高品質3D生成最有希望的一集? GaussianCube在三維生成中全面超越NeRF

本網站AIxiv專欄是發布學術、技術內容的欄位。過去幾年,本站AIxiv專欄接收通報逾2000多篇內容,涵蓋全球各大大學與企業的頂級實驗室,有效促進了學術交流與傳播。如果您有優秀的工作想要分享,歡迎投稿或聯絡報道。投稿信箱:liyazhou@jiqizhixin.com;zhaoyunfeng@jiqizhixin.com。

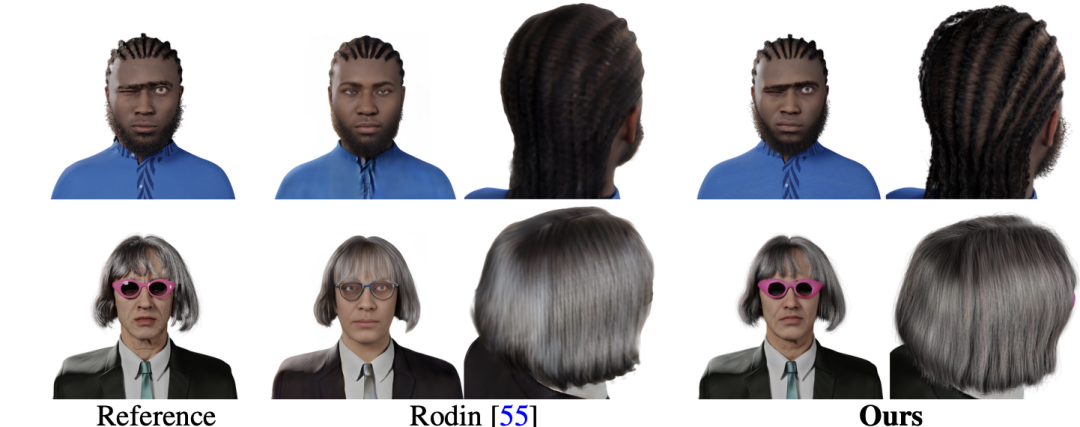
 之後上使用 2. 以輸入肖像來建立數位化身的結果。本文的方法可以極大程度上保留輸入肖像的身份特徵信息,並提供細緻的髮型、服裝建模。
之後上使用 2. 以輸入肖像來建立數位化身的結果。本文的方法可以極大程度上保留輸入肖像的身份特徵信息,並提供細緻的髮型、服裝建模。 

本文產生的三維資產語意明確,具有高品質的幾何結構和材質。

論文名稱:GaussianCube: A Structured and Explicit Radiance Representation for 3D Generative Modeling 專案首頁:https://gaussiancube.github.io/ 論文連結:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2403.19655 程式碼開源:https://github.com/GaussianCube/ GaussianCube 示範影片:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1zy411h7wB/
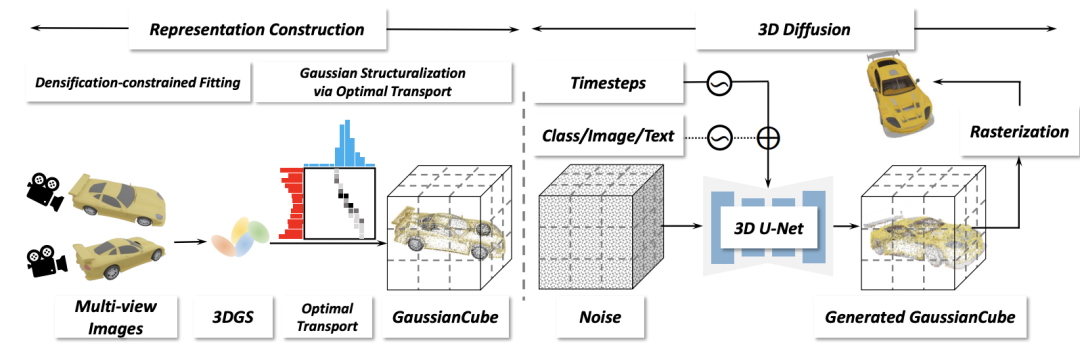
##本文的架構包括兩個主要階段:表示建構和三維擴散。在表示建構階段,給定三維資產的多視角渲染圖,對其進行密度約束的高斯擬合,以獲得具有固定數量的三維高斯。隨後,透過最優化傳輸將三維高斯結構化為 GaussianCube。在三維擴散階段,研究人員對三維擴散模型進行訓練,以便從高斯雜訊中產生 GaussianCube。
#
。為了防止超出預先定義的最大值
 而不影響渲染結果。由於此策略,可以實現了與類似品質的現有工作相比參數量減少了幾個量級的高品質表示,顯著降低了擴散模型的建模難度。
而不影響渲染結果。由於此策略,可以實現了與類似品質的現有工作相比參數量減少了幾個量級的高品質表示,顯著降低了擴散模型的建模難度。 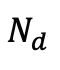
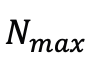
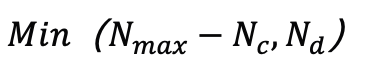

