java常見類別之String類
1.字串概述
字串:就是由多個字符組成的一串字符,也可以看成是字符數組。
String類別代表字串,java程式中的字串字面值,如"abc"等都作為此類的實例實作。
字串是常數,一旦被賦值,就不能被改變。
2.String的建構方法
public String() 空白建構
public String(byte[] bytes) 把位元組數組轉換成一個字節數
int length) 把位元組陣列的指定索引長度的位元組轉換成字串 public String(char[] value) 把字元陣列轉換成字串 public String(char[] values,int offset,int countcount ) 把字元陣列的指定索引長度的字元轉換成字串 public String(String original) 把字串常數值轉換成字串package cn;
/**
* 字符串:就是由多个字符组成的一串字符,也可以看成是字符数组
* 通过查看API,我们可以知道
* 字符串字面值"abc"也可以看成是一个字符串对象。
* 字符串是常量,一旦被赋值,就不能被改变。
*
* 构造方法:
* public String() 空构造
* public String(byte[] bytes) 把字节数组转换成字符串
* public String(byte[] bytes,int offset,int length)
把字节数组的指定索引长度的字节转换成字符串
* public String(char[] value) 把字符数组转换成字符串
* public String(char[] values,int offset,int count)
把字符数组的指定索引长度的字符转换成字符串
* public String(String original) 把字符串常量值转换成字符串
*
* 字符串的方法:
* public int length()获取字符串的长度
*/
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//public String() 空构造
String s1 = new String();
System.out.println("s1:"+s1);//s1:
//public String(byte[] bytes) 把字节数组转换成字符串
byte[] bytes1 = new byte[]{97,98,99};
String s2 = new String(bytes1);
System.out.println("s2:"+s2);//s2:abc
//public String(byte[] bytes,int offset,int length)
// 把字节数组的指定索引长度的字节转换成字符串
byte[] bytes2 = new byte[]{97,98,99,100};
String s3 = new String(bytes2,1,2);
System.out.println("s3:"+s3);//s3:bc
//public String(char[] value) 把字符数组转换成字符串
char[] char1 = new char[]{'a','b','c'};
String s4 = new String(char1);
System.out.println("s4:"+s4);//s4:abc
//public String(char[] values,int offset,int count)
// 把字符数组的指定索引长度的字符转换成字符串
char[] char2 = new char[]{'a','b','c','d','e'};
String s5 = new String(char2,1,2);
System.out.println("s5:"+s5);//s5:bc
//public String(String original) 把字符串常量值转换成字符串
String s6 = new String("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("s6:"+s6);//s6:HelloWorld
