RHEL6上课笔记之acl
Passwd,shadow,gshadow,group 这四个文件是 PAM ( portable authentication module )的数据库。 pam 的文件都是 (.so) 结尾的。 cd /lib64/security 目录中有很多 .so 的文件。其中到迄今为止都没有 bug 的是 pam_unix.so , pam_userdb.so 是的 pam_unix.
Passwd,shadow,gshadow,group 这四个文件是PAM(portable authentication module)的数据库。
pam的文件都是(.so)结尾的。
cd /lib64/security目录中有很多.so的文件。其中到迄今为止都没有bug的是pam_unix.so,pam_userdb.so是的pam_unix.so助手。
PAM的配置文件在/etc/pam.d/下。现在我们来看其中的一个配置文件etc/pam.d/login/。
login中有四类
auth:密码正确性。
passwd:密码最多能用的时间。
account:帐号是否合法。
session:性能(如,分配多少cpu)。
其中有一行是:
account required(必要条件) pam_nologin.so
在etc目录下touch 一个名为nologin的文件,那么用除root以外的用户登入就会提示“鉴定错误”(免打扰模式)。 删掉就恢复正常。
单单针对root的tty:
不让root在某个tty窗口登入。可以配置/etc/securetty的白名单配置文件。例如:如果不想让root在tty4登入,那么就在securetty白名单中把tty4注释掉。
也可以阻止其它用户在某个tty登入。需要配置/etc/security/access.conf配置文件。配置方法如下:
#-:ALL EXCEPT (wheel) shutdown sync:LOCAL
- : gg : tty4 # 不让gg用户在tty4上登入,其它tty可以。(也可以在这里配置root)。配置完access.conf文件后还需要配置一个文件,就是在/etc/pam.d/login文件中加上一句:account required pam_nologin.so
acl:对文件设置acl
给文件添加第二属主。
使用root 用户在tmp1 下
[root@station10 tmp1]# echo “helo body” >> file
[root@station10 tmp1]# getfacl file (查看文件属主)
# file: file
# owner: root
# group: root
user::rw-
group::r--
mask::r--
other::r--
[root@station10 tmp1]# su - eg
[eg@station10 ~]$ cd /root/tmp1/
[eg@station10 tmp1]$ echo 111 >> file
-bash: file: 权限不够
[root@station10 tmp1]# setfacl -m u:eg:rw file (-m 修改。用户:用户名:权限)
[root@station10 tmp1]# getfacl file
# file: file
# owner: root
# group: root
user::rw-
user:eg:rw- #eg用户
group::r--
mask::rw-
other::r--
[root@station10 tmp1]# su - eg
[eg@station10 ~]$ echo xxx >> /root/tmp1/file
[eg@station10 ~]$ cat /root/tmp1/file
helo body
xxx
在做以上实验时如果在执行 setfacl -m u:eg:rw file 的时候提示 不支持的操作,那是因为分区不具备acl品质。那么就需要给分区添上acl的品质。如下:
[root@station10 tmp1]# tune2fs -l /dev/sda3
……
Default mount options: user_xattr acl # 具备acl品质
……
如果没有该品质那么就要给它加上。第1种方式:“ tune2fs -o acl /dev/sda3 “ 添上。第二种方式:使用手工mount -o alc /dev/sda3 。第三种方式:开机自动挂载上,配置fstab如下图:使用mount -a 验证。Mount 查看是否具有acl品质。
defaults后面可以有(noexec,nodev)参数。当然这些参数也可以在挂载的时候写上或则fstab都行。
noexec:如果加了此参数那么在该分区就不能够使用( ./ ) 执行任何可执行文件。就会提示权限不够。
nodev:???
