Java 是最有用的程式語言之一。它具有多種應用,例如架構建構、解決科學計算、建構地圖等。為了讓這些任務變得簡單,Java 提供了java.lang.Math 類別或Java 中的數學函數,可以執行多種運算,例如平方、指數、ceil、對數、立方、abs、三角函數、平方根、floor等
廣告 該類別中的熱門課程 JAVA 掌握 - 專業化 | 78 課程系列 | 15 次模擬測驗開始您的免費軟體開發課程
網頁開發、程式語言、軟體測試及其他
本課程提供兩個領域,這是數學課程的基礎知識。他們是,
Java 提供了大量的數學方法。它們可以分類如下:
現在,讓我們詳細了解它們。
為了更好的理解,我們可以在Java程式中實作上述方法,如下所示:
| 方法 | 回傳值 | 參數 |
範例 |
|
abs() |
參數的絕對值。即正值 | 長整型、整數、浮點數、雙精確度 |
int n1 = Math.abs (80) //n1=80 int n2 =Math.abs (-60) //n2=60 |
|
sqrt() |
參數的平方根 | 雙 |
double n= Math.sqrt (36.0) // n=6.0 |
|
cbrt() |
參數的立方根 | 雙 |
double n= Math.cbrt (8.0) // n=2.0 |
|
max() |
參數中傳遞的兩個值的最大值 | 長整型、整數、浮點數、雙精確度 |
int n=Math.max(15,80) //n=80 |
|
分鐘() |
參數中傳遞的兩個值中的最小值 | 長整型、整數、浮點數、雙精確度 |
int n=Math.min(15,80) //n=15 |
|
ceil() |
將浮點數值向上捨入為整數值 | 雙 | double n=Math.ceil(6.34) //n=7.0 |
| 地板() | 將浮點數值向下捨去為整數值 | 雙 |
double n=Math.floor(6.34) //n=6.0 |
|
圓形() |
將浮點或雙精確度值向上或向下捨去為整數值 | 雙精確度、浮動 | double n = Math.round(22.445);//n=22.0 double n2 = Math.round(22.545); //n=23.0 |
|
戰俘() |
第一個參數的值提升到第二個參數 |
雙 |
double n= Math.pow(2.0, 3.0) //n=8.0 |
|
隨機() |
0 到 1 之間的隨機數 | 雙 | double n= Math.random() //n= 0.2594036953954201 |
|
signum() |
傳遞參數的符號。
如果為正,將顯示 1。 如果為負數,將顯示-1。 如果為0,則顯示0 |
雙精確度、浮動 |
double n = 數學。 Signum (22.4);//n=1.0 double n2 = Math.符號 (-22.5);//n=-1.0 |
|
addExact() |
參數的總和。如果得到的結果超出了 long 或 int 值,則會拋出異常。 | 整數,長 |
int n= Math.addExact(35, 21)//n=56 |
|
incrementExact() |
參數加1。如果取得的結果超出int值,則拋出例外。 | 整數,長 |
int n=數學。 incrementExact(36) //n=37 |
|
subtractExact() |
參數的差異。如果取得的結果超出int值,則拋出例外。 | 整數,長 |
int n= Math.subtractExact(36, 11) //n=25 |
|
multiplyExact() |
參數的總和。如果得到的結果超出了 long 或 int 值,則會拋出異常。 | 整數,長 |
int n= Math.multiplyExact(5, 5) //n=25 |
|
decrementExact() |
參數減1。如果取得的結果超出int或long值,則拋出異常。 | 整數,長 |
int n=數學。 decrementExact (36) //n=35 |
|
negateExact() |
參數的否定。如果取得的結果溢出 int 或 long 值,則會拋出例外。 | 整數,長 |
int n=數學。 negateExact(36) //n=-36 |
|
copySign() |
第一個參數的絕對值以及第二個參數中指定的符號 | 雙精確度、浮動 |
double d= Math.copySign(29.3,-17.0) //n=-29.3 |
|
floorDiv() |
將第一個參數除以第二個參數,並執行向下取整操作。 | 長整型 |
int n= Math.floorDiv(25, 3) //n=8 |
|
hypot() |
參數的平方和並進行平方根運算。中間不應該存在溢出或下溢。 | 雙 |
double n=Math.hypot(4,3) //n=5.0 |
|
getExponent() |
無偏指數。指數以 double 或 float | 表示int |
double n=Math.getExponent(50.45) //n=5 |
代碼:
//Java program to implement basic math functions
public class JavaMathFunctions {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n1 = Math.abs(80);
System.out.println("absolute value of 80 is: "+n1);
int n2 = Math.abs(-60);
System.out.println("absolute value of -60 is: "+n2);
double n3 = Math.sqrt(36.0);
System.out.println("Square root of 36.0 is: "+n3);
double n4 = Math.cbrt(8.0);
System.out.println("cube root 0f 8.0 is: "+n4);
int n5= Math.max(15,80);
System.out.println("max value is: "+n5);
int n6 =Math.min(15,80);
System.out.println("min value is: "+n6);
double n7 = Math.ceil(6.34);
System.out.println("ceil value of 6.34 is "+n7);
double n8 = Math.floor(6.34);
System.out.println("floor value of 6.34 is: "+n8);
double n9 = Math.round(22.445);
System.out.println("round value of 22.445 is: "+n9);
double n10 = Math.round(22.545);
System.out.println("round value of 22.545 is: "+n10);
double n11= Math.pow(2.0, 3.0);
System.out.println("power value is: "+n11);
