How to convert between XML documents and JTree
XMLBecause of its good structure, it is widely used in the definition of document formats. We know that application software generally needs to use configuration file to determine some parameters during runtime. The configuration file of previous applications was generally an .ini file. Although ini files are still in use today, due to the emergence of XML, more and more commercial software is using XML as the configuration file format, such as BEA's Weblogic and IBM's Websphere. Therefore, when we design a software configuration file, we will increasingly consider using XML as the format of the configuration file.
Because configuration files sometimes must be modified by users, providing a visual format for editing configuration files is a reflection of the software's good user interactivity. We must find a visual method for XML documents. The JTree in the Swing component in the Java language is very suitable for the visualization of XML documents. There is a very convenient conversion method between the two. This means that we can easily display the user's operations on the JTree as modifications in the XML file after saving, and we can also conveniently display the XML file as a JTree to the user.
Visualization of XML documents
An XML document is actually a tree structure. For example, the following XML document:
<?xml version=“1.0”encoding=“GB2312”?>
<skin>
<skin1>
<name>古典</name>
<dir>d:\software\App\skin</dir>
<head>head1.bmp</head>
<center>center1.bmp</center>
<foot>foot1.bmp</foot>
</skin1>
<skin2>
<name>现代</name>
<dir>d:\software\App\skin</dir>
<head>head2.bmp</head>
<center>center2.bmp</center>
<foot>foot2.bmp</foot>
</skin2>
</skin>It can be seen that the XML document is the interface of a multi-interface program PictureConfiguration program. If the XML document is visualized, then JTree should be used What is obtained is the result shown in the figure below.
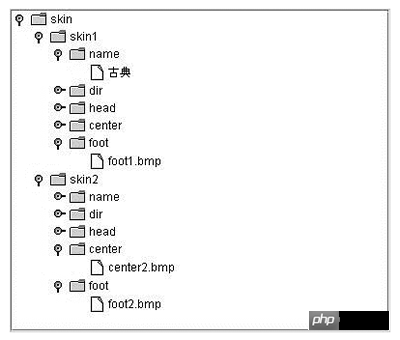
Figure Visualization results
All XML documents can generate such a Jtree. Using XML's Parser and the JTree class in Java, a general visual XML document can be constructed to form a JTree. The result of the XML document parsing by XML Parser is to generate a DOM (Document Object Model) tree. The structure of the DOM tree is actually the same as the structure of the JTree. , which makes the cooperation between JTree and XML Parser very natural. Here’s how to do it.
A class that reads and writes XML files
First you must obtain the XML Parser package, which can be obtained from the following address: http://xml.apache.org/xerces2-j/index. html.
Then design an XMLTree class, inherit from the definition and members of the JTree class variables , functions are defined as follows:
public class XMLTree extends JTree{
private DefaultMutableTreeNode treeNode; //JTree的根节点
private DocumentBuilderFactory dbf;
// 这三个成员变量是xml parser需要的
private DocumentBuilder db;
private Document doc;
XMLTree(String fileName);
//构造函数,做初始化工作
public DefaultMutableTreeNode LoadFile(Node root);
//从某个XML文件生成该树
public void SaveToFile(DefaultMutableTreeNode root,FileWriter fw);
//将该树存盘成XML文件
private Node parseXml( String text )
}where The initialization work done by the constructor is as follows:
XMLTree(String fileName){
dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
//生成dbf的实例
db = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();
//生成db的实例
treeNode = LoadFile( getXMLRoot( text ) );
//解析该xml文件,返回JTree的根节点
setModel( new DefaultTreeModel( treeNode ) );
//根据该根节点生成JTree
}Among them, parseXml is a program that returns the root element of the XML file, as follows:
private Node getXMLRoot( String text ){
ByteArrayInputStream byteStream;
byteStream = new ByteArrayInputStream( text.getBytes() );
//将XML文件读到Stream里去
try{
doc = db.parse( byteStream );
//解析该xml文件。
} catch ( Exception e )
{ e.printStackTrace();}
return ( Node )doc.getDocumentElement();
//返回该XML文件的DOM树的根元素
}The core part of LoadFile is a recursionThe process is as follows:
private DefaultMutableTreeNode createTreeNode( Node root ){
DefaultMutableTreeNode treeNode = null;
//定义要返回的根节点
String name = root.getNodeName();
//获得该节点的NodeName
String value = root.getNodeValue();
//获得该节点的NodeValue
treeNode = new DefaultMutableTreeNode( root.
getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE ? value : name );
//如果为值节点,那么取得该节点的值,否则取得该节点的Tag的名字
if ( root.hasChildNodes() )
//如果该节点有孩子节点,那么递归处理该节点的孩子节点
{ NodeList children = root.getChildNodes();
//取得该节点的子节点列表
if( children != null ){
//判断子节点是否为空
int numChildren = children.getLength();
//取得字节数目
for (int i=0; i < numChildren; i++){
Node node = children.item(i);
//循环处理每个子节点
if( node != null )
{ if( node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE )
{ treeNode.add( createTreeNode(node) );
//如果该子节点还有孩子节点使用递归的方法处理该子节点
} else {
String data = node.getNodeValue();
if( data != null )
{
data = data.trim();
if ( !data.equals(“\n”) && !data.equals(“\r\n”) &&
data.length() > 0 )
{ treeNode.add(new
DefaultMutableTreeNode(node.getNodeValue()));
//如果该节点没有孩子节点,那么直接加到节点下
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
return treeNode; //返回节点 }You can easily make changes on the JTree using the methods in Java's Swing package. You can use the pop-up dialog box method, or you can make changes directly on the JTree. In short, after the JTree is changed, it needs to be written back to the file. Writing a JTree into an XML file is a recursive process. The method is as follows:
public void SaveToFile(DefaultMutableTreeNode, FileWriter fw)
{try {
if (root.isLeaf()) fw.write(root.toString()+“\r\n”);
//如果是叶子节点则直接将该节点输出到文件中
else { //不是叶子节点的话递归输出该节点
fw.write(“<”+root.toString()+“>\r\n”);
for (int i=0; i < root.getChildCount(); i++)
{ DefaultMutableTreeNode childNode =(DefaultMutableTreeNode)
root.getChildAt(i);
saveFile(childNode, fw);
//递归输出该节点的所有子节点 }
fw.write(“</”+root.toString()+“>\r\n”);
}
} catch (Exception e)
{ e.printStackTrace();
} }It must be noted that if the XML file contains Chinese, then it needs to Before calling the above function, enter the encoding method of the XML file in the file as follows:
fw.write(“<?xml version=“1.0” encoding=“GB2312”?>\r\n”);
After calling the function, you should also close the file as follows:
fw.close()
Conclusion
XML files are widely used in configuration files and information transmission. There are many visualization methods. This article introduces one of the implementation methods by combining Java's JTree class. The good combination of Java language and XML makes it flexible and convenient to use Java to compile XML programs.
The above is the detailed content of How to convert between XML documents and JTree. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
The speed of mobile XML to PDF depends on the following factors: the complexity of XML structure. Mobile hardware configuration conversion method (library, algorithm) code quality optimization methods (select efficient libraries, optimize algorithms, cache data, and utilize multi-threading). Overall, there is no absolute answer and it needs to be optimized according to the specific situation.
 How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
It is impossible to complete XML to PDF conversion directly on your phone with a single application. It is necessary to use cloud services, which can be achieved through two steps: 1. Convert XML to PDF in the cloud, 2. Access or download the converted PDF file on the mobile phone.
 How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
It is not easy to convert XML to PDF directly on your phone, but it can be achieved with the help of cloud services. It is recommended to use a lightweight mobile app to upload XML files and receive generated PDFs, and convert them with cloud APIs. Cloud APIs use serverless computing services, and choosing the right platform is crucial. Complexity, error handling, security, and optimization strategies need to be considered when handling XML parsing and PDF generation. The entire process requires the front-end app and the back-end API to work together, and it requires some understanding of a variety of technologies.
 How to open web.xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 06:51 AM
How to open web.xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 06:51 AM
To open a web.xml file, you can use the following methods: Use a text editor (such as Notepad or TextEdit) to edit commands using an integrated development environment (such as Eclipse or NetBeans) (Windows: notepad web.xml; Mac/Linux: open -a TextEdit web.xml)
 Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
XML formatting tools can type code according to rules to improve readability and understanding. When selecting a tool, pay attention to customization capabilities, handling of special circumstances, performance and ease of use. Commonly used tool types include online tools, IDE plug-ins, and command-line tools.
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Use most text editors to open XML files; if you need a more intuitive tree display, you can use an XML editor, such as Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy; if you process XML data in a program, you need to use a programming language (such as Python) and XML libraries (such as xml.etree.ElementTree) to parse.
 xml online formatting
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
xml online formatting
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
XML Online Format Tools automatically organizes messy XML code into easy-to-read and maintain formats. By parsing the syntax tree of XML and applying formatting rules, these tools optimize the structure of the code, enhancing its maintainability and teamwork efficiency.




