Java 中的定時器
Java 中的定時器可在 java 中使用。 util 套件擴展了 Object 類別並實作了 Serialized 和 Cloneable 介面。計時器類別包含用於執行與計時相關的活動的方法。 Java中的Timer類別用於執行與時間相關的任務調度。 Java 執行緒使用 Timer 類別的方法來排程任務,例如在某個時刻後執行一段程式碼,在某個預先定義的時間後重複執行程式碼。每個 Timer 物件都綁定到一個單獨的後台運行線程,該線程負責執行與該線程關聯的所有任務。要注意的是,java中的定時器類別是執行緒安全的;也就是說,在某一時刻,只有一個執行緒可以執行Timer類別的方法。 Timer 類別也使用二進位堆作為底層資料結構來儲存任務。
開始您的免費軟體開發課程
網頁開發、程式語言、軟體測試及其他
Java 中定時器的語法
這是在 java 中如何使用 Timer 類別的基本語法:
文法:
// create a class extending TimerTask
class TimerHelper extends TimerTask
{
//define run method
public void run()
{
// Write Code to be executed by Timer
}
}
class MainClass{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//create timer instance
Timer timer = new Timer();
// create Timer class instance
TimerTask task = new TimerHelper ();
// call timer method
timer.schedule(task, 3000,6000);
//first argument is timer object
// second argument is time in milliseconds after which the code will be first executed
// Third argument is time in milliseconds after which the code will be executed regularly.
}
}上述語法的解釋:該語法展示如何在java中使用Timer類別。使用計時器類別涉及建立一個擴展 TimerTask 的類別並在其中定義 run 方法。 run 方法包含需要在時間驅動的基礎上執行的邏輯。以下是 Timer 類別聲明:
public class Timer extends Object implements Serializable, Cloneable
Java中Timer類別的方法
現在我們將看到 java Timer 類別中可用的不同方法和欄位。以下是 Timer 類別中常用方法的列表:
| Method Name | Description |
| public void schedule(TimerTask task, Date date) | Schedules a task to be executed on the defined date. |
| public void schedule (TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long timeperiod) | The first argument is TimerTask to be executed; the second argument is the time after which the task is executed for the first time, and the third argument is seconds in milliseconds after which task will be executed regularly. |
| public int purge() | Used for removing all canceled tasks from the timer’s queue. |
| public void cancel() | Cancel’s the timer. |
| public void schedule(TimeTask task, long delay) | Schedules the task to be executed after the specified time in milliseconds. |
| public void schedule(TimeTask task, long delay, long period) | The first argument is TimerTask to be executed; the second argument is the time in milliseconds after which task is executed for the first time, and the third argument is seconds in milliseconds after which task will be executed regularly. |
| public void scheduleAtFixedRate(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long timeperiod) | The first argument is TimerTask to be executed; the second argument is the time after which the task is executed for the first time, and the third argument is seconds in milliseconds after which the task will be executed regularly. |
| public void scheduleAtFixedRate (TimeTask task, long delay, long period) | The first argument is TimerTask to be executed; the second argument is the time in milliseconds after which task is executed for the first time, and the third argument is seconds in milliseconds after which task will be executed regularly. |
From the above-stated methods, we have found two methods that are similar in working but different in the name; they are schedule and scheduleAtFixedRate. The difference between the two is that in the case of fixed-rate execution, each execution is scheduled in accordance with the initial execution. If there is a delay in execution, then two or more executions will occur in quick succession to overcome the delay.
Constructors in Timer Class
The timer class contains four constructors for instantiating timer object.
- Timer(): Creates a new Timer Object.
- Timer(boolean isDaemon): Creates a timer object with a corresponding thread specified to run as a daemon.
- Timer(String name): Creates a timer object with a corresponding thread name.
- Timer(String name, boolean isDaemon): This method is a combination of the above two constructors.
One of the above four listed constructors can be called depending on our requirements.
Examples of Implementing Timer in Java
Below is the example of Timer in Java:
Example #1
To start things, let us see a basic example of Timer class. In this example, we will demonstrate the use of the schedule method of the Timer class.
Code:
package com.edubca.timer;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
class TimerHelper extends TimerTask
{
public static int counter = 0;
public void run()
{
counter++;
System.out.println("Timer run Number " + counter);
}
}
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Timer timer = new Timer();
TimerTask timerhelper = new TimerHelper();
timer.schedule(timerhelper, 3000, 2000);
}
}Explanation of the above code: The above code will execute the run method for the first time after 3 seconds as the first argument is 3000, and after every 2 seconds, the run method will be executed regularly. Here is the output that will be displayed:
Output:
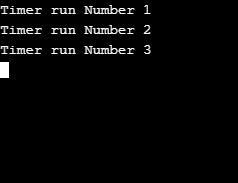
Example #2
In this example, we will see how to terminate a timer thread after a given number of timer runs.