[root@station10 tmp1]# mknod egfile b 8 7
[root@station10 tmp1]# mount egfile /mnt1
/tmp1/egfile
/dev/sda7
acl:对目录设置acl
我们新建一个文件夹,然后使用刚刚对文件增加第二属主的方式来做。如下:
[root@station10 /]# mount /dev/sda7 /mnt
[root@station10 mnt]# mkdir dir
[root@station10 mnt]# getfacl dir/
# file: dir/
# owner: root
# group: root
user::rwx
group::r-x
other::r-x
[root@station10 mnt]# setfacl -m u:eg:rwx dir
setfacl: dir: 不支持的操作 #由于刚刚挂载的时候没有添加acl 品质的结果(一定要注意,如果没有acl 品质那么就不能做acl。)
[root@station10 mnt]# tune2fs -o acl /dev/sda7
[root@station10 mnt]# tune2fs -l /dev/sda7
……
Default mount options: acl #有了
……
[root@station10 /]# umount /mnt
[root@station10 /]# mount /dev/sda7 /mnt
[root@station10 mnt]# setfacl -m u:eg:rwx dir
[root@station10 mnt]# getfacl dir/
# file: dir/
# owner: root
# group: root
user::rwx
user:eg:rwx
group::r-x
mask::rwx
other::r-x
[root@station10 mnt]# cd dir/
[root@station10 dir]# mkdir dir1
[root@station10 dir]# getfacl dir1/
# file: dir1/
# owner: root
# group: root
user::rwx
group::r-x
other::r-x
#我们刚刚用root建的第一个文件夹(dir)我给它添加了第二个属主。现在需要再到dir 目录下再建立一个文件夹(dir1)并且也让它属于eg 用户,可是建完之后它并不属于eg,而是单单属于root。那我又得给它增加第二属主太麻烦了。可以使用一种方法让它一直保持第一层的特性。如下所示:
[root@station10 mnt]# ls -ld dir/
drwxrwxr-x+ 3 root root 1024 6月 4 22:27 dir/
[root@station10 dir]# ls -ld dir1/
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 1024 6月 4 22:36 dir1/
看到dir 与dir1 的ls -ld 有点不一样,那是因为dir1 没有保持dir 的特性(+)。那接下来我就让它保持dir 的特性。
就是在建立文件夹的时候加上一个d,就可以让它里面建立的第二层第三层等等都保持第一层的特性。如下:
[root@station10 mnt]# mkdir Docu
[root@station10 mnt]# setfacl -m d:u:eg:rwx Docu
[root@station10 mnt]# getfacl Docu/
# file: Docu/
# owner: root
# group: root
user::rwx
group::r-x
other::r-x
default:user::rwx
default:user:eg:rwx
default:group::r-x
default:mask::rwx
default:other::r-x
[root@station10 mnt]# cd Docu/
[root@station10 Docu]# mkdir Docu1
[root@station10 Docu]# getfacl Docu1/
# file: Docu1/
# owner: root
# group: root
user::rwx
user:eg:rwx
group::r-x
mask::rwx
other::r-x
default:user::rwx
default:user:eg:rwx
default:group::r-x
default:mask::rwx
default:other::r-x
#观察到实验的结果了吧。
现在我想把第一层文件恢复原来的样子:
[root@station10 mnt]# setfacl -x d:u:eg Docu/ # (-x:删除)恢复只有一个属主,还留有defaults。
[root@station10 mnt]# setfacl -b Docu/ #恢复正常。可以直接使用-b(-b 级别高于-x)。
s位程序:可执行文件
文件被谁运行就归谁所有:
[root@station10 ~]# /bin/sleep 1000
