditional databases follow ACID rules. Nosql (abbreviation for Not Only SQL, a collective name for database management systems that are different from traditional relational databases) is generally distributed and distributed generally follows the CAP theorem.
Github source code: https://github.com/antirez/redis
Redis official website: https://redis.io/
Recommended: "redis Tutorial》
#What data types does Redis support?
String string:
Format: set key value
The string type is binary safe. This means that the redis string can contain any data. For example, jpg images or serialized objects.
The string type is the most basic data type of Redis, and a key can store up to 512MB.
Hash(Hash)
Format: hmset name key1 value1 key2 value2
Redis hash is a set of key-value (key=>value) pairs.
Redis hash is a mapping table of string type fields and values. Hash is particularly suitable for storing objects.
List (List)
Redis list is a simple list of strings, sorted in insertion order. You can add an element to the head (left) or tail (right) of the list
Format: lpush name value
Add a string element to the head of the list corresponding to the key
Format: rpush name value
Add string elements at the end of the key corresponding list
Format: lrem name index
Delete count items from the key corresponding list that are the same as value Element
Format: llen name
Returns the length of the key corresponding to the list
Set (set)
Format: sadd name value
Redis's Set is an unordered collection of string type.
Sets are implemented through hash tables, so the complexity of adding, deleting, and searching is O(1).
zset(sorted set: ordered set)
Format: zadd name score value
Redis zset, like set, is also a collection of string type elements, and duplicates are not allowed member.
The difference is that each element is associated with a double type score. Redis uses scores to sort the members of the collection from small to large.
The members of zset are unique, but the scores can be repeated.
What is Redis persistence? What persistence methods does Redis have? What are the pros and cons?
Persistence is to write the memory data to the disk to prevent the memory data from being lost if the service goes down.
Redis provides two persistence methods: RDB (default) and AOF
RDB:
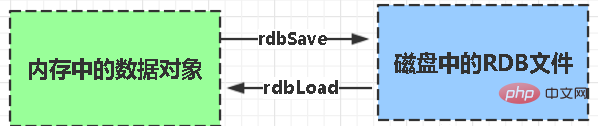
rdb is the abbreviation of Redis DataBase
Function core functions rdbSave (generate RDB file) and rdbLoad (load memory from file) two functions
AOF:
Aof is the abbreviation of Append-only file
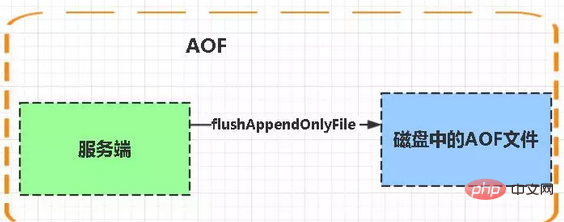
aof write and save: WRITE: According to the conditions, write the cache in aof_buf to the AOF file SAVE: According to the conditions, call the fsync or fdatasync function to save the AOF file to disk.
Storage structure:
The content is command text storage in redis communication protocol (RESP) format.Comparison:
1. Aof files are updated more frequently than rdb, so use aof to restore data first. 2. AOF is safer and larger than rdb3. RDB performance is better than aof4. If both are configured, AOF is loaded firstYou just mentioned the redis communication protocol (RESP) above. Can you explain what RESP is? What are the characteristics? (You can see that many interviews are actually a series of questions. The interviewer is actually waiting for you to answer this point. If you answer the question, it will add another point to your evaluation)
RESP It is a communication protocol previously used by the redis client and server; Characteristics of RESP: simple implementation, fast parsing, and good readabilityFor Simple Strings the first byte of the reply is " " ReplyFor Errors the first byte of the reply is "-" ErrorFor Integers the first byte of the reply is ":" IntegerFor Bulk Strings the first byte of the reply is "$" StringFor Arrays the first byte of the reply is "*" ArrayWhat are the architectural patterns of Redis? Talk about their respective characteristics
stand-alone version
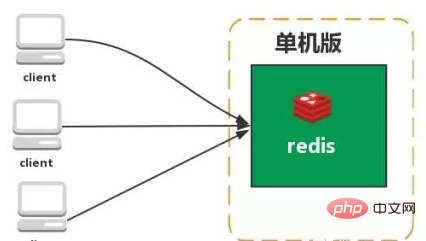
Features: Simple
Problems:
