編輯| 蘿蔔皮
意外的藥物交互作用(DDI) 是藥物研究和臨床應用的重要問題,因為其極有可能引發嚴重的藥物不良反應或藥物停藥。
雖然許多深度學習模型在 DDI 預測方面取得了很好的成果,但模型可解釋性以揭示 DDI 的根本原因尚未得到廣泛探索。
福州大學、福建醫科大學第一附屬醫院以及元星智藥的研究人員提出MeTDDI——一種深度學習框架,具有局部-全局自註意力和共同註意力,用於學習基於主題的DDI 預測圖。
關於可解釋性,研究人員對 73 種藥物(13,786 個 DDI)進行了廣泛的評估,MeTDDI 可以精確解釋涉及 58 種藥物的 5,602 個 DDI 的結構機制。此外,MeTDDI 顯示出解釋複雜 DDI 機制和降低 DDI 風險的潛力。
MeTDDI 為探索 DDI 機制提供了一個新的視角,這將有利於藥物發現和多重用藥,從而為患者提供更安全的治療。
研究以「Learning motif-based graphs for drug–drug interaction prediction via local–global self-attention」為題,於 2024 年 8 月 27 日發佈在《Nature Machine Intelligence》。

由於老化和多重疾病,藥物組合或多重用藥被廣泛使用,並可能對公共衛生和經濟造成影響。儘管多重用藥具有治療效果,但存在發生意外藥物間交互作用 (DDI) 的風險,這可能導致嚴重的藥物不良反應 (ADR) 甚至停藥。
因此,提前預測 DDI 將對藥物研究和臨床環境帶來巨大好處,從而提高藥物安全性並保護患者健康。透過體外和體內實驗進行 DDI 評估很有用,但成本高、耗時且費力,阻礙了大規模 DDI 篩選的實用性。
