七. PHP模式设计----执行及描述任务
七. PHP模式设计----执行及描述任务
1. 解析器模式
//解析器内容类
//用于存放表达式的运算结果,并且能根据传入的表达式返回当初记录的结果
class InterpreterContext{
private $expressionstore=array();
//将对象放进array里面,索引号是对象ID号
function replace(Expression $exp,$value){
$this->expressionstore[$exp->getKey()]=$value;
}
function lookup(Expression $exp){
return $this->expressionstore[$exp->getKey()];
}
}
abstract class Expression{
private static $keyCount=0;
private $key;
abstract function interpret(InterpreterContext $context);
//每一个对象都有一个唯一的key
function getKey(){
if(!isset($this->key)){
$this->key=++self::$keyCount;
}
return $this->key;
}
}
//字符串
class LiteralExpression extends Expression{
private $value;
function __construct($value){
$this->value=$value;
}
function interpret(InterpreterContext $context){
$context->replace($this, $this->value);
}
}
//变量
class VariableExpression extends Expression{
private $value;
private $name;
function __construct($name,$value=null){
$this->name=$name;
$this->value=$value;
}
function setValue($value){
$this->value=$value;
}
function getKey(){
return $this->name;
}
function interpret(InterpreterContext $context){
if(!is_null($this->value)){
$context->replace($this, $this->value);
//设置为空,可以避免在没有修改value的情况下再次调用该方法的时候,
//也第二次调用了InterpreterContext::replece
$this->value=null;
}
}
}
//操作符表达式 抽象基类
abstract class OperatorExpression extends Expression{
//左右操作数
protected $l_op;
protected $r_op;
function __construct(Expression $l_op,Expression $r_op){
$this->l_op=$l_op;
$this->r_op=$r_op;
}
function interpret(InterpreterContext $context){
$this->l_op->interpret($context);
$this->r_op->interpret($context);
$result_l=$context->lookup($this->l_op);
$result_r=$context->lookup($this->r_op);
$this->doInterpret($context, $result_l, $result_r);
}
protected abstract function doInterpret(InterpreterContext $context,$result_l,$result_r);
}
//相等表达式
class EqualsExpression extends OperatorExpression{
//计算后将结果保存进this里...
protected function doInterpret(InterpreterContext $context,$result_l,$result_r){
$context->replace($this, $result_l==$result_r);
}
}
//布尔或表达式
class BooleanOrExpression extends OperatorExpression{
protected function doInterpret(InterpreterContext $context, $result_l, $result_r){
$context->replace($this, $result_l || $result_r);
}
}
//布尔与表达式
class BooleanAndExpression extends OperatorExpression{
protected function doInterpret(InterpreterContext $context, $result_l, $result_r){
$context->replace($this, $result_l && $result_r);
}
}
/*
$context=new InterpreterContext();
$literal=new LiteralExpression("Bob");
$literal->interpret($context);
print $context->lookup($literal);//Bob
$context=new InterpreterContext();
$myvar=new VariableExpression("V","one");
$myvar->interpret($context);
print $context->lookup($myvar);//one
$myothervar=new VariableExpression("V");
$myvar->interpret($context);
print $context->lookup($myvar);//one
*/
//利用上面的代码来检测迷你型语言
//$input equals "4" or $input equals "four"
$context=new InterpreterContext();
//一个没有赋值的变量
$input=new VariableExpression('input');
//定义一个复杂的布尔型变量,初始化的参数被保存在l_op,r_op里面
//注意,此时他们还没有进行相关运算,必须等到调用布尔型变量的interpret()
//之后,布尔型变量里面的参数才会各自调用自身的interpret,形成一个调用栈...
