TreeMap 與抽象類別一起使用,在 Java 中部署 Map 和 NavigableMap 介面。映射根據其鍵的自然順序或通過取決於構建器的預先構建比較器進行排序。這是排序和儲存鍵值對的簡單方法。樹狀圖保留的儲存順序必須與任何其他分類圖相同,無論特定的比較器為何。
開始您的免費軟體開發課程
網頁開發、程式語言、軟體測試及其他
以下是TreeMap的一些屬性。
- 它由獨特的元素組成。
- 它不能有空鍵。
- 可以多次出現空值。
- 非同步。
聲明:
public class TreeMap<Key, Value> extends AbstractMap<Key, Value>implements NavigableMap<Key, Value>, Cloneable, Serializable
登入後複製
這裡,Key 和 Value 分別是這個映射中的鍵和映射值的型別。
TreeMap 的建構子
以下是TreeMap的建構子。
-
TreeMap():將透過自然排序鍵來建構一個新的空白樹狀圖。
-
TreeMap(比較器 Key 將透過對比較器中指定的鍵進行排序來建構一個新的空樹形圖。
- TreeMap( 地圖Koey,? Value> m): 將使用映射m 中的映射建構一個新的樹形圖,並自然地對鍵進行排序。
TreeMap-
( SortedMapKK >V
alue> m):
將使用映射m 中的映射建構一個新的樹狀圖,並對比較器中指定的鍵進行排序。
TreeMap 的方法
TreeMap 提供了廣泛的方法來幫助執行不同的功能。他們是:
-
clear(): All the mapping in the map will be removed.
-
clone(): A shallow copy will be returned for the TreeMap instance.
-
containsKey(Objectk): If there is mapping available for the specified key, true will be returned.
-
containsValue(Objectv): If there is mapping available for one or more keys for the value v, true will be returned.
-
ceilingKey(Kkey): Least key which is larger than or equal to the specified key will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
ceilingEntry(Kkey): Key-value pair for the least key, which is larger than or equal to the specified key will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
firstKey(): First or last key in the map will be returned.
-
firstEntry(): Key-value pair for the least or first key in the map will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
floorKey(Kkey): The Largest key, which is less than or equal to the specified key, will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
floorEntry(Kkey): Key-value pair for the largest key, which is less than or equal to the specified key, will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
lastKey(): Highest or last key in the map will be returned.
-
lastEntry(): Key-value pair for the largest key in the map will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
lowerKey(Kkey): The Largest key, which is strictly smaller than the specified key, will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
lowerEntry(Kkey): Key-value pair for the largest key, which is strictly smaller than the specified key, will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
remove(Objectk): Mapping for the specified key in the map will be removed.
-
size(): Count of key-value pairs in the map will be returned.
-
higherEntry(Kkey): Key-value pair for the smallest key, which is strictly larger than the specified key, will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
higherKey(Kkey): The Smallest key, which is strictly higher than the specified key, will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
descendingMap(): Reverse order will be returned for the mappings.
-
entrySet(): Set view will be returned for the mappings.
-
get(Objectk): The value of the specified key will be returned. If the key does not contain any mapping, then null will be returned.
-
keySet(): Set view will be returned for the keys.
-
navigableKeySet(): NavigableSet view will be returned for the keys.
-
pollFirstEntry(): Key-value pair for the least or first key in the map will be removed and returned. If the map is empty, then null will be returned.
-
pollLastEntry(): Key-value pairs for the greatest key in the map will be removed and returned. If the map is empty, then null will be returned.
-
values(): Collection view will be returned for the values in the map.
Example to Implement TreeMap in Java
Now, let us see a sample program to create a treemap and add elements to it.
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class TreeMapExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Tree Map creation
TreeMap tmap = new TreeMap();
// Add elements to the treemap tmap
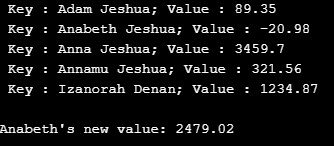
tmap.put("Anna Jeshua", new Double(3459.70));
tmap.put("Annamu Jeshua", new Double(321.56));
tmap.put("Izanorah Denan", new Double(1234.87));
tmap.put("Adam Jeshua", new Double(89.35));
tmap.put("Anabeth Jeshua", new Double(-20.98));
// Retrieve the entry set of treemap
Set set = tmap.entrySet();
// Create an iterator itr
Iterator itr = set.iterator();
// Display the elements in treemap using while loop
while(itr.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry mp = (Map.Entry)itr.next();
System.out.print(" Key : " + mp.getKey() + ";");
System.out.println(" Value : "+ mp.getValue());
}
System.out.println();
// Add 2500 to Anabeth's value
double val = ((Double)tmap.get("Anabeth Jeshua")).doubleValue();
tmap.put("Anabeth Jeshua", new Double(val + 2500));
System.out.println("Anabeth's new value: " + tmap.get("Anabeth Jeshua"));
} }登入後複製
Output:
Keys and corresponding values of the TreeMap will be displayed on executing the code.

Explanation:
- 首先,建立一個TreeMap並在其中加入元素。
- 為了顯示元素,必須建立一個迭代器。
- 使用迭代器,顯示所有按鍵及其對應的值。
- 要將鍵值加 2500,也可以使用 put() 方法。
結論
Java TreeMap 是紅黑樹的實現,有助於按排序順序儲存鍵值對。本文檔詳細討論了Java TreeMap的宣告、建構函式、方法和範例程式等幾個細節。
以上是Java中的TreeMap是什麼?的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!