分頁是處理大型資料集時任何資料庫操作的關鍵部分。它允許您將資料分割成可管理的區塊,從而更容易瀏覽、處理和顯示。 MongoDB 提供了兩種常見的分頁方法:基於偏移量和基於遊標。雖然這兩種方法具有相同的目的,但它們在效能和可用性方面顯著不同,尤其是隨著資料集的成長。
讓我們深入研究這兩種方法,看看為什麼基於遊標的分頁通常優於基於偏移量的分頁。
基於偏移量的分頁非常簡單。它檢索從給定偏移量開始的特定數量的記錄。例如,第一頁可能檢索記錄 0-9,第二頁檢索記錄 10-19,依此類推。
但是,這種方法有一個顯著的缺點:當您移動到更高的頁面時,查詢會變得更慢。這是因為資料庫需要跳過前幾頁的記錄,這涉及掃描它們。
這是基於偏移量的分頁代碼:
async function offset_based_pagination(params) {
const { page = 5, limit = 100 } = params;
const skip = (page - 1) * limit;
const results = await collection.find({}).skip(skip).limit(limit).toArray();
console.log(`Offset-based pagination (Page ${page}):`, results.length, "page", page, "skip", skip, "limit", limit);
}
基於遊標的分頁,也稱為鍵集分頁,依賴唯一識別碼(例如 ID 或時間戳記)來對記錄進行分頁。它不會跳過一定數量的記錄,而是使用最後檢索到的記錄作為取得下一組記錄的參考點。
這種方法更有效率,因為它避免了掃描目前頁面之前的記錄。因此,無論您深入資料集多深,查詢時間都保持一致。
這是基於遊標的分頁代碼:
async function cursor_based_pagination(params) {
const { lastDocumentId, limit = 100 } = params;
const query = lastDocumentId ? { documentId: { $gt: lastDocumentId } } : {};
const results = await collection
.find(query)
.sort({ documentId: 1 })
.limit(limit)
.toArray();
console.log("Cursor-based pagination:", results.length);
}
在此範例中,lastDocumentId 是上一頁中最後一個文件的 ID。當查詢下一頁時,資料庫會取得ID大於該值的文檔,確保無縫過渡到下一組記錄。
讓我們看看這兩種方法如何在大型資料集上執行。
async function testMongoDB() {
console.time("MongoDB Insert Time:");
await insertMongoDBRecords();
console.timeEnd("MongoDB Insert Time:");
// Create an index on the documentId field
await collection.createIndex({ documentId: 1 });
console.log("Index created on documentId field");
console.time("Offset-based pagination Time:");
await offset_based_pagination({ page: 2, limit: 250000 });
console.timeEnd("Offset-based pagination Time:");
console.time("Cursor-based pagination Time:");
await cursor_based_pagination({ lastDocumentId: 170000, limit: 250000 });
console.timeEnd("Cursor-based pagination Time:");
await client.close();
}
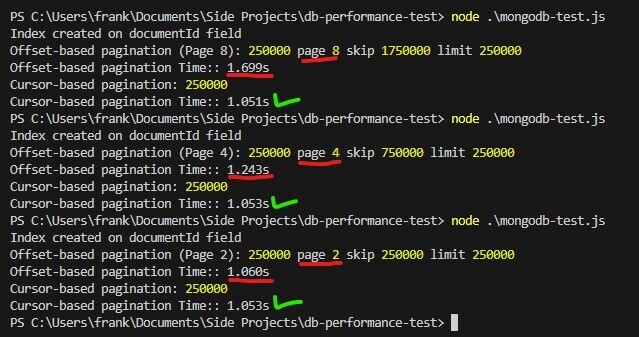
在效能測試中,您會注意到基於偏移分頁需要更長,因為頁碼增加,而遊標基於的分頁保持一致,使其成為大型資料集的更好選擇。此範例還展示了索引的強大功能。嘗試刪除索引然後查看結果!
如果沒有索引,MongoDB 將需要執行集合掃描,這意味著它必須查看集合中的每個文件以查找相關資料。這是低效的,尤其是當資料集成長時。索引可以讓 MongoDB 有效率地找到符合您查詢條件的文檔,顯著提升查詢效能。
在基於遊標的分頁上下文中,索引可確保快速取得下一組文件(基於 documentId),並且不會隨著更多文件添加到集合中而降低效能。
雖然基於偏移的分頁很容易實現,但由於需要掃描記錄,因此對於大型資料集來說它可能會變得低效。另一方面,基於遊標的分頁提供了更具可擴展性的解決方案,無論資料集大小如何,都可以保持效能一致。如果您在 MongoDB 中處理大型集合,值得考慮基於遊標的分頁以獲得更流暢、更快的體驗。
const { MongoClient } = require("mongodb");
const uri = "mongodb://localhost:27017";
const client = new MongoClient(uri);
client.connect();
const db = client.db("testdb");
const collection = db.collection("testCollection");
async function insertMongoDBRecords() {
try {
let bulkOps = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 2000000; i++) {
bulkOps.push({
insertOne: {
documentId: i,
name: `Record-${i}`,
value: Math.random() * 1000,
},
});
// Execute every 10000 operations and reinitialize
if (bulkOps.length === 10000) {
await collection.bulkWrite(bulkOps);
bulkOps = [];
}
}
if (bulkOps.length > 0) {
await collection.bulkWrite(bulkOps);
console.log("? Inserted records till now -> ", bulkOps.length);
}
console.log("MongoDB Insertion Completed");
} catch (err) {
console.error("Error in inserting records", err);
}
}
async function offset_based_pagination(params) {
const { page = 5, limit = 100 } = params;
const skip = (page - 1) * limit;
const results = await collection.find({}).skip(skip).limit(limit).toArray();
console.log(`Offset-based pagination (Page ${page}):`, results.length, "page", page, "skip", skip, "limit", limit);
}
async function cursor_based_pagination(params) {
const { lastDocumentId, limit = 100 } = params;
const query = lastDocumentId ? { documentId: { $gt: lastDocumentId } } : {};
const results = await collection
.find(query)
.sort({ documentId: 1 })
.limit(limit)
.toArray();
console.log("Cursor-based pagination:", results.length);
}
async function testMongoDB() {
console.time("MongoDB Insert Time:");
await insertMongoDBRecords();
console.timeEnd("MongoDB Insert Time:");
// Create an index on the documentId field
await collection.createIndex({ documentId: 1 });
console.log("Index created on documentId field");
console.time("Offset-based pagination Time:");
await offset_based_pagination({ page: 2, limit: 250000 });
console.timeEnd("Offset-based pagination Time:");
console.time("Cursor-based pagination Time:");
await cursor_based_pagination({ lastDocumentId: 170000, limit: 250000 });
console.timeEnd("Cursor-based pagination Time:");
await client.close();
}
testMongoDB();
以上是釋放 MongoDB:為什麼基於遊標的分頁每次都優於基於偏移量的分頁!的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