$statement=new BooleanOrExpression(
new EqualsExpression($input, new LiteralExpression('four')),
new EqualsExpression($input, new LiteralExpression('4')));
$statement->interpret($context);
print $context->lookup($statement);
foreach (array('four','4','52') as $val){
$input->setValue($val);
print "$val:\n";
$statement->interpret($context);
if($context->lookup($statement)){
print "top marks\n";
}else{
print "dunce hat on\n\n";
}
}
/*four:
top marks
4:
top marks
52:
dunce hat on*/
2.策略模式
将类中许多不同操作而且是来自同一个接口的算法,独立起来封装在一个新类中,主类在由分类组合或者聚合而成
//Question类将由Marker聚合而成
abstract class Question{
protected $prompt;
protected $marker;
function __construct($prompt,Marker $marker){
$this->marker=$marker;
$this->prompt=$prompt;
}
//利用委托实现
function mark($response){
return $this->marker->mark($response);
}
}
class TextQuestion extends Question{
//处理文本问题特有的操作
}
class AVQuestion extends Question{
//处理语音问题特有操作
}
//策略对象
//将算法部分独立出来封装在Marker类中....
abstract class Marker{
protected $test;
function __construct($test){
$this->test=$test;
}
abstract function mark($response);
}
//MarkLogic语言
class MarkLogicMarker extends Marker{
protected $engine;
function __construct($test){
parent::__construct($test);
}
function mark($response){
//模拟返回true
return true;
}
}
//直接匹配
class MatchMarker extends Marker{
function mark($response){
return ($this->test==$response);
}
}
//正则表达式
class RegexpMarker extends Marker{
function mark($response){
return (preg_match($this->test, $response));
}
}
//客户端示例代码
$markers=array(new RegexpMarker("/f.ve/"),
new MatchMarker("fivev"),
new MarkLogicMarker('$input equals "five"'));
foreach($markers as $marker){
print get_class($marker)."\n";
//新建一个问题,将marker实例传进去
$question=new TextQuestion("How many beans make five", $marker);
foreach (array("five","four") as $response){
print "\t response:$response: ";
if($question->mark($response)){
print "well done\n";
}else{
print "never mind\n";
}
}
}
/*RegexpMarker
response:five: well done
response:four: never mind
MatchMarker
response:five: never mind
response:four: never mind
MarkLogicMarker
response:five: well done
response:four: well done
*/
3 观察者模式
观察者模式的和兴是把客户元素(观察者)从一个中心类中分离开来.当主体中有事件发生时,观察者必须被通知到!同时观察者和主体类不是通过硬编码实现,而是通过接口组合聚合实现
*问题
// Login类(主体类)
class Login {
const LOGIN_USER_UNKNOWN = 1;
const LOGIN_WRONG_PASS = 2;
const LOGIN_ACCESS = 3;
private $status = array ();
// 登录操
function handleLogin($user, $pass, $ip) {
$ret=false;
switch (rand ( 1, 3 )) {
case 1 :
$this->setStatus ( self::LOGIN_ACCESS, $user, $ip );
$ret=ture;
break;
case 2 :
$this->setStatus ( self::LOGIN_WRONG_PASS, $user, $ip );
$ret=false;
break;
case 3 :
$this->setStatus ( self::LOGIN_USER_UNKNOWN, $user, $ip );
$ret=false;
break;
default:
$ret=false;
}
//如果需要记录IP时
Logger::logIP($user, $ip, $this->getStatus());
//如果需要把登录失败的人的IP发送到管理员邮箱时...
if(!$ret){
Notifier::mailWarning($user, $ip, $this->getStatus());
}
//还需要其他功能时,比如特殊IP需要设置cookie等...
//需要在这里面一直添加...
return $ret;
}
function setStatus($status, $user, $ip) {
$this->status = array ($status,$user,$ip);
}
function getStatus(){
return $this->status;
}
}
class Logger{
static function logIP($user,$ip,$status){}
}
class Notifier{
static function mailWarning($user,$ip,$status){}
}
*利用观察者模式,使代码改动少些....
