在本文中,我們將比較 Documenso 和 AWS S3 映像上傳範例之間將檔案上傳到 AWS S3 所涉及的步驟。
我們從 Vercel 提供的簡單範例開始。
Vercel 提供了一個將檔案上傳到 AWS S3 的良好範例。
此範例的自述文件提供了兩個選項,您可以使用現有的 S3 儲存桶或建立新儲存桶。了解這一點有幫助
您正確配置了上傳功能。
又到了我們看源碼的時間了。我們正在尋找 type=file 的輸入元素。在 app/page.tsx 中,您將找到以下程式碼:
return (
<main>
<h1>Upload a File to S3</h1>
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<input
>
<h2>
<strong>onChange</strong>
</h2>
<p>onChange updates state using setFile, but it does not do the uploading. upload happens when you submit this form.<br>
</p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">onChange={(e) => {
const files = e.target.files
if (files) {
setFile(files[0])
}
}}
handleSubmit 函數中發生了很多事情。我們需要分析這個handleSubmit函數中的操作列表。我已在此程式碼片段中編寫了註釋來解釋這些步驟。
const handleSubmit = async (e: React.FormEvent<HTMLFormElement>) => {
e.preventDefault()
if (!file) {
alert('Please select a file to upload.')
return
}
setUploading(true)
const response = await fetch(
process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_BASE_URL + '/api/upload',
{
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify({ filename: file.name, contentType: file.type }),
}
)
if (response.ok) {
const { url, fields } = await response.json()
const formData = new FormData()
Object.entries(fields).forEach(([key, value]) => {
formData.append(key, value as string)
})
formData.append('file', file)
const uploadResponse = await fetch(url, {
method: 'POST',
body: formData,
})
if (uploadResponse.ok) {
alert('Upload successful!')
} else {
console.error('S3 Upload Error:', uploadResponse)
alert('Upload failed.')
}
} else {
alert('Failed to get pre-signed URL.')
}
setUploading(false)
}
api/upload/route.ts 有以下程式碼:
import { createPresignedPost } from '@aws-sdk/s3-presigned-post'
import { S3Client } from '@aws-sdk/client-s3'
import { v4 as uuidv4 } from 'uuid'
export async function POST(request: Request) {
const { filename, contentType } = await request.json()
try {
const client = new S3Client({ region: process.env.AWS_REGION })
const { url, fields } = await createPresignedPost(client, {
Bucket: process.env.AWS_BUCKET_NAME,
Key: uuidv4(),
Conditions: [
['content-length-range', 0, 10485760], // up to 10 MB
['starts-with', '$Content-Type', contentType],
],
Fields: {
acl: 'public-read',
'Content-Type': contentType,
},
Expires: 600, // Seconds before the presigned post expires. 3600 by default.
})
return Response.json({ url, fields })
} catch (error) {
return Response.json({ error: error.message })
}
}
handleSubmit 中的第一個請求是 /api/upload 並發送內容類型和檔案名稱作為負載。解析如下:
const { filename, contentType } = await request.json()
下一步是建立一個 S3 用戶端,然後建立一個傳回 url 和欄位的預簽名貼文。您將使用此網址上傳您的檔案。
有了這些知識,我們來分析一下Documenso中的上傳工作原理並進行一些比較。
讓我們從 type=file 的輸入元素開始。 Documenso 中的程式碼組織方式不同。您會在名為 document-dropzone.tsx.
的檔案中找到輸入元素
<input {...getInputProps()} />
<p className="text-foreground mt-8 font-medium">{_(heading[type])}</p>
這裡getInputProps回傳的是useDropzone。 Documenso 使用react-dropzone。
import { useDropzone } from 'react-dropzone';
onDrop 呼叫 props.onDrop,你會在 upload-document.tsx 中找到一個名為 onFileDrop 的屬性值。
<DocumentDropzone
className="h-[min(400px,50vh)]"
disabled={remaining.documents === 0 || !session?.user.emailVerified}
disabledMessage={disabledMessage}
onDrop={onFileDrop}
onDropRejected={onFileDropRejected}
/>
讓我們看看 onFileDrop 函數會發生什麼事。
const onFileDrop = async (file: File) => {
try {
setIsLoading(true);
const { type, data } = await putPdfFile(file);
const { id: documentDataId } = await createDocumentData({
type,
data,
});
const { id } = await createDocument({
title: file.name,
documentDataId,
teamId: team?.id,
});
void refreshLimits();
toast({
title: _(msg`Document uploaded`),
description: _(msg`Your document has been uploaded successfully.`),
duration: 5000,
});
analytics.capture('App: Document Uploaded', {
userId: session?.user.id,
documentId: id,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
});
router.push(`${formatDocumentsPath(team?.url)}/${id}/edit`);
} catch (err) {
const error = AppError.parseError(err);
console.error(err);
if (error.code === 'INVALID_DOCUMENT_FILE') {
toast({
title: _(msg`Invalid file`),
description: _(msg`You cannot upload encrypted PDFs`),
variant: 'destructive',
});
} else if (err instanceof TRPCClientError) {
toast({
title: _(msg`Error`),
description: err.message,
variant: 'destructive',
});
} else {
toast({
title: _(msg`Error`),
description: _(msg`An error occurred while uploading your document.`),
variant: 'destructive',
});
}
} finally {
setIsLoading(false);
}
};
發生了很多事情,但為了我們的分析,我們只考慮名為 putFile 的函數。
putPdfFile 定義在 upload/put-file.ts
/**
* Uploads a document file to the appropriate storage location and creates
* a document data record.
