冒泡排序是電腦科學中最簡單的排序演算法之一。它以每次迭代時較小的元素“冒泡”到列表頂部的方式命名,是教授排序演算法基礎知識的絕佳工具。雖然對於大型資料集來說不是最有效的,但它的簡單性使其成為理解排序演算法如何運作的一個很好的起點。
冒泡排序的工作原理是重複遍歷列表,比較相鄰元素,如果順序錯誤則交換它們。重複這個過程,直到不再需要交換為止,表示清單已排序。
這是一步一步的細分:
讓我們可視化這個過程:
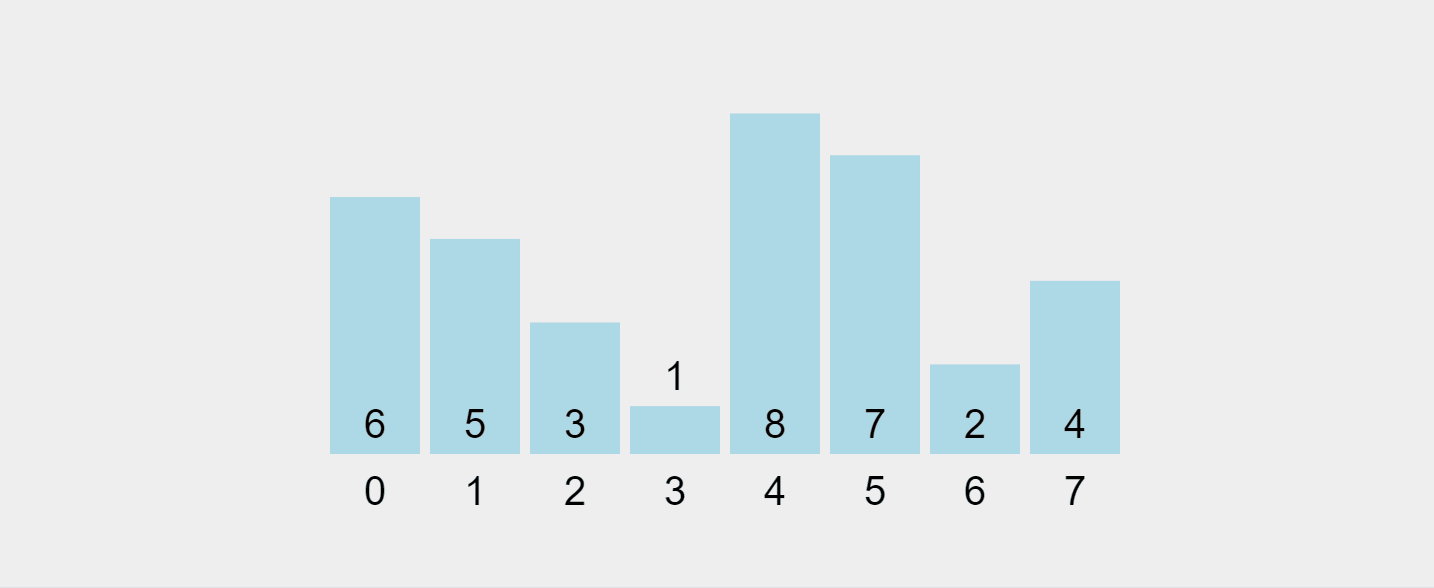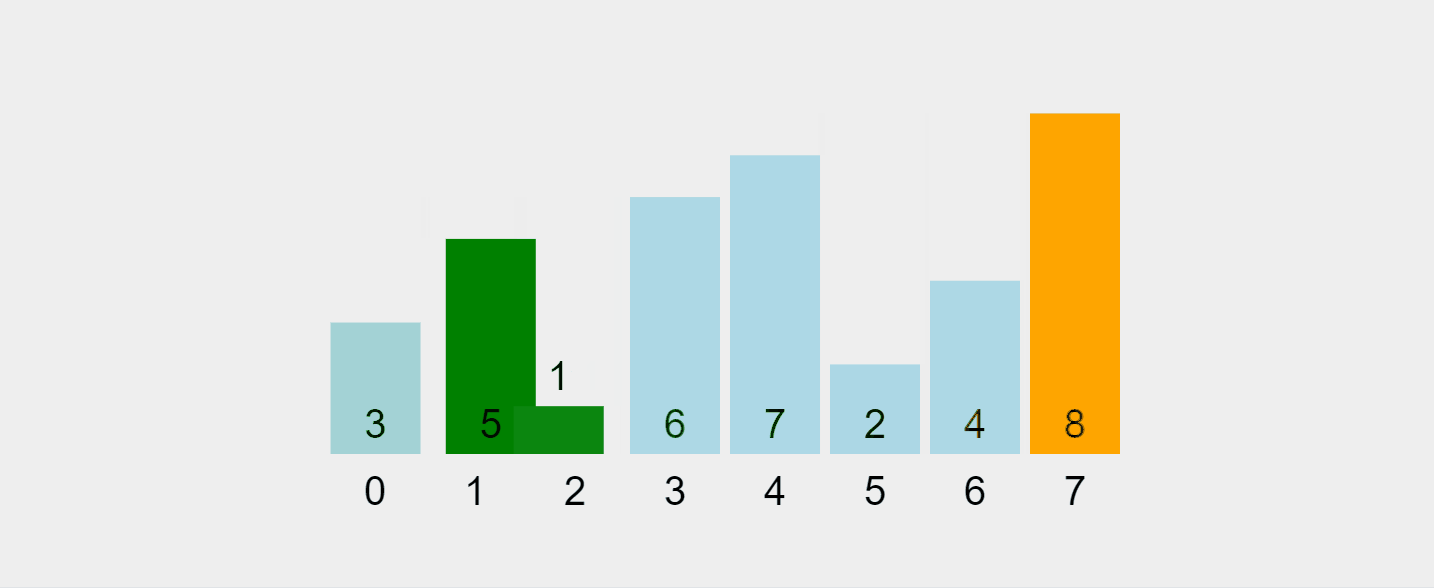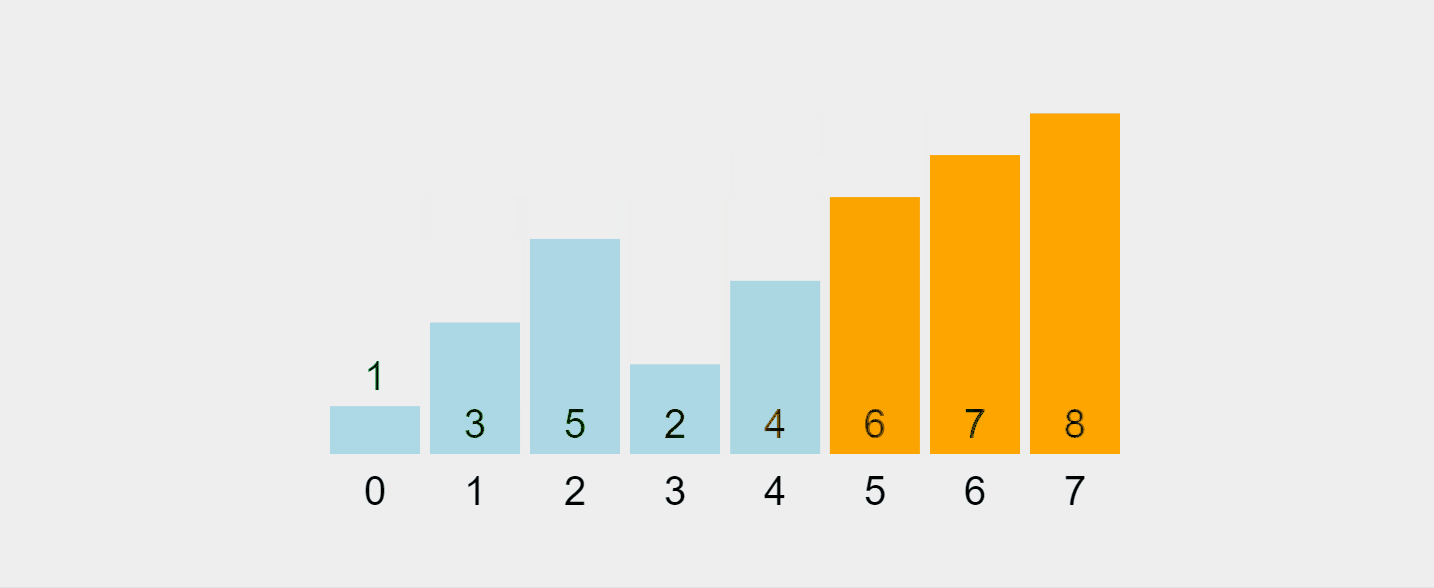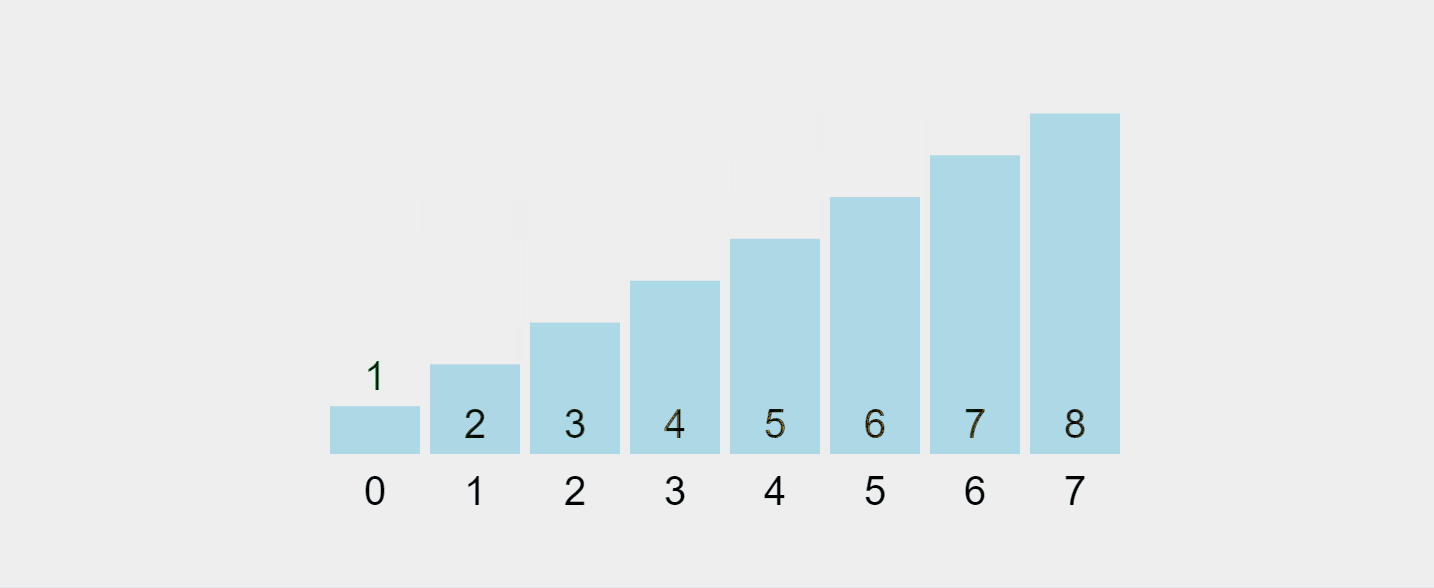
錄製的 gif 來自 https://visualgo.net/en/sorting
讓我們研究一下 JavaScript 中冒泡排序的三種實現,每種實現的最佳化等級都在增加。
function bubbleSort(list) {
// Outer loop: iterate through the entire list
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// Inner loop: compare adjacent elements
for (let j = 0; j < list.length - 1; j++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next one
if (list[j] > list[j + 1]) {
// Swap the elements using destructuring assignment
[list[j], list[j + 1]] = [list[j + 1], list[j]];
}
}
}
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
這個基本實作使用巢狀循環來比較和交換相鄰元素。外循環確保我們對數組進行了足夠的遍歷,而內循環則執行比較和交換。
function bubbleSort(list) {