// 主体类的抽象接口
interface Observable{
//附加
function attach(Observer $observer);
//删除
function detach(Observer $observer);
//通知
function notify();
}
// Login类(主体类)
class Login implements Observable{
const LOGIN_USER_UNKNOWN = 1;
const LOGIN_WRONG_PASS = 2;
const LOGIN_ACCESS = 3;
private $observers;
private $status = array ();
// 登录操作
function handleLogin($user, $pass, $ip) {
$ret=false;
switch (rand ( 1, 3 )) {
case 1 :
$this->setStatus ( self::LOGIN_ACCESS, $user, $ip );
$ret=ture;
break;
case 2 :
$this->setStatus ( self::LOGIN_WRONG_PASS, $user, $ip );
$ret=false;
break;
case 3 :
$this->setStatus ( self::LOGIN_USER_UNKNOWN, $user, $ip );
$ret=false;
break;
default:
$ret=false;
}
//使用观察者模式之后,如果需要增加新功能,只需要在本类中添加观察者实例即可...
$this->notify();
return $ret;
}
function setStatus($status, $user, $ip) {
$this->status = array ($status,$user,$ip);
}
function getStatus(){
return $this->status;
}
function attach(Observer $observer){
$this->observers[]=$observer;
}
function detach(Observer $observer){
$newObserver=array();
foreach ($this->observers as $obs){
if($obs!==$observer){
$newObserver[]=$obs;
}
}
$this->observers=$newObserver;
}
//通知所有观察者
function notify(){
foreach ($this->observers as $bos){
$bos->update($this);
}
}
}
//观察者接口
interface Observer{
function update(Observable $observable);
}
class SecurityMonitor implements Observer{
function update(Observable $observable){
//getStatus()不是Observable接口规定的方法
$status=$observable->getStatus();
//对status的判断也涉及到耦合问题
if($status[0]==Login::LOGIN_WRONG_PASS){
//发送邮件给管理员
print __CLASS__.":\t sending mail to sysadmin\n";
}
}
}
$login=new Login();
$login->attach(new SecurityMonitor());
$login->handleLogin("coco", "123456", "127.0.0.1");//有可能输出发送消息到管理员
*改进后的观察者模式
//可观察元素:主体类的基接口
interface Observable{
//附加
function attach(Observer $observer);
//删除
function detach(Observer $observer);
//通知
function notify();
}
// Login类(主体类)
class Login implements Observable{
const LOGIN_USER_UNKNOWN = 1;
const LOGIN_WRONG_PASS = 2;
const LOGIN_ACCESS = 3;
private $observers;
private $status = array ();
// 登录操作
function handleLogin($user, $pass, $ip) {
$ret=false;
switch (rand ( 1, 3 )) {
case 1 :
$this->setStatus ( self::LOGIN_ACCESS, $user, $ip );
$ret=ture;
break;
case 2 :
$this->setStatus ( self::LOGIN_WRONG_PASS, $user, $ip );
$ret=false;
break;
case 3 :
$this->setStatus ( self::LOGIN_USER_UNKNOWN, $user, $ip );
$ret=false;
break;
default:
$ret=false;
}
//使用观察者模式之后,如果需要增加新功能,只需要在本类中添加观察者实例即可...
$this->notify();
return $ret;
}
function setStatus($status, $user, $ip) {
$this->status = array ($status,$user,$ip);
}
function getStatus(){
return $this->status;
}
function attach(Observer $observer){
$this->observers[]=$observer;
}
function detach(Observer $observer){
$newObserver=array();
foreach ($this->observers as $obs){
if($obs!==$observer){
$newObserver[]=$obs;
}
}
$this->observers=$newObserver;
}
//通知所有观察者
function notify(){
foreach ($this->observers as $bos){
$bos->update($this);
}
}
}
//观察者接口
interface Observer{
function update(Observable $observable);
}
//Login:观察者超类(用于解决直接在Observer中调用具体的Observable子类造成的风险)
abstract class LoginObserver implements Observer{
private $login;
function __construct(Login $login){
$this->login=$login;
$this->login->attach($this);
}
//该方法在Observable的子类某些方法被调用时触发
function update(Observable $observable){
//触发该方法时,传入的参数必须是Login才有效...
