举例讲解Python设计模式编程中对抽象工厂模式的运用
抽象工厂模式:提供一个创建一系列相关或相互依赖对象的接口,而无需指定它们具体的类。
优点:易于交换“产品系列”,只要更改相应的工厂即可。
缺点:建立产品的时候很繁琐,需要增加和修改很多东西。
优化1:为了避免客户端有过多的逻辑判断,可以封装出一个简单工厂类来生成产品类。
优化2:为了减少简单工厂类里面的逻辑判断,可以采用“反射”机制,直接根据外部的配置文件读取出需要使用产品类的信息。
#encoding=utf-8
#
#by panda
#抽象工厂模式
def printInfo(info):
print unicode(info, 'utf-8').encode('gbk')
#抽象产品A:user表
class IUser():
def Insert(self):
pass
def GetUser(self):
pass
#sqlserver实现的User
class SqlserverUser(IUser):
def Insert(self):
printInfo("在SQL Server中给User表增加一条记录")
def GetUser(self):
printInfo("在SQL Server中得到User表的一条记录")
#Access实现的User
class AccessUser(IUser):
def Insert(self):
printInfo("在Access中给User表增加一条记录")
def GetUser(self):
printInfo("在Access中得到User表一条记录")
#抽象产品B:部门表
class IDepartment():
def Insert(self):
pass
def GetUser(self):
pass
#sqlserver实现的Department
class SqlserverDepartment(IUser):
def Insert(self):
printInfo("在SQL Server中给Department表增加一条记录")
def GetUser(self):
printInfo("在SQL Server中得到Department表的一条记录")
#Access实现的Department
class AccessDepartment(IUser):
def Insert(self):
printInfo("在Access中给Department表增加一条记录")
def GetUser(self):
printInfo("在Access中得到Department表一条记录")
#抽象工厂
class IFactory():
def CreateUser(self):
pass
def CreateDepartment(self):
pass
#sql server工厂
class SqlServerFactory(IFactory):
def CreateUser(self):
return SqlserverUser()
def CreateDepartment(self):
return SqlserverDepartment()
#access工厂
class AccessFactory(IFactory):
def CreateUser(self):
return AccessUser()
def CreateDepartment(self):
return AccessDepartment()
#优化一:采用一个简单工厂类,封装逻辑判断操作
class DataAccess():
# db = "Sqlserver"
db = "Access"
@staticmethod
def CreateUser():
if (DataAccess.db == "Sqlserver"):
return SqlserverUser()
elif(DataAccess.db == "Access"):
return AccessUser()
@staticmethod
def CreateDepartment():
if (DataAccess.db == "Sqlserver"):
return SqlserverDepartment()
elif(DataAccess.db == "Access"):
return AccessDepartment()
#优化二:采用反射机制,避免使用太多判断
##以下信息可以从配置文件中获取
DBType = 'Sqlserver' #'Access'
DBTab_User = 'User'
DBTab_Department = 'Department'
class DataAccessPro():
# db = "Sqlserver"
db = "Access"
@staticmethod
def CreateUser():
funName = DBType + DBTab_User
return eval(funName)() #eval 将其中的字符串转化为python表达式
@staticmethod
def CreateDepartment():
funName = DBType + DBTab_Department
return eval(funName)()
def clientUI():
printInfo("\n--------抽象工厂方法--------")
factory = SqlServerFactory()
iu = factory.CreateUser()
iu.Insert()
iu.GetUser()
id = factory.CreateDepartment()
id.Insert()
id.GetUser()
printInfo("\n--抽象工厂方法+简单工厂方法--")
iu = DataAccess.CreateUser()
iu.Insert()
iu.GetUser()
id = DataAccess.CreateDepartment()
id.Insert()
id.GetUser()
printInfo("\n-抽象工厂方法+简单工厂方法+反射-")
iu = DataAccessPro.CreateUser()
iu.Insert()
iu.GetUser()
id = DataAccessPro.CreateDepartment()
id.Insert()
id.GetUser()
return
if __name__ == '__main__':
clientUI();
类图:
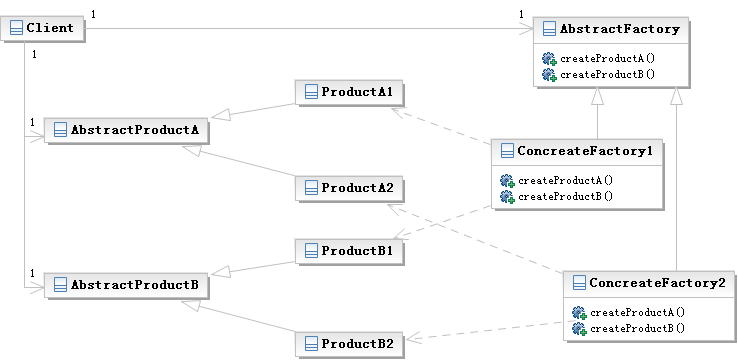
工厂模式和抽象工厂模式的区别:工厂模式是在派生类中定义一个工厂的抽象接口,然后基类负责创建具体对象;抽象工厂模式是维护一个产品家族,由基类定义产品被生产的方法,客户根据派生类的接口进行开发。
实例:人民群众喜闻乐见的披萨店例子这里又可以搬出来了,这次我们根据抽象工厂模式的特点,用不同原材料制作不同口味的披萨,创建不同原材料的工厂,不同实体店做出口味不同的披萨。创建一个产品家族(Dough、Sauce、Cheese和Clam)的抽象类型(PizzaIngredientFactory),这个类型的子类(NYPizzaIngredientFactory和ChicagoPizzaIngredientFactory)定义了产品被产生的方法。
代码:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import sys