// Outer loop: iterate through the entire list
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// Flag to check if any swaps occurred in this pass
let swapped = false;
// Inner loop: compare adjacent elements
for (let j = 0; j < list.length - 1; j++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next one
if (list[j] > list[j + 1]) {
// Swap the elements using destructuring assignment
[list[j], list[j + 1]] = [list[j + 1], list[j]];
// Set the swapped flag to true
swapped = true;
}
}
// If no swaps occurred in this pass, the list is sorted
if (!swapped) {
break; // Exit the outer loop early
}
}
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
此版本引入了一個交換標誌來檢查一次傳遞中是否進行了任何交換。如果沒有發生交換,則清單已經排序,我們可以提前跳出循環。
function bubbleSort(list) {
// Outer loop: iterate through the entire list
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// Flag to check if any swaps occurred in this pass
let swapped = false;
// Inner loop: compare adjacent elements
// Note: We reduce the upper bound by i in each pass
for (let j = 0; j < list.length - 1 - i; j++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next one
if (list[j] > list[j + 1]) {
// Swap the elements using destructuring assignment
[list[j], list[j + 1]] = [list[j + 1], list[j]];
// Set the swapped flag to true
swapped = true;
}
}
// If no swaps occurred in this pass, the list is sorted
if (!swapped) {
break; // Exit the outer loop early
}
}
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
最終的最佳化在每次傳遞中將內部循環的範圍減少了 i。這是因為每次傳遞後,最大的未排序元素「冒泡」到陣列末端的正確位置。
冒泡排序的效能特性如下:
時間複雜度:
空間複雜度:O(1) - 冒泡排序是一種就地排序演算法,只需要恆定量的額外記憶體。
與快速排序(平均O(n log n))或合併排序(O(n log n))等更高級的演算法相比,冒泡排序的二次時間複雜度使其對於大型資料集效率低下。
優點:
缺點:
雞尾酒排序,也稱為雞尾酒搖排序或雙向冒泡排序,是冒泡排序的改進版本。它雙向遍歷列表,有助於更有效地將元素移動到正確的位置。
Cocktail Sort is particularly useful in cases where the array has elements that are initially large at the beginning and small at the end, as it can reduce the total number of passes needed compared to traditional Bubble Sort.
