資料結構是組織資料的工具。不僅是為了存儲,也是為了解決一些問題。 Python中有一些資料結構,包括列表、字典、元組和集合。
列表是一種使用索引順序儲存項目的資料結構。這是列表資料結構的圖示。

在 Python 中建立清單的方法有很多種。
items = [1,2,3,4]
items = []
可以透過索引直接存取清單中的項目。
items = [1,2,3,4,5] # access item at index 2 result = items[2] print(result) # returns 3
可以使用 for 迴圈檢索清單中的所有項目。這是一個例子。
# create a new list
items = [1,2,3,4,5]
# retrieve each item inside a list
for item in items:
print(item)
輸出
1 2 3 4 5
根據上面的程式碼,名為 items 的清單是使用指定的 item 建立的。使用 for 迴圈檢索每個項目。
append() 函數將一個新項目加入到清單中。這是append() 用法的範例。
# create empty list
shopping_list = []
# add some items
shopping_list.append("apple")
shopping_list.append("milk")
shopping_list.append("cereal")
# retrieve all items
for item in shopping_list:
print(item)
輸出
apple milk cereal
append() 如下圖所示。

除了append()函數之外,insert()函數會在特定索引中新增一個項目。這是一個例子。
items = ["apple","banana","mango","coffee"]
# add new item at index 1
items.insert(1,"cereal")
# retrieve all items
for item in items:
print(item)
輸出
apple cereal banana mango coffee
insert() 如下圖所示。

更新清單中的項目非常簡單。只需指定項目的索引,然後使用更新的項目來變更它。
# create a list
drinks = ["milkshake","black tea","banana milk","mango juice"]
# update value at index 2
drinks[2] = "chocolate milk"
print(f"value at index 2: {drinks[2]}")
輸出
value at index 2: chocolate milk
remove() 函數從清單中刪除一個項目。這是一個例子。
items = ["apple","banana","mango","coffee"]
# remove "mango"
items.remove("mango")
# remove item at index 1
items.remove(items[1])
print("after removed")
for item in items:
print(item)
輸出
after removed apple coffee
可以透過指定清單的起始索引和結束索引來選擇清單中的項目。這是在清單中選擇項目的基本結構。
list_name[start:end]
項目是從開始索引到但不包括結束索引選擇的。這是在清單中選擇項目的範例。
items = ["apple","mango","papaya","coconut","banana"]
# select items from index 1 up to but not including index 3
selected = items[1:3]
# show all items
print(f"all items: {items}")
# show the selected items
print(f"selected: {selected}")
輸出
all items: ['apple', 'mango', 'papaya', 'coconut', 'banana'] selected: ['mango', 'papaya']
列表理解是一種建立清單的「函數式」方式。為了理解列表理解,讓我們來看一個使用迭代方法建立包含偶數值的列表的範例。
evens = []
for i in range(1,11):
evens.append(i*2)
print(evens)
輸出
items = [1,2,3,4]
基於上面的程式碼,偶數是使用 for 迴圈的迭代方法產生的。上面的例子也可以使用列表理解來實現。這是使用列表理解產生偶數的範例。
items = []
輸出
items = [1,2,3,4,5] # access item at index 2 result = items[2] print(result) # returns 3
基於上面的程式碼,列表理解方法提供了更簡潔的程式碼,並且與先前的迭代方法相同的結果。
列表推導式可以與 if 分支一起使用。在此範例中,清單理解用於根據特定條件過濾某些值。
# create a new list
items = [1,2,3,4,5]
# retrieve each item inside a list
for item in items:
print(item)
輸出
1 2 3 4 5
這是上一個範例的迭代版本。
# create empty list
shopping_list = []
# add some items
shopping_list.append("apple")
shopping_list.append("milk")
shopping_list.append("cereal")
# retrieve all items
for item in shopping_list:
print(item)
列表可以像矩陣一樣以多維方式儲存。這是聲明用於儲存數字矩陣的多維列表的範例。
apple milk cereal
可以使用雙方括號 ([x][y]) 存取該項目,方法是指定 x 表示主列表的索引,而 y 表示嵌套列表內項目的索引。這是數字矩陣的圖示。
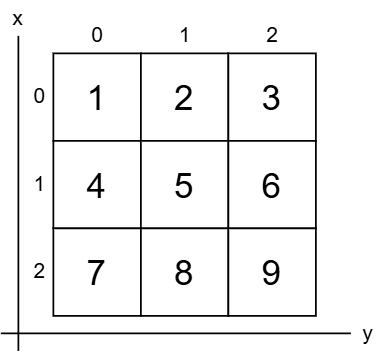
多維列表中的項目可以透過使用巢狀的 for 迴圈來檢索。
items = ["apple","banana","mango","coffee"]
# add new item at index 1
items.insert(1,"cereal")
# retrieve all items
for item in items:
print(item)
輸出
apple cereal banana mango coffee
字典是一種將記錄儲存為鍵值對的資料結構。每個鍵必須是唯一的,同時允許重複值。這說明了字典的資料結構:

創建字典的方法有很多種:
# create a list
drinks = ["milkshake","black tea","banana milk","mango juice"]
# update value at index 2
drinks[2] = "chocolate milk"
print(f"value at index 2: {drinks[2]}")
value at index 2: chocolate milk
可以使用for迴圈來擷取字典中的所有記錄。這是一個例子。
items = ["apple","banana","mango","coffee"]
# remove "mango"
items.remove("mango")
# remove item at index 1
items.remove(items[1])
print("after removed")
for item in items:
print(item)
輸出
after removed apple coffee
要在字典中插入新項目,請指定該項目的鍵值對。確保密鑰是唯一的。
list_name[start:end]
這是在字典中插入新項目的範例。
items = ["apple","mango","papaya","coconut","banana"]
# select items from index 1 up to but not including index 3
selected = items[1:3]
# show all items
print(f"all items: {items}")
# show the selected items
print(f"selected: {selected}")
輸出
all items: ['apple', 'mango', 'papaya', 'coconut', 'banana'] selected: ['mango', 'papaya']
要更新字典中的項目,請指定項目的鍵,然後插入更新的值。
evens = []
for i in range(1,11):
evens.append(i*2)
print(evens)
輸出
[2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20]
字典中的鍵和值可以使用不同的方法獨立存取。
evens = [x*2 for x in range(1,11)] # using list comprehension print(evens)
輸出
items = [1,2,3,4]
pop() 方法根據給定的鍵從字典中刪除項目。
items = []
輸出
items = [1,2,3,4,5] # access item at index 2 result = items[2] print(result) # returns 3
clear() 方法會刪除字典中的所有項目。
# create a new list
items = [1,2,3,4,5]
# retrieve each item inside a list
for item in items:
print(item)
輸出
1 2 3 4 5
元組是一種不可變的資料結構,用於儲存許多值。元組可以包含可變值。建立新元組有兩種方法。
# create empty list
shopping_list = []
# add some items
shopping_list.append("apple")
shopping_list.append("milk")
shopping_list.append("cereal")
# retrieve all items
for item in shopping_list:
print(item)
輸出
apple milk cereal
items = ["apple","banana","mango","coffee"]
# add new item at index 1
items.insert(1,"cereal")
# retrieve all items
for item in items:
print(item)
元組是不可變的,這意味著它的值一旦創建就無法更改或更新。
apple cereal banana mango coffee
可以使用「元組解包」來檢索元組中的值(此概念類似於 JavaScript 中的物件解構)。
解包時,解包值的大小必須等於元組的大小。
# create a list
drinks = ["milkshake","black tea","banana milk","mango juice"]
# update value at index 2
drinks[2] = "chocolate milk"
print(f"value at index 2: {drinks[2]}")
輸出
value at index 2: chocolate milk
集合是一種無序的資料結構,僅包含唯一的項。建立集合的方法有很多種。
items = ["apple","banana","mango","coffee"]
# remove "mango"
items.remove("mango")
# remove item at index 1
items.remove(items[1])
print("after removed")
for item in items:
print(item)
可以使用 set() 函數建立空集。
after removed apple coffee
集合資料結構會自動刪除重複值。
list_name[start:end]
輸出
items = ["apple","mango","papaya","coconut","banana"]
# select items from index 1 up to but not including index 3
selected = items[1:3]
# show all items
print(f"all items: {items}")
# show the selected items
print(f"selected: {selected}")
可以使用 for 迴圈存取集合內的值。
all items: ['apple', 'mango', 'papaya', 'coconut', 'banana'] selected: ['mango', 'papaya']
輸出
evens = []
for i in range(1,11):
evens.append(i*2)
print(evens)
集合資料結構提供並、交、差、對稱差等多種運算。
並集運算傳回兩個集合中的所有項目。