如今,深度學習模型已成為高通量準確 DDI 預測以及根本原因解釋的有前途的替代方案。
在最新的研究中,福州大學、福建醫科大學第一附屬醫院以及元星智藥的研究團隊重點關注代謝介導的藥物相互作用(MMDDI)的預測,並提出了基於分子結構的深度學習框架MeTDDI,用於預測MMDDI。
此方法主要用於解決DDI 預測的三個挑戰:(1) 學習分子內和分子間亞結構相互作用,(2) 預測DDI 相關的藥物代謝,(3) 廣泛提供和評估模型的可解釋性。

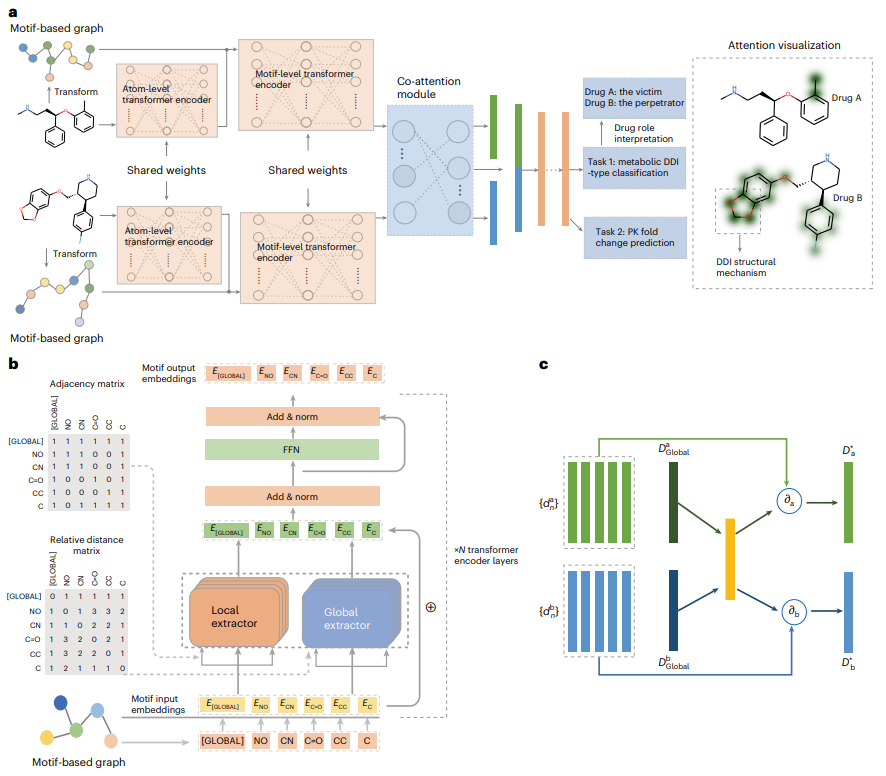
圖示:MeTDDI 架構概述。 (資料來源:論文)
受益於局部-全局自註意力和共同註意力結構,MeTDDI 可以有效地學習基於基序的圖內/圖之間的分子內和分子間子結構相互作用,從而進行DDI 推理。
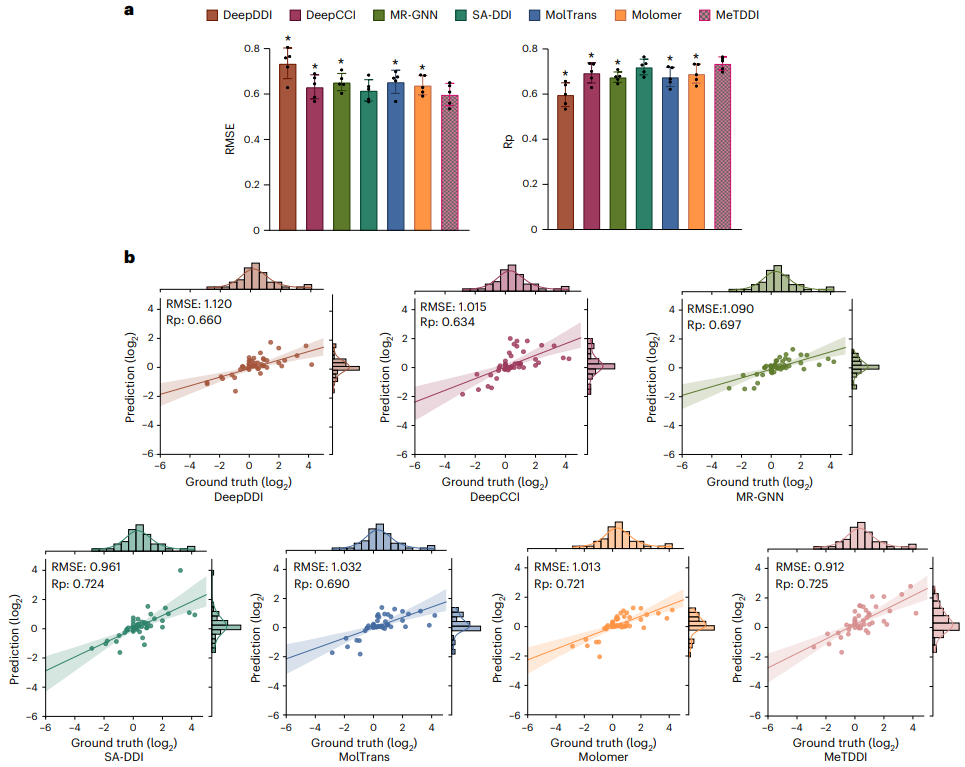
評估結果表明,它在分類和回歸任務中都取得了與基線相比具有競爭力的表現。 MeTDDI 還可以準確識別藥物(perpetrator 或 victim)在 DDI 中的機製作用,並量化 perpetrator 對 victim PK 的影響,這對藥物研究和臨床應用都非常有益。

圖示:模型在預測AUC FC值的表現比較。 (資料來源:論文)
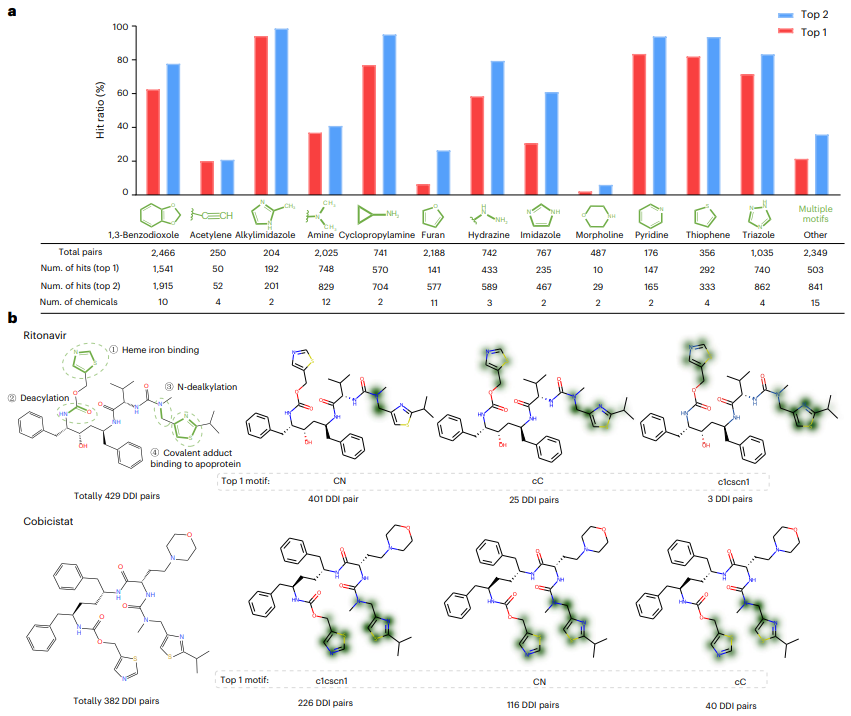
關於模型的可解釋性,MeTDDI 展示了識別與 DDI 相關的關鍵機制子結構的能力。
首先,MeTDDI 視覺化的關鍵子結構與文獻中對 73 種代表性化合物(具有 13,786 個 DDI 對)的分析中報道的關鍵子結構大致匹配。

圖示:MeTDDI 的可解釋性分析用於解釋 DDI 機制。 (資料來源:論文)
其次,研究人員評估了 MeTDDI 以及兩個最先進的模型(即 CIGIN 和 CGIB)的模型可解釋性。結果表明,MeTDDI 在模型可解釋性方面也表現出優異的性能。
此外,MeTDDI 可以突顯與酵素抑制相關的化學物質的代謝位點。
MeTDDI 的優勢
傳統方法僅透過體外測試 perpetrator 的代謝酶抑制來解釋 DDI 機制,而沒有充分考慮 victim。這是有問題的,因為 perpetrator 對酵素抑制的效力可以根據 victim 的化學特性而改變。
Victim may alter the binding or interaction pattern of perpetrators with metabolic enzymes (especially CYP), resulting in various enzyme inhibition mechanisms. This may explain why some chemicals, such as ethinyl estradiol and gestodene, which are potent inhibitors of metabolic enzymes when used alone in vitro, are less effective when combined with their victims. This may explain why only two reactions were observed in the study with ethinyl estradiol, which is thought to be a mechanism for inactivating CYP3A4 in vitro.