[root@station10 ~]# ps -eo command,group,user | grep sleep | grep -v grep
/bin/sleep 1000 root root
[eg@station10 ~]$ /bin/sleep 1000
[eg@station10 ~]$ ps -eo command,group,user | grep sleep | grep -v grep
/bin/sleep 1000 eg eg
观察如上实验,就可发现不管是root还是eg 运行sleep ,它的属主都是运行者的。
在工业环境中,有时会要求我们用某个用户来运行某个程序,但是这个程序却不归我们这个用户所有。也就只有S 位程序能够实现。
[root@station10 ~]# ls -l /bin/sleep
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 27880 6月 14 2010 /bin/sleep
[root@station10 ~]# chmod 4755 /bin/sleep
[root@station10 ~]# ls -l /bin/sleep
[eg@station10 ~]$ /bin/sleep 1000
[eg@station10 ~]$ ps -eo command,group,user | grep sleep | grep -v grep
/bin/sleep 1000 eg root
完全和刚刚的相反了,属主是root,而不是eg。(也可以是组)
s位程序:目录
对于目录而言,研究s程序只研究组。
[root@station10 mnt]# mkdir dir
[root@station10 mnt]# chown wang5:eg dir/ #dir属于wang5用户,属于eg组。
[root@station10 mnt]# chmod 2755 dir/
[root@station10 mnt]# ls -ld dir/
drwxr-sr-x. 2 wang5 eg 1024 6月 4 23:40 dir/
[root@station10 mnt]# cd dir
[root@station10 dir]# mkdir d1 #在dir里新建d1
[root@station10 dir]# ls -ld d1/
drwxr-sr-x. 2 root eg 1024 6月 4 23:40 d1/
root 建立的都必须归eg 组。连root都必须尊守。
原理:新建内节点。
[root@station10 dir]# cp -rp /etc/ ./
[root@station10 dir]# ls -ld *
drwxr-sr-x. 2 root eg 1024 6月 5 09:19 d1
drwxr-sr-x. 117 root root 8192 6月 5 09:19 etc
漏洞:移动或拷贝文件,组就会归移动者。
Other t位 (对文件的保护)
t 位 只对777目录,一般是tmp。
[root@station10 mnt]# mkdir tmp
[root@station10 mnt]# chmod 1777 tmp
[root@station10 mnt]# ls -ld tmp/
[root@station10 mnt]# cd tmp/
[root@station10 tmp]# touch 1.txt
[root@station10 tmp]# ls -l 1.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Jun 6 21:55 1.txt
[root@station10 tmp]# su – wang5
[wang5@station10 ~]$ cd /mnt/tmp/
[wang5@station10 tmp]$ rm -rf 1.txt
rm: 无法删除"1.txt": 不允许的操作
增加了t位,是对777目录的保护,只能是自己本身和root可以删除外其它用户不可删除。
REDHAT6

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 小紅書筆記怎麼刪除
Mar 21, 2024 pm 08:12 PM
小紅書筆記怎麼刪除
Mar 21, 2024 pm 08:12 PM
小紅書筆記怎麼刪除?在小紅書APP中是可以編輯筆記的,多數的用戶不知道小紅書筆記如何的刪除,接下來就是小編為用戶帶來的小紅書筆記刪除方法圖文教程,有興趣的用戶快來一起看看吧!小紅書使用教學小紅書筆記怎麼刪除1、先打開小紅書APP進入到主頁面,選擇右下角【我】進入到專區;2、之後在我的專區,點擊下圖所示的筆記頁面,選擇要刪除的筆記;3、進入到筆記頁面,右上角【三個點】;4、最後下方會展開功能欄,點選【刪除】即可完成。
 小紅書刪除的筆記能恢復嗎
Oct 31, 2023 pm 05:36 PM
小紅書刪除的筆記能恢復嗎
Oct 31, 2023 pm 05:36 PM
小紅書刪除的筆記不能恢復。小紅書作為知識分享和購物平台,為使用者提供了記錄筆記和收藏有用資訊的功能。根據小紅書的官方說明,已經刪除的筆記是無法恢復的。小紅書平台並沒有提供專門的筆記恢復功能。這意味著,一旦在小紅書中刪除了筆記,無論是不小心誤刪還是其他原因,一般情況下是無法從平台上找回被刪除的內容的。如果遇到特殊情況,可以嘗試聯絡小紅書的客服團隊,看是否能夠協助解決問題。