Here's a visualization of Cocktail Sort:
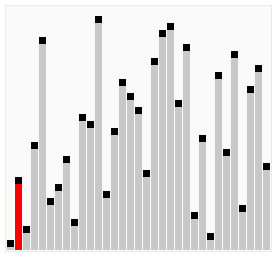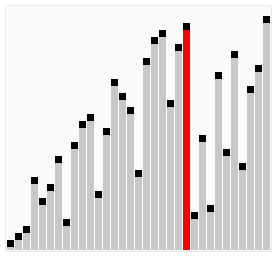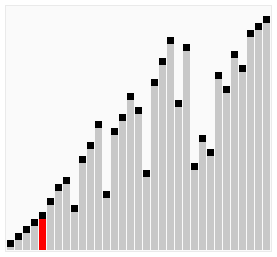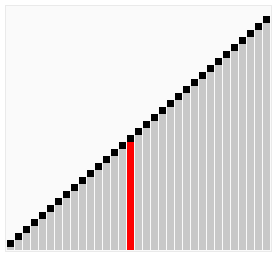
Visual from Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cocktail_shaker_sort
function cocktailSort(list) {
let swapped;
// The do...while loop ensures the sorting continues until no swaps are needed
do {
// Reset the swapped flag at the beginning of each complete iteration
swapped = false;
// First pass: left to right (like standard bubble sort)
for (let i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) {
// If the current element is greater than the next, swap them
if (list[i] > list[i + 1]) {
[list[i], list[i + 1]] = [list[i + 1], list[i]];
// Mark that a swap occurred
swapped = true;
}
}
// If no swaps occurred in the first pass, the array is sorted
if (!swapped) {
break; // Exit the do...while loop early
}
// Reset the swapped flag for the second pass
swapped = false;
// Second pass: right to left (this is what makes it "cocktail" sort)
for (let i = list.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
// If the current element is greater than the next, swap them
if (list[i] > list[i + 1]) {
[list[i], list[i + 1]] = [list[i + 1], list[i]];
// Mark that a swap occurred
swapped = true;
}
}
// The loop will continue if any swaps occurred in either pass
} while (swapped);
// Return the sorted list
return list;
}
This implementation alternates between forward and backward passes through the list, potentially reducing the number of iterations needed to sort the array.
While Bubble Sort isn't typically used in production environments for large-scale applications, it can still find use in certain scenarios:
Bubble Sort, despite its inefficiencies with large datasets, offers valuable insights into the world of sorting algorithms and algorithm analysis. Its straightforward approach makes it an excellent teaching tool for beginners in computer science.
Key takeaways are:
While you're unlikely to use Bubble Sort in production code for large-scale applications, the principles behind it are fundamental to many algorithms. The process of optimizing Bubble Sort teaches valuable lessons about algorithm improvement, serving as a stepping stone to more advanced computational problem-solving.
When it comes to algorithms, there's rarely a one-size-fits-all solution. The best algorithm for a given task depends on the specific requirements, constraints, and characteristics of your data. Bubble Sort, with all its limitations, still has its place in this diverse algorithmic ecosystem.
以上是使用 Javascript 進行演算法之旅 - 冒泡排序的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