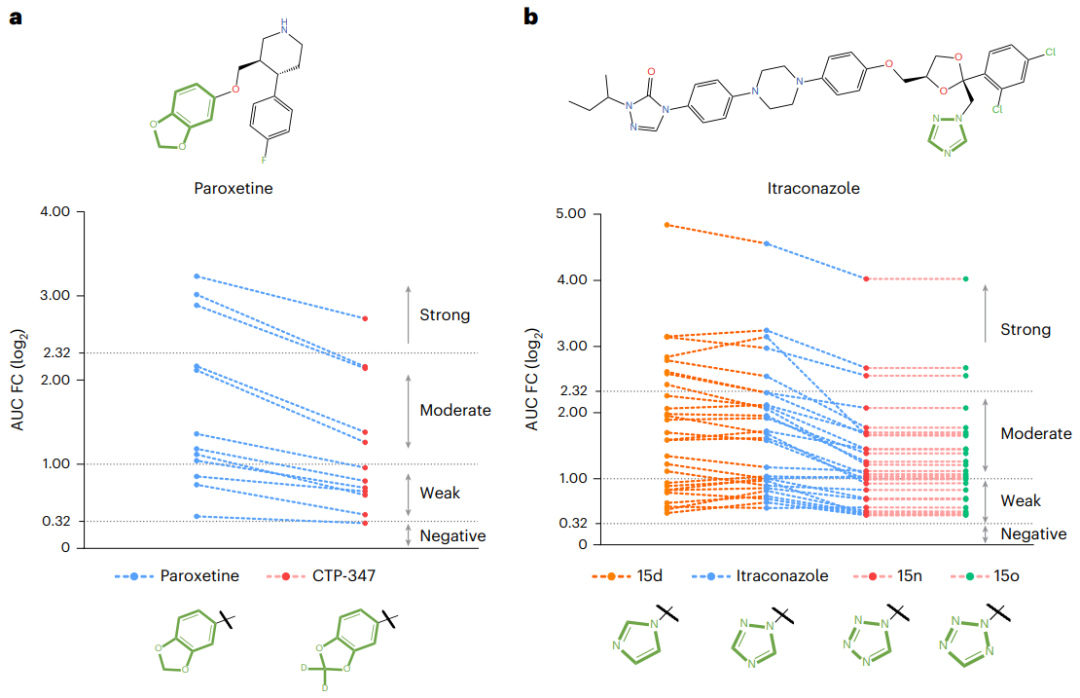
Additionally, case studies of paroxetine and itraconazole show that MeTDDI correctly predicts motif changes in chemicals and matches results from biological experiments, demonstrating its potential to help researchers modify drugs Structure to mitigate MMDDI risks.
In summary, MeTDDI enhances DDI prediction capabilities and provides a new perspective for understanding and exploring DDI mechanisms, which will facilitate drug development and polypharmacy, thereby providing safer treatments for patients.

Illustration: Two case studies of DDI mitigation using MeTDDI. (Source: Paper) Improvement Directions of MeTDDI
MeTDDI has many advantages, but at the same time, it also has some limitations.
First, accurate prediction is challenging in difficult scenarios. This may stem from the diversity and complexity of DDI mechanisms and the limitations of relying solely on drug structure.
Since MMDDI requires both drugs to interact on the same metabolic enzymes, enzyme features can be incorporated into the model for better learning. However, some metabolic enzymes (such as CYP) exhibit extraordinary flexibility in drug-enzyme interaction sites; therefore, modeling of enzyme characteristics remains a challenge.
Second, the dataset trained on MeTDDI is based on FDA drug labels, which are statistical observations of the population and may not reflect the characteristics of individual patients. Therefore, where available, individual patient data should be considered in order to develop models and make more precise predictions in the future. Third, MeTDDI may have difficulty predicting interactions of more than two drugs simultaneously.
However, a general practice to ensure polypharmacy is to search for pairwise DDIs between all possible drug pairs; MeTDDI can be directly deployed to predict DDIs between multiple drugs by enumerating all drug pairs.
Finally, for newly discovered substructures underlying DDI, alternative techniques such as molecular docking can be employed as complementary approaches to enhance the credibility of MeTDDI visualization capabilities. And, the researchers say, molecular docking is a valuable complementary tool to MeTDDI.
Paper link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s42256-024-00888-6
以上是高效準確預測DDI,福大、元星智藥團隊解釋性藥物AI模型,登Nature子刊的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!