 小紅書發布過的筆記不見了怎麼辦?它剛發的筆記搜不到的原因是什麼?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 09:30 PM
小紅書發布過的筆記不見了怎麼辦?它剛發的筆記搜不到的原因是什麼?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 09:30 PM
作為一名小紅書的用戶,我們都曾經遇到過發布過的筆記突然不見了的情況,這無疑讓人感到困惑和擔憂。在這種情況下,我們該怎麼辦呢?本文將圍繞著「小紅書發布過的筆記不見了怎麼辦」這個主題,為你詳細解答。一、小紅書發布過的筆記不見了怎麼辦?首先,不要驚慌。如果你發現筆記不見了,保持冷靜是關鍵,不要慌張。這可能是由於平台系統故障或操作失誤引起的。檢查發布記錄很簡單。只要打開小紅書App,點擊“我”→“發布”→“所有發布”,就可以查看自己的發布記錄。在這裡,你可以輕鬆找到之前發布的筆記。 3.重新發布。如果找到了之
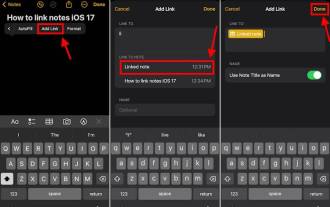 如何在最新的iOS 17系統中連接iPhone上的Apple Notes
Sep 22, 2023 pm 05:01 PM
如何在最新的iOS 17系統中連接iPhone上的Apple Notes
Sep 22, 2023 pm 05:01 PM
使用新增連結功能在iPhone上連結AppleNotes。筆記:如果您已安裝iOS17,則只能在iPhone上的AppleNotes之間建立連結。在iPhone上開啟「備忘錄」應用程式。現在,打開要在其中添加連結的註釋。您也可以選擇建立新備忘錄。點擊螢幕上的任何位置。這將向您顯示一個選單。點擊右側的箭頭以查看“新增連結”選項。點擊它。現在,您可以鍵入註解的名稱或網頁URL。然後,點擊右上角的完成,新增的連結將出現在筆記中。如果要添加指向某個單字的鏈接,只需雙擊該單字即可將其選中,選擇“添加鏈接”並按
 小紅書怎麼在筆記中加入商品連結 小紅書在筆記中加入商品連結教學
Mar 12, 2024 am 10:40 AM
小紅書怎麼在筆記中加入商品連結 小紅書在筆記中加入商品連結教學
Mar 12, 2024 am 10:40 AM
小紅書怎麼在筆記中添加商品連結?在小紅書這款app中用戶不僅可以瀏覽各種內容還可以進行購物,所以這款app中關於購物推薦、好物分享的內容是非常多的,如果小夥伴在這款app也是一個達人的話,也可以分享一些購物經驗,找到商家進行合作,在筆記中添加連結之類的,很多人都願意使用這款app購物,因為不僅方便,而且有很多達人會進行一些推薦,可以一邊瀏覽有趣內容,一邊看看有沒有適合自己的衣服商品。一起看看如何在筆記中添加商品連結吧!小紅書筆記添加商品連結方法 在手機桌面上開啟app。 在app首頁點擊
 Nginx反向代理中基於HTTP動詞和路徑的ACL配置
Jun 10, 2023 am 09:22 AM
Nginx反向代理中基於HTTP動詞和路徑的ACL配置
Jun 10, 2023 am 09:22 AM
Nginx是一款高效能的Web伺服器和反向代理伺服器,其強大的設定能力使得Nginx能夠用於各種不同的場景。其中,基於HTTP動詞和路徑的ACL配置是Nginx反向代理中常用的方法,本文將介紹它的原理和實作方法。一、ACL的概念ACL(AccessControlList)即存取控制列表,是一種基於規則的存取控制技術。透過定義一些規則,可以對不同的訪問
 如何在Zend框架中使用ACL(Access Control List)進行權限控制
Jul 29, 2023 am 09:24 AM
如何在Zend框架中使用ACL(Access Control List)進行權限控制
Jul 29, 2023 am 09:24 AM
如何在Zend框架中使用ACL(AccessControlList)進行權限控制導言:在一個Web應用程式中,權限控制是至關重要的功能。它可以確保使用者只能存取其有權存取的頁面和功能,並防止未經授權的存取。 Zend框架提供了一種方便的方法來實現權限控制,即使用ACL(AccessControlList)元件。本文將介紹如何在Zend框架中使用ACL
 小紅書發筆記教學怎麼弄?它發布筆記可以屏蔽人嗎?
Mar 25, 2024 pm 03:20 PM
小紅書發筆記教學怎麼弄?它發布筆記可以屏蔽人嗎?
Mar 25, 2024 pm 03:20 PM
小紅書作為一個生活風格分享平台,涵蓋了美食、旅行、美妝等各個領域的筆記。許多用戶希望在小紅書上分享自己的筆記,但卻不清楚如何操作。在這篇文章中,我們將詳細介紹小紅書發布筆記的流程,並探討如何在平台上封鎖特定使用者。一、小紅書發布筆記教學怎麼弄? 1.註冊登入:首先,需要在手機上下載小紅書APP,並完成註冊登入。在個人中心完善個人資料是很重要的。透過上傳個人資料、填寫暱稱和個人簡介,可以讓其他使用者更容易了解你的訊息,也能幫助他們更好地關注你的筆記。 3.選擇發布頻道:在首頁下方,點選「發筆記」按鈕,選擇你想