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding('utf-8')
'''
披萨
'''
class Pizza:
name = ""
dough = None
sauce = None
cheese = None
clam = None
def prepare(self):
pass
def bake(self):
print "烘烤25分钟在350。".decode('utf-8')
def cut(self):
print "切割成对角线切片。".decode('utf-8')
def box(self):
print "放在官方的盒子中。".decode('utf-8')
def get_name(self):
return self.name
def set_name(self, name):
self.name = name
def to_string(self):
string = "%s:\n" % self.name
string += " 面团: %s\n" % self.dough.to_string() if self.dough else ""
string += " 酱汁: %s\n" % self.sauce.to_string() if self.sauce else ""
string += " 奶酪: %s\n" % self.cheese.to_string() if self.cheese else ""
string += " 文蛤: %s\n" % self.clam.to_string() if self.clam else ""
return string
'''
什么类别的披萨
'''
class CheesePizza(Pizza):
def __init__(self, ingredient_factory):
self.ingredient_factory = ingredient_factory
def prepare(self):
print "准备: %s" % self.name
self.dough = self.ingredient_factory.create_dough()
self.sauce = self.ingredient_factory.create_sauce()
self.cheese = self.ingredient_factory.create_cheese()
class ClamPizza(Pizza):
def __init__(self, ingredient_factory):
self.ingredient_factory = ingredient_factory
def prepare(self):
print "准备: %s" % self.name
self.dough = self.ingredient_factory.create_dough()
self.sauce = self.ingredient_factory.create_sauce()
self.clam = self.ingredient_factory.create_clam()
'''
披萨店
'''
class PizzaStore:
def order_pizza(self, pizza_type):
self.pizza = self.create_pizza(pizza_type)
self.pizza.prepare()
self.pizza.bake()
self.pizza.cut()
self.pizza.box()
return self.pizza
def create_pizza(self, pizza_type):
pass
'''
纽约披萨实体店1
'''
class NYPizzaStore(PizzaStore):
def create_pizza(self, pizza_type):
ingredient_factory = NYPizzaIngredientFactory()
if pizza_type == "cheese":
pizza = CheesePizza(ingredient_factory)
pizza.set_name("纽约风格芝士披萨".decode('utf-8'))
elif pizza_type == "clam":
pizza = ClamPizza(ingredient_factory)
pizza.set_name("纽约风格文蛤披萨".decode('utf-8'))
else:
pizza = None
return pizza
'''
芝加哥披萨实体店2
'''
class ChicagoPizzaStore(PizzaStore):
def create_pizza(self, pizza_type):
ingredient_factory = ChicagoPizzaIngredientFactory()
if pizza_type == "cheese":
pizza = CheesePizza(ingredient_factory)
pizza.set_name("芝加哥风格芝士披萨".decode('utf-8'))
elif pizza_type == "clam":
pizza = ClamPizza(ingredient_factory)
pizza.set_name("芝加哥风格文蛤披萨".decode('utf-8'))
else:
pizza = None
return pizza
'''
生产披萨的工厂
'''
class PizzaIngredientFactory:
def create_dough(self):
pass
def create_sauce(self):
pass
def create_cheese(self):
pass
def create_clam(self):
pass
'''
生产披萨的实体工厂1
'''
class NYPizzaIngredientFactory(PizzaIngredientFactory):
def create_dough(self):
return ThinDough()
def create_sauce(self):
return MarinaraSauce()
def create_cheese(self):
return FreshCheese()
def create_clam(self):
return FreshClam()
'''
生产披萨的实体工厂2
'''
class ChicagoPizzaIngredientFactory(PizzaIngredientFactory):
def create_dough(self):
return ThickDough()
def create_sauce(self):
return MushroomSauce()
def create_cheese(self):
return BlueCheese()
def create_clam(self):
return FrozenClam()
class Dough:
def to_string(self):
pass
class ThinDough(Dough):
def to_string(self):
return "薄的面团"
class ThickDough(Dough):
def to_string(self):
