- Front-end
- HTML| CSS| JavaScript| Vue.js
Latest Recommendations
-

Php8, I'm coming too
84669 person learning
- native foundation
- HTML| CSS| HTML5| CSS3| JavaScript
Latest Recommendations
-

Learn website layout in 30 minutes
152542 person learning
- Introduction to Fundamentals
- MySQL| SQL Server
Latest Recommendations
-

Shangguan Oracle Beginner to Proficient Video Tutorial
20005 person learning
Latest Recommendations
-

Your first line of UNI-APP code
5487 person learning
-

Flutter from scratch to app launch
7821 person learning
- Tool usage
- PhpStudy| Git| Other tools
Latest Recommendations
-
Brother Lian New Linux Video Tutorial
359900 person learning
Latest Recommendations
-

AXURE 9 Video Tutorial (Suitable for Product Manager Interactive Product Design UI)
3350 person learning
-

Zero Basic Proficiency PS Video Tutorial
180660 person learning
-

16 day UI video tutorial to get you started
48569 person learning
-

PS Techniques and Slicing Techniques Video Tutorial
18603 person learning
- Class Library Classification
- HTTP| TCP/IP| basic programming
Latest Recommendations
-

Alibaba Cloud Environment Construction and Project Launch Video Tutorial
40936 person learning
-

Overview of Computer Networks - Basic Knowledge that Programmers Must Master
1549 person learning
-

Essential Tutorial for Programmers - HTTP Protocol Explanation
1183 person learning
-

Websocket Video Tutorial
32909 person learning











![[Web front-end] Node.js quick start](https://img.php.cn/upload/course/000/000/067/662b5d34ba7c0227.png)




After asking GTF through office hour last week, I successfully wrote a code that can be run
In the end, I got nearly full marks. The shortcoming is that I can turn two for loops into one. The standard answer professor has not been uploaded yet. I will update it after it is uploaded.
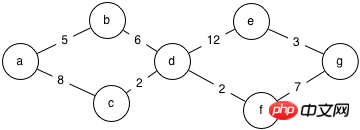
The standard answer is as follows
The code prompts to use the depth first search algorithm.
Go all the way to the end and choose an untraveled point at each step.