The researchers modeled it as an optimal transmission problem, used the Jonker-Volgenant algorithm to obtain the corresponding mapping relationship, and then organized the Gaussians are organized into corresponding voxels to obtain GaussianCube, and the position of the original Gaussian is replaced with the offset of the current voxel center to reduce the solution space of the diffusion model. The final GaussianCube representation is not only structured, but also maintains the structural relationship between adjacent Gaussians to the greatest extent, which provides strong support for efficient feature extraction for 3D generative modeling.
In the three-dimensional diffusion stage, this article uses a three-dimensional diffusion model to model the distribution of GaussianCube. Thanks to the spatially structured organization of GaussianCube, standard 3D convolution is sufficient to effectively extract and aggregate features of neighboring Gaussians without the need for complex network or training designs. Therefore, the researchers took advantage of standard U-Net network diffusion and directly replaced the original 2D operators (including convolution, attention, upsampling, and downsampling) with their 3D implementations.
The three-dimensional diffusion model of this article also supports a variety of condition signals to control the generation process, including category label condition generation, creating digital avatars based on image conditions, and generating three-dimensional digital assets based on text. . The generation capability based on multimodal conditions greatly expands the application scope of the model and provides a powerful tool for future 3D content creation.
Indicates that different objects share implicit feature decoders. All methods are evaluated with 30K iterations. 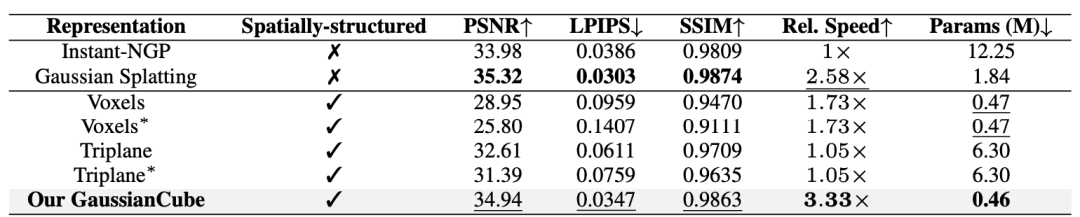

2 2. Do unconditional generation on Shapenet CAR, Chair, and quantitative comparison of category conditions on Omniobject3D. 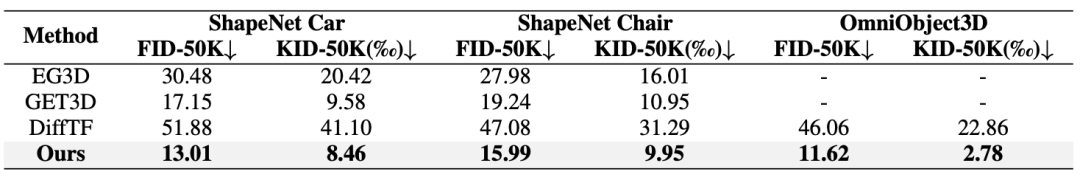