if($this->login===$observable){
$this->doUpdate($observable);
}
}
abstract function doUpdate(Login $login);
}
//改进后的观察者能保证调用的Observable实例方法一定存在
class SecurityMonitor extends LoginObserver{
function doUpdate(Login $login){
$status=$login->getStatus();
//对status的判断也涉及到耦合问题
if($status[0]==Login::LOGIN_WRONG_PASS){
//发送邮件给管理员
print __CLASS__.":\t sending mail to sysadmin\n";
}
}
}
//日常记录
class GeneralLogger extends LoginObserver{
function doUpdate(Login $login){
$status=$login->getStatus();
//添加记录到log中
//...
print __CLASS__."\t add login data to log\n";
}
}
//合作伙伴工具类
class PartnershipTool extends LoginObserver{
function doUpdate(Login $login){
$status=$login->getStatus();
//检查IP,如果匹配,则设置cookie...
//...
print __CLASS__."\t set cookie if IP matches a list\n";
}
}
//客户端代码有一点点改变...
$login=new Login();
new SecurityMonitor($login);
new GeneralLogger($login);
new PartnershipTool($login);
$login->handleLogin("coco", "123456", "127.0.0.1");
/*
* 有可能输出
*SecurityMonitor: sending mail to sysadmin
*GeneralLogger add login data to log
*PartnershipTool set cookie if IP matches a list
**/
4. 访问者模式
当使用对象集合时,我们可能需要对结构上每一个单独的组件应用各种操作.这样的操作可以内建于组件本身,毕竟组件内部调用其他组件是最方便的.
但是这种方法也存在问题,因为我们并不知道所有可能需要的执行的操作.如果每增加一个操作,就在类中增加一个对于新操作的支持,类就会变得越来越臃肿.访问者模式可以解决这个问题.
//本例是基于"文明"游戏的代码建立而成...
//*战斗单元类
abstract class Unit{
//深度
protected $depth=0;
//攻击强度
abstract function bombardStrength();
function getComposite(){
return null;
}
//为访问者模式打造的方法
function accept(ArmyVisitor $visitor){
//构建一个根据自己规则定义的方法名,然后交给visitor自身调用
$method="visit".get_class($this);
$visitor->$method($this);
}
//用于计算Unit在对象树中的深度
protected function setDepth($depth){
$this->depth==$depth;
}
function getDepth(){
return $this->depth;
}
}
//复合抽象类
abstract class CompositeUnit extends Unit{
protected $units=array();
//为访问者模式打造的方法
function accept(ArmyVisitor $visitor){
//构建一个根据自己规则定义的方法名,然后交给visitor自身调用
//先调用父类accept(),再遍历调用子元素accept()
parent::accept($visitor);
foreach ($this->units as $thisunit){
$thisunit->accept($visitor);
}
}
//可以不用写bombardStrength()
function getComposite(){
return $this;
}
//添加单元
//同时标记节点在对象树中的深度
function addUnit(Unit $unit){
if(!empty($unit)){
if(in_array($unit, $this->units,true)){
return;
}
//可以用下面代码替换in_array()函数
// foreach ($this->units as $thisunit){
// if($thisunit===$unit){
// return;
// }
// }
//计算好深度先...
$unit->setDepth($this->depth+1);
array_push($this->units, $unit);
}
}
function removeUnit(Unit $unit){
$this->units=array_udiff($this->units, array($unit), function ($a,$b){return ($a===$b?0:1);});
}
}
//射手
class Archer extends Unit{
function bombardStrength(){
return 4;
}
}
//激光塔
class LaserCannonUnit extends Unit{
function bombardStrength(){
return 44;
}
}
//军队:由战斗单元组成
class Army extends CompositeUnit{
//计算总强度
function bombardStrength(){
$ret=0;
foreach ($this->units as $unit){
$ret+=$unit->bombardStrength();
}
return $ret;
}
//移动能力,防御能力...省略
}
//运兵船:一个类似军队的单元,它具备10个战斗单元,有攻击力
class TroopCarrier extends CompositeUnit{
//具备和军队差不多的方法和属性
function bombardStrength(){
//Do something...
}
}
//军队访问者基类
abstract class ArmyVisitor{
//相关方法待会写...
//Army可能有多少种Unit,这里就有多少个visit方法...