return "厚的生面团"
class Sauce:
def to_string(self):
pass
class MarinaraSauce(Sauce):
def to_string(self):
return "番茄酱"
class MushroomSauce(Sauce):
def to_string(self):
return "蘑菇酱"
class Cheese:
def to_string(self):
pass
class FreshCheese(Cheese):
def to_string(self):
return "新鲜的奶酪"
class BlueCheese(Cheese):
def to_string(self):
return "蓝纹奶酪"
class Clam:
def to_string(self):
pass
class FreshClam(Clam):
def to_string(self):
return "新鲜的文蛤"
class FrozenClam(Clam):
def to_string(self):
return "冷冻的文蛤"
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 创建了两个披萨实体店
ny_store = NYPizzaStore()
chicago_store = ChicagoPizzaStore()
# 在第一个披萨对象中订购了一个cheese风味的披萨
pizza = ny_store.order_pizza("cheese")
print pizza.to_string()
print "迈克订购了一个 %s" % pizza.get_name()
print
pizza = chicago_store.order_pizza("clam")
print pizza.to_string()
print "约翰订购了一个%s" % pizza.get_name()
结果:
准备: 纽约风格芝士披萨 烘烤25分钟在350。 切割成对角线切片。 放在官方的盒子中。 纽约风格芝士披萨: 面团: 薄的面团 酱汁: 番茄酱 奶酪: 新鲜的奶酪 迈克订购了一个 纽约风格芝士披萨 准备: 芝加哥风格文蛤披萨 烘烤25分钟在350。 切割成对角线切片。 放在官方的盒子中。 芝加哥风格文蛤披萨: 面团: 厚的生面团 酱汁: 蘑菇酱 文蛤: 冷冻的文蛤 约翰订购了一个芝加哥风格文蛤披萨

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 PHP和Python:解釋了不同的範例
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP和Python:解釋了不同的範例
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP主要是過程式編程,但也支持面向對象編程(OOP);Python支持多種範式,包括OOP、函數式和過程式編程。 PHP適合web開發,Python適用於多種應用,如數據分析和機器學習。
 在PHP和Python之間進行選擇:指南
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
在PHP和Python之間進行選擇:指南
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP適合網頁開發和快速原型開發,Python適用於數據科學和機器學習。 1.PHP用於動態網頁開發,語法簡單,適合快速開發。 2.Python語法簡潔,適用於多領域,庫生態系統強大。
 sublime怎麼運行代碼python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
sublime怎麼運行代碼python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
在 Sublime Text 中運行 Python 代碼,需先安裝 Python 插件,再創建 .py 文件並編寫代碼,最後按 Ctrl B 運行代碼,輸出會在控制台中顯示。
 PHP和Python:深入了解他們的歷史
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP和Python:深入了解他們的歷史
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP起源於1994年,由RasmusLerdorf開發,最初用於跟踪網站訪問者,逐漸演變為服務器端腳本語言,廣泛應用於網頁開發。 Python由GuidovanRossum於1980年代末開發,1991年首次發布,強調代碼可讀性和簡潔性,適用於科學計算、數據分析等領域。
 Python vs. JavaScript:學習曲線和易用性
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:學習曲線和易用性
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python更適合初學者,學習曲線平緩,語法簡潔;JavaScript適合前端開發,學習曲線較陡,語法靈活。 1.Python語法直觀,適用於數據科學和後端開發。 2.JavaScript靈活,廣泛用於前端和服務器端編程。
 Golang vs. Python:性能和可伸縮性
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang vs. Python:性能和可伸縮性
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang在性能和可擴展性方面優於Python。 1)Golang的編譯型特性和高效並發模型使其在高並發場景下表現出色。 2)Python作為解釋型語言,執行速度較慢,但通過工具如Cython可優化性能。
 vscode在哪寫代碼
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
vscode在哪寫代碼
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
在 Visual Studio Code(VSCode)中編寫代碼簡單易行,只需安裝 VSCode、創建項目、選擇語言、創建文件、編寫代碼、保存並運行即可。 VSCode 的優點包括跨平台、免費開源、強大功能、擴展豐富,以及輕量快速。
 notepad 怎麼運行python
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
notepad 怎麼運行python
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
在 Notepad 中運行 Python 代碼需要安裝 Python 可執行文件和 NppExec 插件。安裝 Python 並為其添加 PATH 後,在 NppExec 插件中配置命令為“python”、參數為“{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}”,即可在 Notepad 中通過快捷鍵“F6”運行 Python 代碼。