以上是高品質3D生成最有希望的一集? GaussianCube在三維生成中全面超越NeRF的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 DeepMind機器人打乒乓球,正手、反手溜到飛起,全勝人類初學者
Aug 09, 2024 pm 04:01 PM
DeepMind機器人打乒乓球,正手、反手溜到飛起,全勝人類初學者
Aug 09, 2024 pm 04:01 PM
但可能打不過公園裡的老大爺?巴黎奧運正在如火如荼地進行中,乒乓球項目備受關注。同時,機器人打乒乓球也取得了新突破。剛剛,DeepMind提出了第一個在競技乒乓球比賽中達到人類業餘選手等級的學習型機器人智能體。論文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2408.03906DeepMind這個機器人打乒乓球什麼程度呢?大概和人類業餘選手不相上下:正手反手都會:對手採用多種打法,機器人也能招架得住:接不同旋轉的發球:不過,比賽激烈程度似乎不如公園老大爺對戰。對機器人來說,乒乓球運動
 首配機械爪!元蘿蔔亮相2024世界機器人大會,發布首個走進家庭的西洋棋機器人
Aug 21, 2024 pm 07:33 PM
首配機械爪!元蘿蔔亮相2024世界機器人大會,發布首個走進家庭的西洋棋機器人
Aug 21, 2024 pm 07:33 PM
8月21日,2024世界機器人大會在北京隆重召開。商湯科技旗下家用機器人品牌「元蘿蔔SenseRobot」家族全系產品集體亮相,並最新發布元蘿蔔AI下棋機器人-國際象棋專業版(以下簡稱「元蘿蔔國象機器人」),成為全球首個走進家庭的西洋棋機器人。作為元蘿蔔的第三款下棋機器人產品,全新的國象機器人在AI和工程機械方面進行了大量專項技術升級和創新,首次在家用機器人上實現了透過機械爪拾取立體棋子,並進行人機對弈、人人對弈、記譜複盤等功能,
 Claude也變懶了!網友:學會給自己放假了
Sep 02, 2024 pm 01:56 PM
Claude也變懶了!網友:學會給自己放假了
Sep 02, 2024 pm 01:56 PM
開學將至,該收心的不只即將開啟新學期的同學,可能還有AI大模型。前段時間,Reddit擠滿了吐槽Claude越來越懶的網友。 「它的水平下降了很多,經常停頓,甚至輸出也變得很短。在發布的第一周,它可以一次性翻譯整整4頁文稿,現在連半頁都輸出不了!」https:// www.reddit.com/r/ClaudeAI/comments/1by8rw8/something_just_feels_wrong_with_claude_in_the/在一個名為“對Claude徹底失望了的帖子裡”,滿滿地
 世界機器人大會上,這家承載「未來養老希望」的國產機器人被包圍了
Aug 22, 2024 pm 10:35 PM
世界機器人大會上,這家承載「未來養老希望」的國產機器人被包圍了
Aug 22, 2024 pm 10:35 PM
在北京舉行的世界機器人大會上,人形機器人的展示成為了現場絕對的焦點,在星塵智能的展台上,由於AI機器人助理S1在一個展區上演揚琴、武術、書法三台大戲,能文能武,吸引了大量專業觀眾和媒體的駐足。在有彈性的琴弦上優雅的演奏,讓S1展現出速度、力度、精準度兼具的精細操作與絕對掌控。央視新聞對「書法」背後的模仿學習和智慧控制進行了專題報道,公司創始人來傑解釋到,絲滑動作的背後,是硬體側追求最好力控和最仿人身體指標(速度、負載等),而是在AI側則採集人的真實動作數據,讓機器人遇強則強,快速學習進化。而敏捷
 李飛飛團隊提出ReKep,讓機器人具備空間智能,還能整合GPT-4o