//方法命名规则为visit+类名
//默认的visit
abstract function visit(Unit $unit);
function visitArcher(Archer $node){
$this->visit($node);
}
function visitLaserCannonUnit(LaserCannonUnit $node){
$this->visit($node);
}
function visitArmy(Army $node){
$this->visit($node);
}
function visitTroopCarrier(TroopCarrier $node){
$this->visit($node);
}
}
//具体的Army访问者类,用于转存文本
class TextDumpArmyVisitor extends ArmyVisitor{
private $text="";
function visit(Unit $node){
$ret="";
$pad=4*$node->getDepth();
$ret.=sprintf("%{$pad}s","");
$ret.=get_class($node).":";
$ret.="bombard: ".$node->bombardStrength()."\n";
$this->text.=$ret;
}
function getText(){
return $this->text;
}
}
//客户端实例代码
$army=new Army();
$army->addUnit(new Archer());
$army->addUnit(new LaserCannonUnit());
$textdump=new TextDumpArmyVisitor();
$army->accept($textdump);
print $textdump->getText();
/*
* Army:bombard: 48
* Archer:bombard: 4
* LaserCannonUnit:bombard: 44
*/
5. 命令模式
//命令模式
//命令模式最初来源于图形化用户界面设计,但现在广泛应用于企业应用设计,特别促进了控制器(请求和分法处理)
//和领域模型(应用逻辑)的分离.说得更简单一点,命令模式有助于系统更好地进行组织,并易于扩展
//Command可以设计成接口,因为它很简单...
//Commands/Command.php
abstract class Command{
abstract function execute(CommandContext $context);
}
require_once("Command.php");
class Registry{
//一个空类...
static function getAccessManager(){
return new AccessManager();
}
}
class AccessManager{
function login(){
return new stdClass();
}
function getError(){}
}
class LoginCommand extends Command{
function execute(CommandContext $context){
$manager=Registry::getAccessManager();
$user=$context->get('username');
$user=$context->get('pass');
//虚构出来的空类空方法
$user_obj=$manager->login();
if(is_null($user_obj)){
$context->setError($manager->getError());
return false;
}
$context->addParam("user", $user);
return true;
}
}
//CommandContext类用来做任务扩增用,在这儿主要功能是传递数据给Command类
class CommandContext{
private $params=array();
private $error="";
function __construct(){
$this->params=$_REQUEST;
}
function addParam($key,$val){
$this->params[$key]=$val;
}
function get($key){
return $this->params[$key];
}
function setError($error){
$this->error=$error;
}
function getError(){
return $this->error;
}
}
//客户端代码(用于创建命令)已经调用者代码
class CommandNotFoundException extends Exception{
}
//创建命令的工厂
class CommandFactory{
private static $dir="Commands";
//根据参数action,以及类文件存放目录$dir动态创建相应的$action+Command类
static function getCommand($action='default'){
//匹配是否出现非法字符(非字母数字下划线)
if(preg_match('/\W/', $action)){
throw new Exception("Illegal characters in action");
}
$class=ucfirst(strtolower($action)."Command");
$file=self::$dir.DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR."{$class}.php";
if(!file_exists($file)){
throw new CommandNotFoundException("File could not be find !");
}
require_once("$file");
if(!class_exists($class)){
throw new CommandNotFoundException("Class could not be find !");
}
return new $class();
}
}
//调用者,里面包含一个CommandContext对象实例,用于存放web请求的数据
class Controller{
private $context;
function __construct(){
$this->context=new CommandContext();
}
function getContext(){
return $this->context;
}
function process(){
$cmd=CommandFactory::getCommand($this->getContext()->get('action'));
if(!$cmd->execute($this->context)){
//处理失败
print "Faile in process!";
}else{
//处理成功,可以显示相应的视图层
print "Success in process!";
}
}
}
$controller=new Controller();
$context=$controller->getContext();
$context->addParam('action', 'Login');
$context->addParam('user', 'cocos');
$context->addParam('pass', 'tiddles');
//controller执行process方法,需要不理解command的意义.