double n12= Math.random();
System.out.println("random value is: "+n12);
double n13 = Math. signum (22.4);
System.out.println("signum value of 22.4 is: "+n13);
double n14 = Math. signum (-22.5);
System.out.println("signum value of 22.5 is: "+n14);
int n15= Math.addExact(35, 21);
System.out.println("added value is: "+n15);
int n16=Math. incrementExact(36);
System.out.println("increment of 36 is: "+n16);
int n17 = Math.subtractExact(36, 11);
System.out.println("difference is: "+n17);
int n18 = Math.multiplyExact(5, 5);
System.out.println("product is: "+n18);
int n19 =Math. decrementExact (36);
System.out.println("decrement of 36 is: "+n19);
int n20 =Math. negateExact(36);
System.out.println("negation value of 36 is: "+n20);
}
}輸出:

以下是實現表中提到的三角數學函數的Java程式:
|
Method |
Return value | Arguments | Example |
|
sin() |
Sine value of the parameter | double |
double num1 = 60; //Conversion of value to radians double value = Math.toRadians(num1); print Math.sine (value) //output is 0.8660254037844386 |
|
cos() |
Cosine value of the parameter | double |
double num1 = 60; //Conversion of value to radians double value = Math.toRadians(num1); print Math.cos (value) //output is 0.5000000000000001 |
|
tan() |
tangent value of the parameter | double |
double num1 = 60; //Conversion of value to radians double value = Math.toRadians(num1); print Math.tan(value) //output is 1.7320508075688767 |
|
asin() |
Arc Sine value of the parameter. Or Inverse sine value of the parameter | double |
Math.asin(1.0) // 1.5707963267948966 |
|
acos() |
Arc cosine value of the parameter Or Inverse Cosine value of the parameter | double |
Math.acos(1.0) //0.0 |
|
atan() |
Arctangent value of the parameter Or Inverse tangent value of the parameter | double |
Math.atan(6.267) // 1.4125642791467878 |
sin()
雙 num1 = 60; //將值轉換為弧度
雙精確值 = Math.toRadians(num1); print Math.sine (value) //輸出為0.8660254037844386
cos()
雙 num1 = 60; //將值轉換為弧度
雙精確度值 = Math.toRadians(num1); print Math.cos (value) //輸出為 0.5000000000000001
tan()
雙 num1 = 60; //將值轉換為弧度
雙精確值 = Math.toRadians(num1); print Math.tan(value) //輸出為 1.7320508075688767
asin()
Math.asin(1.0) // 1.5707963267948966
acos()
Math.acos(1.0) //0.0
atan()
Math.atan(6.267) // 1.4125642791467878
Code:
//Java program to implement trigonometric math functions
public class JavaMathFunctions {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double num1 = 60;
// Conversion of value to radians
double value = Math.toRadians(num1);
System.out.println("sine value is : "+Math.sin(value));
System.out.println("cosine value is : "+Math.cos(value));
System.out.println("tangent value is : "+Math.tan(value));
double num2 = 1.0;
System.out.println("acosine value is : "+Math.acos(num2));
System.out.println("asine value is : "+Math.asin(num2));
double num3 = 6.267;
System.out.println("atangent value is : "+Math.atan(num3)); <strong>Output:</strong>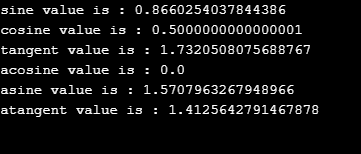
Following is the sample program that implements Logarithmic math methods:
|
Method |
Return Value | Arguments |
Example |
|
expm1() |
Calculate E’s power and minus 1 from it. E is Euler’s number. So here, it is ex-1. | double |
double n = Math.expm1(2.0) // n = 6.38905609893065 |
|
exp() |