[2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20]
輸出
evens = [x*2 for x in range(1,11)] # using list comprehension print(evens)
交集運算傳回集合交集中存在的所有項目。

[2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20]
輸出
samples = [12,32,55,10,2,57,66] result = [s for s in samples if s % 4 == 0] # using list comprehension print(result)
差異運算傳回僅存在於某個集合中的所有項目。

[12, 32]
輸出
samples = [12,32,55,10,2,57,66]
result = []
for s in samples:
if s % 4 == 0:
result.append(s)
print(result)
對稱差分運算傳回任一集合中存在但不在交集中的所有項目。

matrix = [ [1,2,3], [4,5,6], [7,8,9], ]
輸出
items = [1,2,3,4]
函數是一個包含指令的可呼叫單元,旨在減少程式碼重複和組織複雜的任務。有兩種類型:void 函數(無返回值)和有返回值的函數。
這是Python中函數的基本結構。
items = []
這是Python中void函數(無回傳值)的範例。
items = [1,2,3,4,5] # access item at index 2 result = items[2] print(result) # returns 3
輸出
# create a new list
items = [1,2,3,4,5]
# retrieve each item inside a list
for item in items:
print(item)
基於上面的程式碼,建立了名為 hello() 的函數。透過指定函數名稱後面跟著括號 () 來呼叫函數。
這是有回傳值的函數範例。
1 2 3 4 5
輸出
# create empty list
shopping_list = []
# add some items
shopping_list.append("apple")
shopping_list.append("milk")
shopping_list.append("cereal")
# retrieve all items
for item in shopping_list:
print(item)
基於上面的程式碼,創建了名為 add() 的函數來對兩個數字求和。 add() 函數的回傳值儲存在 result 變數中。
使用傳回值函數時,請確保使用返回值。
Python 中函數的主題將在單獨的章節中詳細解釋。
讓我們建立一個簡單的待辦事項清單應用程式。該應用程式使用清單作為待辦事項的存儲,並利用函數來實現更清晰的程式碼。
第一步是匯入 uuid 套件並建立一個名為 todos 的列表,用於儲存 todo 記錄。 uuid 套件用作 todo 記錄的識別碼 (ID)。
apple milk cereal
之後,建立一個 view_todos() 函數來檢索所有待辦事項記錄。所有待辦事項記錄均使用 for 迴圈檢索。
items = ["apple","banana","mango","coffee"]
# add new item at index 1
items.insert(1,"cereal")
# retrieve all items
for item in items:
print(item)
建立一個view_todo()函數,透過指定的ID檢索todo記錄。在 for 迴圈內檢查每個待辦事項記錄,以檢查目前待辦事項 ID 是否等於指定的 ID。如果匹配,則顯示待辦事項記錄。
apple cereal banana mango coffee
建立一個create_todo()函數來建立一個新的待辦事項。 todo 記錄表示為帶有 id 和 title 欄位的字典。
# create a list
drinks = ["milkshake","black tea","banana milk","mango juice"]
# update value at index 2
drinks[2] = "chocolate milk"
print(f"value at index 2: {drinks[2]}")
建立 update_todo() 函數來更新待辦事項。在此函數中,todo 記錄根據指定的 ID 進行更新。
value at index 2: chocolate milk
建立一個delete_todo()函數來刪除一個todo。在此函數中,刪除指定ID的todo記錄。
items = ["apple","banana","mango","coffee"]
# remove "mango"
items.remove("mango")
# remove item at index 1
items.remove(items[1])
print("after removed")
for item in items:
print(item)
最後,建立一個名為 display_menu() 的函數來顯示應用程式的主選單。
after removed apple coffee
這是完整的程式碼。
list_name[start:end]
這是應用程式的輸出。

希望這篇文章對你學習Python有幫助。如果您有任何意見,請在評論區告訴我。
以上是Python 教程 - ata 結構的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




