code show as below:
# -*- coding:gb2312 -*-
class CarStore(object):
def order(self,car_type):
return Factory.select(car_type)
class Factory(object):
def select(car_type): #为什么这个地方的方法,没有self参数也可以运行?
if car_type == "索纳塔":
return Suonata()
elif car_type == "名图":
return Mingtu()
else:
print("没有您要的车型!")
class Car(object):
def move(self):
print("车在移动...")
def music(self):
print("正在播放音乐...")
def stop(self):
print("车在停止...")
class Suonata(Car):
def __init__(self):
print("索纳塔")
class Mingtu(Car):
def __init__(self):
print("名图")
car_store = CarStore()
suonata = car_store.order("索纳塔")
#car.move()
#car.music()
#car.stop()
suonata.move()Results of the:

This code itself has no problem and can be executed.
My question is why the seventh line of code def select(car_type): can be executed even though there is no self in this place? I remember when I was learning classes, I was taught that each method in the instance method must add a self parameter, but there is no parameter here. Then I added self here and made an error, as shown below: 
The result is an error:
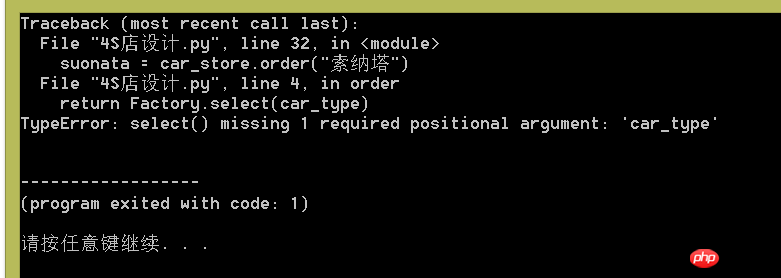
Why is this happening?
Are you using python3?
In python3, if the member function does not add self, it means that the function is a static member function and can be called directly using the form of "class name. function name (parameter)".
But if you add self, this function is a member function of the class. In other calling classes, it must be called like this: "Class name. Function name (self, parameter)", or implement an instance in the calling class, " Instance name. Function name (parameter)
Python3 is like this, my test, it is not in python2.
You added self in the select function, but when calling it in CarStore::order(), you used the form of "class name. function name (parameter)", so it is incorrect. When you call CarStore::order(), change it to "class name. Function name (self, parameter)" or implement an instance in CarStore::order(), using the form "instance name. Function name (parameter)" Try it.
I saw it last night, it was too late, so I tested it this morning.
selfis not magic,can be changed to any name
It doesn’t have to be
selfAccording to this way of writing,
selectis an object method, and the call needs to be associated with an instanceFactory(). When called, the object instance is bound to the first parametercar_type. This parameter name is generally agreed to beself, but it is not required.You need to understand that the following two calling methods are different:
The first way, use the instance object to call, the first parameter
car_typeis automatically bound to the instance objectf;The second way, use the class to call, the first parameter (
car_type) is not Binding; you need to bind it yourself to avoid errors - that is, thecar_typeyou pass in:Factory.selct(car_type)this line.However, when you add
self, this function has two parameters, but you only bindcar_type, which is bound to the first parameterself. The second one has no value, so it must be error.What you have to do here is actually to implement
selectinto a class method:So, when called with
Factory.select(car_type),clsis automatically bound toFactory, andcar_typeis bound tocar_type.The above, whether it is
selforcls, are just agreed names, and what works is Python’s class-object-methodmodel.It is recommended to read "Python Source Code Analysis" to at least understand how @classmethod works, otherwise you will not be able to write this type of code well.