$controller->process();//Success in process

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

AI Hentai Generator
免費產生 AI 無盡。

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)

熱門話題
 模擬山羊3恐怖走廊任務怎麼做
Feb 25, 2024 pm 03:40 PM
模擬山羊3恐怖走廊任務怎麼做
Feb 25, 2024 pm 03:40 PM
恐怖走廊是模擬山羊3之中的一個任務,這個任務要怎麼樣才能夠去完成呢,掌握到詳細的過關方式和對應的流程,能夠完成這個任務的相應挑戰,下面就為大家帶來模擬山羊3恐怖走廊攻略,了解相關的資訊。模擬山羊3恐怖走廊攻略1、首先需要玩家前往地圖左上角的寂靜嶺處。 2.在這裡可以看到一個屋頂上寫著RESTSTOP的房子,玩家需要操作山羊進入這棟房子。 3.進入房間之後,我們先向前直走,然後向右轉,在這裡盡頭有一扇門,我們直接從這裡進去。 4.進入之後同樣是先向前走隨後右轉,在這裡走到門前門會關上,我們需要回頭找到
 模擬山羊3帝陵任務怎麼過
Mar 11, 2024 pm 01:10 PM
模擬山羊3帝陵任務怎麼過
Mar 11, 2024 pm 01:10 PM
模擬山羊3是有著經典模擬玩法的遊戲,可讓玩家充分體驗到休閒動作類操作模擬的樂趣,遊戲中還擁有很多特色任務的精彩,其中模擬山羊3帝陵任務是需要玩家找尋到鐘塔上的三個鐘並操作的,有些玩家還不清楚要怎麼弄,下面帶來模擬山羊3帝陵任務攻略流程分享!模擬山羊3帝陵任務攻略流程按照順序敲擊鐘即可。詳細步驟拓展1、首先玩家需要打開地圖到霧丘公墓。 2.然後上到鐘樓上,裡面會有三個鐘。 3.接著按照從大到小的順序,依照222312312熟悉怒敲擊。 4、完成敲擊後即可完成任務,並打開大門以獲得光劍。
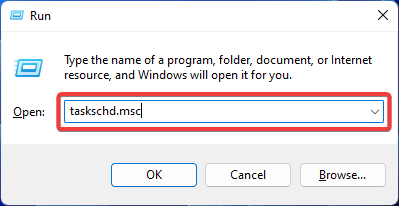 修正: 操作員拒絕 Windows 工作排程程式中的要求錯誤
Aug 01, 2023 pm 08:43 PM
修正: 操作員拒絕 Windows 工作排程程式中的要求錯誤
Aug 01, 2023 pm 08:43 PM
要自動化任務和管理多個系統,任務規劃軟體是您武器庫中的寶貴工具,尤其是對於系統管理員而言。 Windows任務規劃程式完美地完成了這項工作,但最近許多人報告說操作員拒絕了請求錯誤。這個問題存在於作業系統的所有迭代中,即使已經廣泛報告和涵蓋,也沒有有效的解決方案。繼續閱讀以找到真正對其他人有用的內容!操作員或管理員拒絕了任務計畫程式0x800710e0中的請求是什麼?任務計劃程式允許在沒有使用者輸入的情況下自動執行各種任務和應用程式。您可以使用它來安排和組織特定應用程式、配置自動通知、幫助傳遞訊息等。它
 微信的免打擾模式有什麼作用
Feb 23, 2024 pm 10:48 PM
微信的免打擾模式有什麼作用
Feb 23, 2024 pm 10:48 PM
微信勿擾模式什麼意思如今,隨著智慧型手機的普及和行動網路的快速發展,社群媒體平台已成為人們日常生活中不可或缺的一部分。而微信作為國內最受歡迎的社群媒體平台之一,幾乎每個人都有一個微信帳號。我們可以透過微信與朋友、家人、同事進行即時溝通,分享生活中的點滴,了解彼此的近況。然而,在這個時代,我們也不可避免地面臨資訊過載和隱私洩漏的問題,特別是對於那些需要專注或
 模擬山羊3營救史蒂夫任務怎麼做
Feb 25, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
模擬山羊3營救史蒂夫任務怎麼做
Feb 25, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
營救史蒂夫是模擬山羊3中的一個獨特任務,具體需要怎麼做才能夠完成呢,這個任務比較簡單,但是我們需要注意不要理解錯意思,下面就為大家帶來模擬山羊3營救史蒂夫任務攻略,能夠更好的完成相關的任務。模擬山羊3營救史蒂夫任務攻略1、先來到地圖中右下角的溫泉。 2.在來到溫泉邊之後就可以觸發營救史蒂夫的這個任務。 3.注意在溫泉裡有個男人,雖然他也叫史蒂夫,但是並不是這次任務的目標。 4.在這個溫泉裡找到一條叫史蒂夫的魚,並且將其帶上岸,即可完成這個任務。
 iPhone上的睡眠模式有何用途?