E’s power to the given parameter. That is, ex | double |
double n=Math.exp(2.0) //n = 7.38905609893065 |
|
log() |
Natural logarithm of parameter | double |
double n=Math.log(38.9) //n=3.6609942506244004 |
|
log10() |
Base 10 logarithm of parameter | double |
double n = Math.log10(38.9) //n= 1.5899496013257077 |
|
log1p() |
Natural logarithm of the sum of parameter and one. ln(x+1) | double |
double n = Math.log1p(26) //n= 3.295836866004329 |
Code:
//Java program to implement logarithmic math functions
public class JavaMathFunctions {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double n1 = Math.expm1(2.0);
double n2 = Math.exp(2.0);
double n3 = Math.log(38.9);
double n4 = Math.log10(38.9);
double n5 = Math.log1p(26);
System.out.println("expm1 value of 2.0 is : "+n1);
System.out.println("exp value of 2.0 is : "+n2);
System.out.println("log of 38.9 is : "+n3);
System.out.println("log10 of 38.9 is : "+n4);
System.out.println("log1p of 26 is : "+n5);
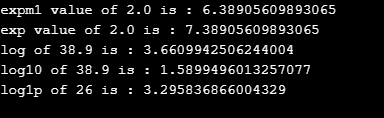
}}Output:
Following is the Java program to implement hyperbolic math functions mentioned in the table:
|
Method |
Return value | Arguments |
Example |
|
sinh() |
Hyperbolic Sine value of the parameter. i.e (ex – e -x)/2 Here, E is the Euler’s number. | double |
double num1=Math.sinh (30) //output is 5.343237290762231E12 |
|
cosh() |
Hyperbolic Cosine value of the parameter. i.e. (ex + e -x)/2 Here, E is the Euler’s number. | double |
double num1 = Math.cosh (60.0) //output is 5.710036949078421E25 |
|
tanh() |
Hyperbolic tangent value of the parameter | double |
double num1= Math.tanh (60.0) //output is 1.0 |
Code:
//Java program to implement HYPERBOLIC math functions
public class JavaMathFunctions {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double n1 = Math.sinh (30);
double n2 = Math.cosh (60.0);
double n3 = Math.tanh (60.0);
System.out.println("Hyperbolic sine value of 300 is : "+n1);
System.out.println("Hyperbolic cosine value of 60.0 is : "+n2);
System.out.println("Hyperbolic tangent value of 60.0 is : "+n3);
}
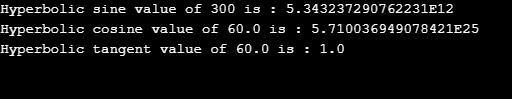
}Output:
| Method | Return Value | Arguments | Example |
| toRadians() | Degree angle converts to radian angle | double |
double n = Math.toRadians(180.0) //n= 3.141592653589793 |
| toDegrees() | Radian angle converts to Degree angle | double |
double n = Math. toDegrees (Math.PI) //n=180.0 |
Now, let us see a sample program to demonstrate Angular Math methods.
Code:
//Java program to implement Angular math functions
public class JavaMathFunctions {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double n1 = Math.toRadians(180.0);
double n2 = Math. toDegrees (Math.PI);
System.out.println("Radian value of 180.0 is : "+n1);
System.out.println("Degree value of pi is : "+n2);
}
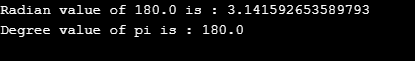
}Output:
Java offers a wide variety of math functions to perform different tasks such as scientific calculations, architecture designing, structure designing, building maps, etc. This document discusses several basic, trigonometric, logarithmic and angular math functions in detail with sample programs and examples.
以上是Java 中的數學函數的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