Sep 03, 2024 pm 05:18 PM
李飛飛團隊提出ReKep,讓機器人具備空間智能,還能整合GPT-4o
Sep 03, 2024 pm 05:18 PM
視覺與機器人學習的深度融合。當兩隻機器手絲滑地互相合作疊衣服、倒茶、將鞋子打包時,加上最近老上頭條的1X人形機器人NEO,你可能會產生一種感覺:我們似乎開始進入機器人時代了。事實上,這些絲滑動作正是先進機器人技術+精妙框架設計+多模態大模型的產物。我們知道,有用的機器人往往需要與環境進行複雜精妙的交互,而環境則可被表示成空間域和時間域上的限制。舉個例子,如果要讓機器人倒茶,那麼機器人首先需要抓住茶壺手柄並使之保持直立,不潑灑出茶水,然後平穩移動,一直到讓壺口與杯口對齊,之後以一定角度傾斜茶壺。這
 ACL 2024獎項發表:華科大破解甲骨文最佳論文之一、GloVe時間檢驗獎
Aug 15, 2024 pm 04:37 PM
ACL 2024獎項發表:華科大破解甲骨文最佳論文之一、GloVe時間檢驗獎
Aug 15, 2024 pm 04:37 PM
本屆ACL大會,投稿者「收穫滿滿」。為期六天的ACL2024正在泰國曼谷舉辦。 ACL是計算語言學和自然語言處理領域的頂級國際會議,由國際計算語言學協會組織,每年舉辦一次。一直以來,ACL在NLP領域的學術影響力都名列第一,它也是CCF-A類推薦會議。今年的ACL大會已是第62屆,接收了400餘篇NLP領域的前沿工作。昨天下午,大會公佈了最佳論文等獎項。此次,最佳論文獎7篇(兩篇未公開)、最佳主題論文獎1篇、傑出論文獎35篇。大會也評出了資源論文獎(ResourceAward)3篇、社會影響力獎(
 分散式人工智慧盛會DAI 2024徵稿:Agent Day,強化學習之父Richard Sutton將出席!顏水成、Sergey Levine以及DeepMind科學家將做主旨報告
Aug 22, 2024 pm 08:02 PM
分散式人工智慧盛會DAI 2024徵稿:Agent Day,強化學習之父Richard Sutton將出席!顏水成、Sergey Levine以及DeepMind科學家將做主旨報告
Aug 22, 2024 pm 08:02 PM
會議簡介隨著科技的快速發展,人工智慧成為了推動社會進步的重要力量。在這個時代,我們有幸見證並參與分散式人工智慧(DistributedArtificialIntelligence,DAI)的創新與應用。分散式人工智慧是人工智慧領域的重要分支,這幾年引起了越來越多的關注。基於大型語言模型(LLM)的智能體(Agent)異軍突起,透過結合大模型的強大語言理解和生成能力,展現了在自然語言互動、知識推理、任務規劃等方面的巨大潛力。 AIAgent正在接棒大語言模型,成為目前AI圈的熱門話題。 Au
 鴻蒙智行享界S9全場景新品發表會,多款重磅新品齊發
Aug 08, 2024 am 07:02 AM
鴻蒙智行享界S9全場景新品發表會,多款重磅新品齊發
Aug 08, 2024 am 07:02 AM
今天下午,鸿蒙智行正式迎来了新品牌与新车。8月6日,华为举行鸿蒙智行享界S9及华为全场景新品发布会,带来了全景智慧旗舰轿车享界S9、问界新M7Pro和华为novaFlip、MatePadPro12.2英寸、全新MatePadAir、华为毕昇激光打印机X1系列、FreeBuds6i、WATCHFIT3和智慧屏S5Pro等多款全场景智慧新品,从智慧出行、智慧办公到智能穿戴,华为全场景智慧生态持续构建,为消费者带来万物互联的智慧体验。鸿蒙智行:深度赋能,推动智能汽车产业升级华为联合中国汽车产业伙伴,为