Nov 04, 2023 am 11:13 AM
iPhone上的睡眠模式有何用途?
Nov 04, 2023 am 11:13 AM
長期以來,iOS設備一直能夠使用「健康」應用程式追蹤您的睡眠模式等。但是,當您在睡覺時被通知打擾時,這不是很煩人嗎?這些通知可能無關緊要,因此在此過程中會擾亂您的睡眠模式。雖然免打擾模式是避免睡覺時分心的好方法,但它可能會導致您錯過夜間收到的重要電話和訊息。值得慶幸的是,這就是睡眠模式的用武之地。讓我們了解更多關於它以及如何在iPhone上使用它的資訊。睡眠模式在iPhone上有什麼作用睡眠模式是iOS中專用的專注模式,會根據你在「健康」App中的睡眠定時自動啟動。它可以幫助您設定鬧鐘,然後可以
 抖音粉絲團任務在哪裡看?抖音粉絲團會掉等級嗎?
Mar 07, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
抖音粉絲團任務在哪裡看?抖音粉絲團會掉等級嗎?
Mar 07, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
抖音作為當下最受歡迎的社群媒體平台之一,吸引了大量用戶參與其中。在抖音上,有許多粉絲團任務可供用戶完成,以獲得一定的獎勵和福利。那麼,抖音粉絲團任務在哪裡可以找到呢?一、抖音粉絲團任務在哪裡看?為了找到抖音粉絲團任務,你需要造訪抖音的個人首頁。在主頁上,你會看到一個名為「粉絲團」的選項。點擊這個選項,你就可以瀏覽你所加入的粉絲團和相關任務。在粉絲團任務欄位中,你會看到各種不同類型的任務,例如按讚、留言、分享、轉發等。每個任務都有對應的獎勵和要求,一般來說,完成任務後會獲得一定數量的金幣或經驗值
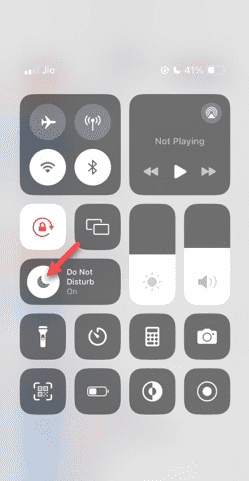 請勿打擾模式在iPhone中不起作用:修復
Apr 24, 2024 pm 04:50 PM
請勿打擾模式在iPhone中不起作用:修復
Apr 24, 2024 pm 04:50 PM
即使在「請勿打擾」模式下接聽電話也可能是一種非常煩人的體驗。顧名思義,請勿打擾模式可關閉來自郵件、訊息等的所有來電通知和警報。您可以按照這些解決方案集進行修復。修復1–啟用對焦模式在手機上啟用對焦模式。步驟1–從頂部向下滑動以存取控制中心。步驟2–接下來,在手機上啟用「對焦模式」。專注模式可在手機上啟用「請勿打擾」模式。它不會讓您的手機上出現任何來電提醒。修復2–更改對焦模式設定如果對焦模式設定中存在一些問題,則應進行修復。步驟1–打開您的iPhone設定視窗。步驟2–接下來,開啟「對焦」模式設






