
編輯 | KX
先前,Google DeepMind 研究人員開發的費米子神經網路 (FermiNet) 非常適合對大量電子的量子基態進行建模。
FermiNet 最初專注於分子的基態。但是,當分子和材料受到大量能量的刺激時,例如暴露在光或高溫下,電子可能會被踢入更高的能量狀態—激發態。
激發態在物理學和化學等領域都很重要;然而,從第一原理出發對激發態特性進行可擴展、準確且穩健的計算仍然面臨重要的理論挑戰。
現在,DeepMind 研究人員開發了一種計算激發態的新方法,它比以前的方法更強大、更通用。該方法可以應用於任何類型的數學模型,包括 FermiNet 和其他神經網路。
所提出的方法對許多原子和分子實現了精確的激發態計算,遠遠優於現有的使用深度學習計算激發態特性的方法(尤其是在較大的系統上),並且可以應用於各種量子系統。
論文一作兼通訊作者David Pfau 激動發文「這是深度學習首次準確解決量子物理學中一些最難的問題。希望朝著深度學習的通用量子模擬邁出新的一步。」

相關研究以「Accurate computation of quantum excited states with neural networks」為題,登上Science !
論文連結:https://www.science.org/doi/abs/10.1126/science.adn0137
分子激發態
分子激發態暴露在光或高溫下,它們的電子就會被踢入一種臨時的新結構,稱為激發態。
分子在狀態之間轉換時吸收和釋放的確切能量量為不同的分子和材料創建了獨特的指紋。這影響了從太陽能電池板和 LED 到半導體和光催化劑等技術的性能。它們還在涉及光的生物過程中發揮關鍵作用,包括光合作用和視覺。
然而,這種指紋極難建模,因為激發電子本質上是量子的,這意味著它們在分子中的位置永遠不確定,只能用機率來表示。
FermiNet 可以在一系列具有各種不同定性正電子結合特性的原子和小分子中產生高度精確的、在某些情況下是最先進的基態能量。 然而 FermiNet 最初專注於分子的基態。但是,當分子和材料受到大量能量的刺激時,例如暴露在光或高溫下,電子可能會被踢入更高的能量狀態—激發態。
準確計算激發態的能量比計算基態能量困難得多。即使是基態化學的黃金標準方法,如耦合簇,在激發態上也顯示出數十倍的誤差。雖然研究人員想將其在 FermiNet 上的工作擴展到激發態,但現有方法的效果不足以使神經網路與最先進的方法相媲美。
更強大、更通用的激發態計算新方法
Crucially, this method has no free parameters to adjust and no penalty term to force orthogonalization. The researchers examined the accuracy of this approach using two different neural network architectures: FermiNet and Psiformer.
From single atoms to benzene
The researchers tested their method on a benchmark system that goes from single atoms to benzene-sized molecules. The accuracy of NES-VMC on first-row atoms is verified to be very close to experimental results, and on a series of small molecules, high-precision energies and oscillations are obtained that are comparable to the best existing theoretical estimates. device strength.
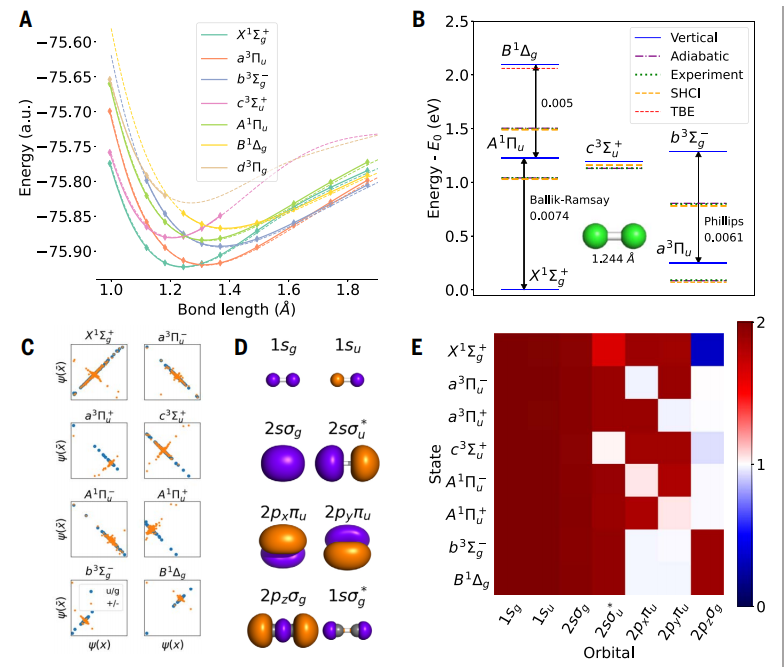
Illustration: excited state of carbon dimer. (Source: Paper)
Achieved a mean absolute error (MAE) of 4 meV on a small, complex molecule called a carbon dimer, which is five times more accurate than previous gold standard calculations.

Illustration: excited states and conic intersections of ethylene. (Source: paper)
In the case of ethylene, NES-VMC correctly describes the conic intersections of the twisted molecule and is in high agreement with high-precision multiple reference configuration interaction (MR-CI) results.

Illustration: Excited states of a larger double-excitation system. (Source: Paper)
The study also considered five challenging systems with low-lying double excitations, including multiple benzene-class molecules. In a system where all methods have good agreement on vertical excitation energies, Psiformer is chemically accurate across states, including butadiene, the ordering of some of which has also been controversial for decades.
For tetrazines and cyclopentadienones, where state-of-the-art calculations from a few years ago are known to be inaccurate, NES-VMC results are inconsistent with recent sophisticated diffusion Monte Carlo (DMC) and fully active space third-order perturbation theories (CASPT3) calculation is very close.

Illustration: excited state of benzene. (Source: paper)
Finally, the benzene molecule was also studied, where NES-VMC combined with Psiformer ansatz gave better results with the theoretical best estimate compared to other methods, including neural network ansatz using the penalty method. consistency. This not only verifies the mathematical correctness of the proposed method, but also shows that neural networks can accurately represent the excited states of molecules at the limits of current computational methods.
How to be applied to many-body quantum mechanics in the future
NES-VMC is a parameter-free and mathematically sound excited state variation principle. Combining this with neural network ansätze, significant accuracy can be achieved on a wide range of benchmark problems.
Accurate VMC methods for excited states of quantum systems open up many possibilities and greatly expand the application range of neural network wave functions.
Although this study only considered electronic excitations of molecular systems and neural network ansatz, NES-VMC is applicable to any quantum Hamiltonian and any ansatz, allowing for precise computational studies that can improve scientists' understanding of vibrational electronic coupling, optics Understanding of band gaps, nuclear physics, and other challenging problems.
The researchers said: "We are looking forward to how NES-VMC and deep neural networks will be applied to the most challenging problems in many-body quantum mechanics in the future."
Reference content:
https://x. com/pfau/status/1826681648597135464
https://deepmind.google/discover/blog/ferminet-quantum-physics-and-chemistry-from-first-principles/
https://www.imperial .ac.uk/news/255673/ai-tackles-most-difficult-challenges-quantum/
以上是AI首次解決量子物理學難題,DeepMind精確計算量子激發態,登Science的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




