Java 非同步等待被定義為執行 I/O 綁定操作,不需要任何應用程式回應能力。這些函數通常用於檔案和網路操作,因為它們需要在操作完成時執行回呼;另外這個函數總是會傳回一個值。借助 awake 關鍵字,在常規控制流語句內使用非同步調用,並且它是非阻塞代碼。在本主題中,我們將學習 Java 非同步等待。
廣告 該類別中的熱門課程 JAVA 掌握 - 專業化 | 78 課程系列 | 15 次模擬測驗開始您的免費軟體開發課程
網頁開發、程式語言、軟體測試及其他
文法
async/await 的一般簽名為
async void test() {
print('Welcome to EDUCBA');
}等待就像
const test=async() =>
{
await test ();
Print ("completed");
}非同步等待函數有助於編寫同步程式碼,同時在程式碼後面執行非同步任務。我們需要有 async 關鍵字。接下來是等待的部分,它表示正常運行非同步程式碼並繼續執行下一行程式碼。當在非同步函數中使用時,新的運算子「Await」會自動等待承諾來解析正在執行的進程。但是,在任何其他情況下使用時,它都會導致語法錯誤。
如果函數在錯誤處理中拋出錯誤,非同步函數的 Promise 將被拒絕。如果對應的函數恰好傳回一個值,則承諾將被解決。此非阻塞程式碼在單獨的執行緒上運行,並通知主執行緒任務完成或失敗。 Try-catch 在函數中使用來同步處理錯誤。讓我們以
開頭的範例async function hello() {
//process waiting
await new Promise(res => setTimeout(res, 2000));
// Rejection with 20 %
if (Math.random() > 0.2) {
throw new Error('Check the number.')
}
return 'number';
}上面的程式碼表示函數 hello() 是異步的,透過傳回一個數字來解決它,並透過檢查數字來拋出錯誤。
接下來,使用await和return一起暫停一個進程
async function miss() {
try {
return await hello();
} catch (e) {
return 'error caught';
}
}使用此函數更好的有前途的連結如下
async function promise1( req,res)
{
try
{
let a=await a.get(req,uid);
let b=await cart.get (yser,uid);
Res.send(await dosome(a,cart));
}
catch (err)
{
res.send(err);
}
}所以這裡await關鍵字指示函數get()在捕獲錯誤之前完成。
有了這個 Completable future,它會回傳一個 future 物件。這個 Completable future 是對非同步計算的引用並實現了 future。
private static CompletableFuture<Void> hello{
try {
String intermediate = await(doA());
String res = await(doB(intermediate));
reportSuccess(res);
} catch (Throwable th) {
reportFailure(th);
}
return completedFuture(null);
}所以在本節中,我們將了解 async 和 wait 的優點是如何在這裡工作的。
代碼:
import 'dart:async';
void main() async {
var a = await ten();
print(a);
}
Future<int> ten() async {
return 10;
}說明
上面的程式碼使用了future,Java 7版本的API,等待十秒鐘顯示10。
輸出:

代碼:
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
class Comput1 implements Runnable
{
public static int item = 0;
public void run()
{
item = 3 * 3;
try
{
CyclicBarrierAwaitExample2.newBarrier.await();
}
catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class Comput2 implements Runnable
{
public static int total = 0;
public void run()
{
// check if newBarrier is broken or not
System.out.println("Is it broken? - " + CyclicBarrierAwaitExample2.newBarrier.isBroken());
total = 20 + 20;
try
{
CyclicBarrierAwaitExample2.newBarrier.await(2000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
System.out.println("Number of rooms waiting at the barrier "+
"here = " + CyclicBarrierAwaitExample2.newBarrier.getNumberWaiting());
}
catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (TimeoutException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class CyclicBarrierAwaitExample2 implements Runnable
{
public static CyclicBarrier newBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(3);
public static void main(String[] args)
{
CyclicBarrierAwaitExample2 test = new CyclicBarrierAwaitExample2();
Thread t = new Thread(test);
t.start();
}
@Override
public void run()
{
System.out.println("Number of parties required to trip the barrier = "+
newBarrier.getParties());
System.out.println("Sum of product and sum = " + (Comput1.item +
Comput2.total));
Comput1 comp1 = new Comput1();
Comput2 comp2 = new Comput2();
Thread t = new Thread(comp1);
Thread t2 = new Thread(comp2);
t.start();
t2.start();
TimeUnit unit = TimeUnit.SECONDS;
try
{
CyclicBarrierAwaitExample2.newBarrier.await(1,unit);
}
catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException | TimeoutException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Sum of item and total = " + (Comput1.item +
Comput2.total));
newBarrier.reset();
System.out.println(" reset successful");
}
}說明
當另一個執行緒正在處理任務時,該值會被求和。
輸出:

代碼:
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class Async {
static List<Task> tasks = new ArrayList<>();
static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3);
public static void main(String[] args) {
createTasks();
executeTasks();
}
private static void createTasks() {
for (int k= 0; k < 10; k++) {
tasks.add(new Task(k));
}
}
private static void executeTasks() {
for (Task task : tasks) {
executor.submit(task);
}
}
static class Task extends Thread {
int n;
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random (). nextInt (1000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
printNum();
}
private void printNum() {
System.out.print(n + " ");
}
public Task(int n) {
this.n = n;
}
}
}說明
上面的程式碼透過指派一個執行緒值來啟動一個任務,即工作執行緒。這裡我們在 print numb() 函數中停止同步任務。因此,輸出如下圖所示:
輸出:
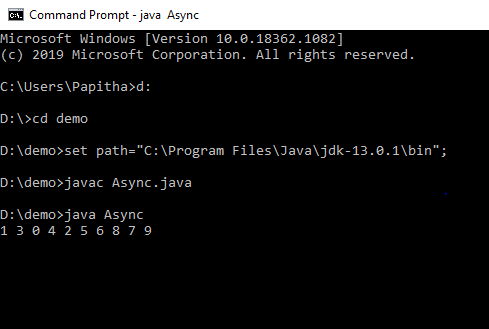
Async.html
<html>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<body> Understanding JavaScript Program Execution</br>
<script type="text/javascript">
function tensec()
{
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{ setTimeout(() => {
console.log('EDUCBA PAge -I take 20 second');
resolve();
}, 10000);
});
}
async function run()
{
console.log('EDUCBA PAge : Page executed immediately');
await tensec();
console.log('EDUCBA PAge : Next process');
}
run();
</script>
</body>
</html>說明
上面的程式碼執行它的promise並在async-await的幫助下顯示它們的等待時間間隔。例如,上面的腳本等待 20 秒才能完成任務。
輸出:

總而言之,編寫非同步程式碼有點困難,最重要的是,Promise 是定義延遲執行流程的通用方法。在本文中,我們學習如何編寫看起來像同步的非同步程式碼。在複雜的程式碼中使用非同步更為重要。 JavaScript 開發人員必須深入了解這個概念。
以上是Java 非同步等待的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