Code:
package com.edubca.timer;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
class TimerHelper extends TimerTask
{
public static int counter = 0;
public void run()
{
counter++;
if(counter ==3){
this.cancel();
System.out.println("Now Cancelling Thread!!!!!");
return;
}
System.out.println("Timer run Number " + counter);
}
}
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Timer timer = new Timer();
TimerTask helper = new TimerHelper();
helper.schedule(task, 3000, 2000);
}
}In the above example, the timer will cancel after the three times run method is called using the timer class’s cancel method.
Output:
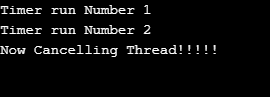
以上是Java 中的定時器的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 突破或從Java 8流返回?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
突破或從Java 8流返回?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8引入了Stream API,提供了一種強大且表達力豐富的處理數據集合的方式。然而,使用Stream時,一個常見問題是:如何從forEach操作中中斷或返回? 傳統循環允許提前中斷或返回,但Stream的forEach方法並不直接支持這種方式。本文將解釋原因,並探討在Stream處理系統中實現提前終止的替代方法。 延伸閱讀: Java Stream API改進 理解Stream forEach forEach方法是一個終端操作,它對Stream中的每個元素執行一個操作。它的設計意圖是處
 PHP:網絡開發的關鍵語言
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP:網絡開發的關鍵語言
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP是一種廣泛應用於服務器端的腳本語言,特別適合web開發。 1.PHP可以嵌入HTML,處理HTTP請求和響應,支持多種數據庫。 2.PHP用於生成動態網頁內容,處理表單數據,訪問數據庫等,具有強大的社區支持和開源資源。 3.PHP是解釋型語言,執行過程包括詞法分析、語法分析、編譯和執行。 4.PHP可以與MySQL結合用於用戶註冊系統等高級應用。 5.調試PHP時,可使用error_reporting()和var_dump()等函數。 6.優化PHP代碼可通過緩存機制、優化數據庫查詢和使用內置函數。 7
 PHP與Python:了解差異
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP與Python:了解差異
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP和Python各有優勢,選擇應基於項目需求。 1.PHP適合web開發,語法簡單,執行效率高。 2.Python適用於數據科學和機器學習,語法簡潔,庫豐富。
 PHP與其他語言:比較
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP與其他語言:比較
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP適合web開發,特別是在快速開發和處理動態內容方面表現出色,但不擅長數據科學和企業級應用。與Python相比,PHP在web開發中更具優勢,但在數據科學領域不如Python;與Java相比,PHP在企業級應用中表現較差,但在web開發中更靈活;與JavaScript相比,PHP在後端開發中更簡潔,但在前端開發中不如JavaScript。
 PHP與Python:核心功能
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP與Python:核心功能
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP和Python各有優勢,適合不同場景。 1.PHP適用於web開發,提供內置web服務器和豐富函數庫。 2.Python適合數據科學和機器學習,語法簡潔且有強大標準庫。選擇時應根據項目需求決定。
 Java程序查找膠囊的體積
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java程序查找膠囊的體積
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
膠囊是一種三維幾何圖形,由一個圓柱體和兩端各一個半球體組成。膠囊的體積可以通過將圓柱體的體積和兩端半球體的體積相加來計算。本教程將討論如何使用不同的方法在Java中計算給定膠囊的體積。 膠囊體積公式 膠囊體積的公式如下: 膠囊體積 = 圓柱體體積 兩個半球體體積 其中, r: 半球體的半徑。 h: 圓柱體的高度(不包括半球體)。 例子 1 輸入 半徑 = 5 單位 高度 = 10 單位 輸出 體積 = 1570.8 立方單位 解釋 使用公式計算體積: 體積 = π × r2 × h (4
 PHP的影響:網絡開發及以後
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHP的影響:網絡開發及以後
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHPhassignificantlyimpactedwebdevelopmentandextendsbeyondit.1)ItpowersmajorplatformslikeWordPressandexcelsindatabaseinteractions.2)PHP'sadaptabilityallowsittoscaleforlargeapplicationsusingframeworkslikeLaravel.3)Beyondweb,PHPisusedincommand-linescrip
 PHP:許多網站的基礎
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP:許多網站的基礎
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP成為許多網站首選技術棧的原因包括其易用性、強大社區支持和廣泛應用。 1)易於學習和使用,適合初學者。 2)擁有龐大的開發者社區,資源豐富。 3)廣泛應用於WordPress、Drupal等平台。 4)與Web服務器緊密集成,簡化開發部署。






