圖片來源:medium
排序是資料結構和演算法中最重要的部分之一。排序演算法有很多種,這是最簡單的演算法之一:冒泡排序。
排序演算法是電腦科學的基礎,而冒泡排序是最簡單、最直觀的排序演算法之一。這篇文章將探討冒泡排序的工作原理,分析其時間複雜度,並演練 JavaScript 實作。
在本系列中,我將分享使用 Javascript 的完整排序演算法資料結構和演算法,並從冒泡排序開始。如果您喜歡並希望我透過範例分享完整的排序演算法,請按讚並關注我。它激勵我為你們創作和準備內容。
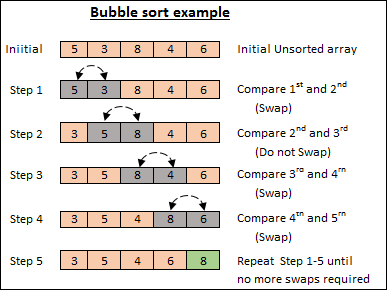
冒泡排序是一種簡單的排序演算法,它重複遍歷列表,比較相鄰元素(下一個元素),如果順序錯誤則交換它們。重複此過程直到清單排序完畢。該演算法因其較小的元素“冒泡”到列表頂部而得名。
讓我們深入程式碼看看冒泡排序是如何在 JavaScript 中實現的:
// By default ascending order
function bubble_sort(array) {
const len = array.length; // get the length of an array
//The outer loop controls the inner loop, which means the outer loop will decide how many times the inner loop will be run.
//If the length is n then the outer loop runs n-1 times.
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
// Inner loop will run based on the outer loop and compare the value,
//If the first value is higher than the next value then swap it, loop must go on for each lowest value
for (let j = 0; j > len - i -1; j++) {
// checking if the first element greater than to the next element
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array; // return the sorted array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [3, 7, 9, 11, 12];
// Descending order
function bubble_sort_descending_order(array) {
const len = array.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < len - i -1; j++) {
// checking if first element greter than next element,
if (array[j] < array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort_descending_order(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [ 12, 11, 9, 7, 3 ]

已經加入了註解並解釋了上面的每一行程式碼。但我也會詳細解釋,以幫助您理解完整的流程和程式碼。
// By default ascending order
function bubble_sort(array) {
const len = array.length; // get the length of an array
//The outer loop controls the inner loop, which means the outer loop will decide how many times the inner loop will be run.
//If the length is n then the outer loop runs n-1 times.
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
// Inner loop will run based on the outer loop and compare the value,
//If the first value is higher than the next value then swap it, loop must go on for each lowest value
for (let j = 0; j > len - i -1; j++) {
// checking if the first element greater than to the next element
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array; // return the sorted array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [3, 7, 9, 11, 12];
// Descending order
function bubble_sort_descending_order(array) {
const len = array.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < len - i -1; j++) {
// checking if first element greter than next element,
if (array[j] < array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort_descending_order(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [ 12, 11, 9, 7, 3 ]
// optimized version:
function bubble_sort(array) {
const len = array.length; // get the length of the array
//The outer loop controls the inner loop, which means the outer loop will decide how many times the inner loop will be run.
//If the length is n then the outer loop run n-1 times.
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
// Inner loop will run based on the outer loop and compare the value,
//If the first value is higher than the next value then swap it, loop must go on for each lowest value
let isSwapped = false;
for (let j = 0; j < len - i -1; j++) {
//check if the first element is greater than the next element
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
isSwapped = true;
}
}
//If no element swap by inner loop then break;
if (isSwapped === false) {
break;
}
}
return array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [3, 7, 9, 11, 12];
在最壞和平均情況下,冒泡排序的時間複雜度為 (O(n²)),其中 (n) 是數組中元素的數量。這是因為每個元素都會與其他元素進行比較。在最好的情況下,當數組已經排序時,如果添加最佳化以在不需要交換時停止演算法,則時間複雜度可以是 (O(n))。
在最好的情況下,當陣列已經排序時,由於 isSwapped 最佳化,演算法可以提前終止,導致時間複雜度為 (O(n))。
整體而言,由於其二次時間複雜度,冒泡排序對於大型資料集效率不高,但它對於小型數組很有用,或者作為理解排序演算法的教育工具。
冒泡排序因其簡單性而成為一種用於教育目的的優秀演算法。然而,由於其二次時間複雜度,它不適合大型資料集。儘管冒泡排序效率低下,但理解冒泡排序為學習更高級的排序演算法奠定了基礎。
以上是了解冒泡排序演算法:逐步指南的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