1. Limited memory capacity 2. Limited processing power 3. Unable to be highly available.
Master-slave replication
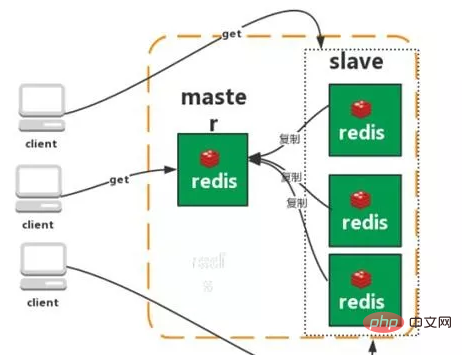
Sentinel
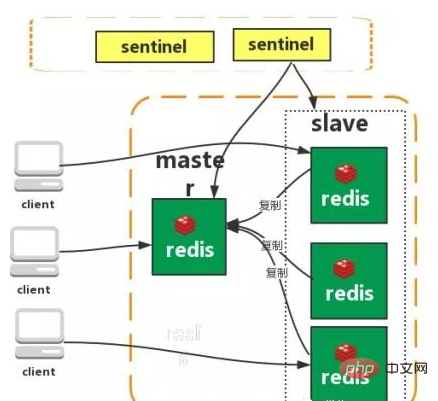
Cluster (proxy type):
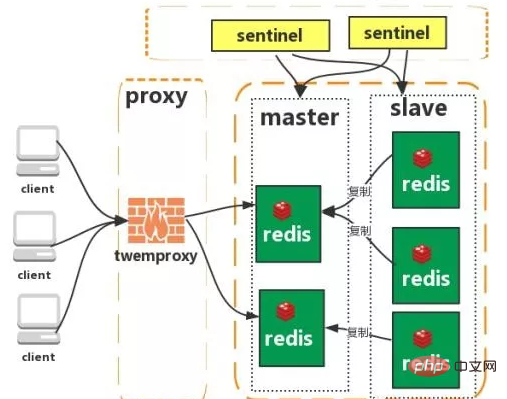
Cluster (direct Connection type):
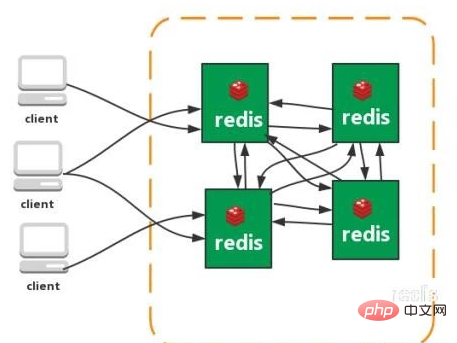
What is a consistent hash algorithm? What is a hash slot?
Commonly used commands in Redis?
Keys pattern* means allocating all starting with bitCheck whether the Exists key existsSet Set the value corresponding to the key to a string type value. setnxSet the value corresponding to key to the value of string type. If key already exists, return 0, nx means not exist. Delete a keyReturns 1 for the first time and returns 0 for the second time after deleting itExpire Set expiration time (in seconds)TTL view How much time is leftIf a negative number is returned, the key will be invalid and the key does not existSetexSet the value corresponding to the key to a string type value, and specify the corresponding value of this key validity period. MsetSet the values of multiple keys at one time. Returning ok on success means that all values are set, and returning 0 on failure means that no value is set. GetsetSet the value of key and return the old value of key.Mget
Get the values of multiple keys at one time. If the corresponding key does not exist, nil will be returned accordingly.
Incr
Add the value of key and return the new value. Note that if incr is a value that is not int, an error will be returned. If incr is a key that does not exist, set the key to 1
incrby
is similar to incr, add the specified value, and it will be set when the key does not exist key, and thinks that the original value is 0
Decr
The value of the key is subtracted. If the decr key does not exist, set the key to -1
Decrby
Same as decr, minus the specified value.
Append
Append value to the string value of the specified key and return the length of the new string value.
Strlen
Get the length of the value of the specified key.
persist xxx (cancel expiration time)
Select database (0-15 database)
Select 0 //Select database
move age 1// Move age to 1 library
Randomkey randomly returns a key
Rename rename
Type returns the data type
08
Have you ever used Redis distributed lock? How is it implemented?
First use setnx to grab the lock. After grabbing it, use expire to add an expiration time to the lock to prevent the lock from forgetting to release.
What happens if the process crashes unexpectedly or needs to be restarted for maintenance before expire is executed after setnx?
The set instruction has very complex parameters. This should be able to combine setnx and expire into one instruction at the same time!
09
Have you ever used Redis as an asynchronous queue? How did you use it? What are the disadvantages?
Generally use the list structure as the queue, rpush produces messages, and lpop consumes messages. When there is no message from lpop, sleep for a while and try again.
Disadvantages:
When the consumer goes offline, the produced messages will be lost, so you have to use a professional message queue such as rabbitmq, etc.
Can I produce it once and consume it multiple times?
Using the pub/sub topic subscriber mode, a 1:N message queue can be achieved.
10
What is cache penetration? How to avoid it? What is cache avalanche? How to avoid it?
Cache Penetration
General cache systems cache queries based on key. If the corresponding value does not exist, it should be searched in the back-end system (such as DB). Some malicious requests will deliberately query non-existent keys. If the request volume is large, it will put a lot of pressure on the back-end system. This is called cache penetration.
How to avoid?
1: The query result is also cached when it is empty. The cache time is set shorter, or the cache is cleared after the data corresponding to the key is inserted.
2: Filter keys that must not exist. You can put all possible keys into a large Bitmap and filter through the bitmap when querying.
Cache Avalanche
When the cache server is restarted or a large number of caches fail in a certain period of time, this will put a lot of pressure on the back-end system when it fails. causing the system to crash.
How to avoid?
1: After the cache expires, control the number of threads that read the database and write the cache through locking or queuing. For example, only one thread is allowed to query data and write cache for a certain key, while other threads wait.
2: Make a second-level cache, A1 is the original cache, A2 is the copy cache, when A1 fails, you can access A2, A1 cache expiration time is set to short-term, A2 is set to long-term
3 : Different keys, set different expiration times, so that the cache invalidation time is as even as possible.
The above is the detailed content of Share common Redis interview questions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 How to check server status
How to check server status
 How to solve the computer prompt of insufficient memory
How to solve the computer prompt of insufficient memory
 How to optimize a single page
How to optimize a single page
 What should I do if the web video cannot be opened?
What should I do if the web video cannot be opened?
 How to implement linked list in go
How to implement linked list in go
 How to buy and sell Bitcoin legally
How to buy and sell Bitcoin legally
 Introduction to the main work content of the backend
Introduction to the main work content of the backend
 Use of jQuery hover() method
Use of jQuery hover() method
 Why does the computer have a blue screen?
Why does the computer have a blue screen?