*/
export const putPdfFile = async (file: File) => {
const isEncryptedDocumentsAllowed = await getFlag('app_allow_encrypted_documents').catch(
() => false,
);
const pdf = await PDFDocument.load(await file.arrayBuffer()).catch((e) => {
console.error(`PDF upload parse error: ${e.message}`);
throw new AppError('INVALID_DOCUMENT_FILE');
});
if (!isEncryptedDocumentsAllowed && pdf.isEncrypted) {
throw new AppError('INVALID_DOCUMENT_FILE');
}
if (!file.name.endsWith('.pdf')) {
file.name = `${file.name}.pdf`;
}
removeOptionalContentGroups(pdf);
const bytes = await pdf.save();
const { type, data } = await putFile(new File([bytes], file.name, { type: 'application/pdf' }));
return await createDocumentData({ type, data });
};
這會呼叫 putFile 函數。
/**
* Uploads a file to the appropriate storage location.
*/
export const putFile = async (file: File) => {
const NEXT_PUBLIC_UPLOAD_TRANSPORT = env('NEXT_PUBLIC_UPLOAD_TRANSPORT');
return await match(NEXT_PUBLIC_UPLOAD_TRANSPORT)
.with('s3', async () => putFileInS3(file))
.otherwise(async () => putFileInDatabase(file));
};
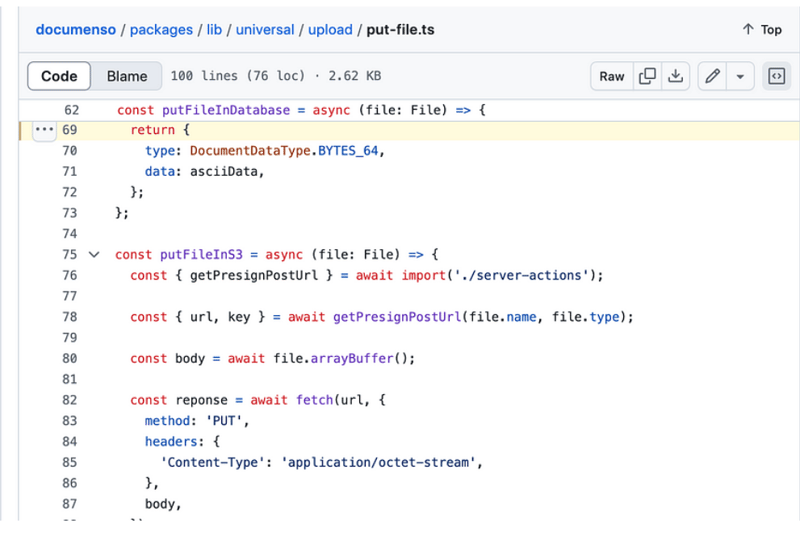
const putFileInS3 = async (file: File) => {
const { getPresignPostUrl } = await import('./server-actions');
const { url, key } = await getPresignPostUrl(file.name, file.type);
const body = await file.arrayBuffer();
const reponse = await fetch(url, {
method: 'PUT',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/octet-stream',
},
body,
});
if (!reponse.ok) {
throw new Error(
`Failed to upload file "${file.name}", failed with status code ${reponse.status}`,
);
}
return {
type: DocumentDataType.S3_PATH,
data: key,
};
};
export const getPresignPostUrl = async (fileName: string, contentType: string) => {
const client = getS3Client();
const { getSignedUrl } = await import('@aws-sdk/s3-request-presigner');
let token: JWT | null = null;
try {
const baseUrl = APP_BASE_URL() ?? 'http://localhost:3000';
token = await getToken({
req: new NextRequest(baseUrl, {
headers: headers(),
}),
});
} catch (err) {
// Non server-component environment
}
// Get the basename and extension for the file
const { name, ext } = path.parse(fileName);
let key = `${alphaid(12)}/${slugify(name)}${ext}`;
if (token) {
key = `${token.id}/${key}`;
}
const putObjectCommand = new PutObjectCommand({
Bucket: process.env.NEXT_PRIVATE_UPLOAD_BUCKET,
Key: key,
ContentType: contentType,
});
const url = await getSignedUrl(client, putObjectCommand, {
expiresIn: ONE_HOUR / ONE_SECOND,
});
return { key, url };
};
您在 Documenso 中看不到任何 POST 要求。它使用名為 getSignedUrl 的函數來取得 url,而
vercel 範例向 api/upload 路由發出 POST 請求。
在 Vercel 範例中可以輕鬆找到輸入元素,因為這只是一個範例,但找到了 Documenso
使用react-dropzone並且輸入元素根據業務上下文定位。
在 Thinkthroo,我們研究大型開源專案並提供架構指南。我們開發了使用 Tailwind 建構的可重複使用元件,您可以在您的專案中使用它們。
我們提供 Next.js、React 和 Node 開發服務。
與我們預約會面討論您的專案。

https://github.com/documenso/documenso/blob/main/packages/lib/universal/upload/put-file.ts#L69
https://github.com/vercel/examples/blob/main/solutions/aws-s3-image-upload/README.md
https://github.com/vercel/examples/tree/main/solutions/aws-s3-image-upload
https://github.com/vercel/examples/blob/main/solutions/aws-s3-image-upload/app/page.tsx#L58C5-L76C12
https://github.com/vercel/examples/blob/main/solutions/aws-s3-image-upload/app/api/upload/route.ts
https://github.com/documenso/documenso/blob/main/packages/ui/primitives/document-dropzone.tsx#L157
https://react-dropzone.js.org/
https://github.com/documenso/documenso/blob/main/apps/web/src/app/(dashboard)/documents/upload-document.tsx#L61
https://github.com/documenso/documenso/blob/main/packages/lib/universal/upload/put-file.ts#L22
以上是Documenso 和 aws-smage-upload 範例之間的 Spload 功能比較的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