}
}登入後複製
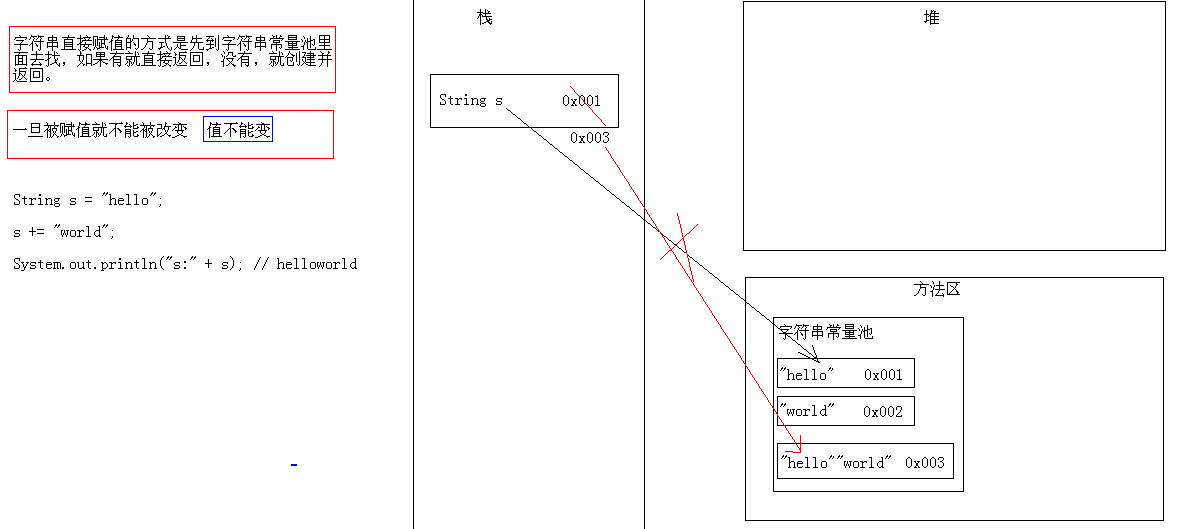
package com;
/**
* 字符串的特点:一旦被赋值,就不能被改变。
* 指的是字符串"hello"不可以改变 吗,而不是变量s
*
* 字符串直接赋值的方式是先到字符串常量池里面去找,
* 如果有就直接返回,没有,就创建并返回。
*
*/
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
s += "world";
System.out.println("s:"+s);//s:helloworld
}
}登入後複製
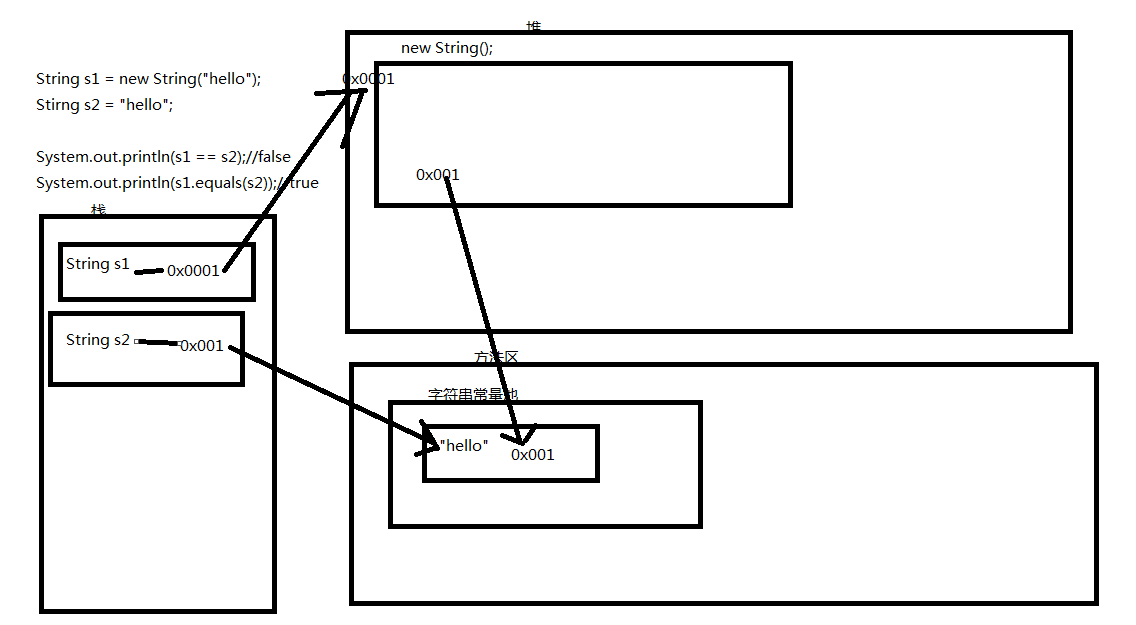
package com;
/**
* String s1 = "hello";和 String s2 = new String("hello")的区别
* 前者会创建2个对象,后者会创建一个对象。
*
* ==在基本类型中,比较的是值是否相等。在引用类型中,比较的是地址值是否相等。
* equals()在Object类中比较的是地址值是否相等。
* 但是String重写了equals()方法,所以在String比较的是内容是否相等。
*/
public class StringDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//false
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
}
}登入後複製
package com;
/**
* 看程序写结果
*/
public class StringDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//false
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
String s3 = new String("hello");
String s4 = "hello";
System.out.println(s3 == s4);//false
System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));//true
String s5 = "hello";
String s6 = "hello";
System.out.println(s5 == s6 );//true
System.out.println(s5.equals(s6));//true
}
}登入後複製
package com;
/**
* 看程序,写结果
* 字符串如果是变量相加,先开辟空间,再拼接
* 字符串如果是常量相加,是先相加,然后再在常量池中寻找,如果有就直接返回,否则,就创建
*/
public class StringDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "world";
String s3 = "helloworld";
System.out.println(s1.hashCode()+s2.hashCode());
System.out.println(s3.hashCode());
/**
* s3 就相当于是s3.hashCode()
* 而s1 + s2 就相当于s1.hashCode() + s2.hashCode()
* 当然不一样了
*/
System.out.println(s3 == s1 + s2);//false
System.out.println(s3.equals(s1 + s2));//true
System.out.println(s3 == "hello"+"world");//true
System.out.println(s3.equals("hello"+"world"));//true
/**
* 通过反编译,看源码,我们知道这里已经做好了处理
*/
System.out.println(s3=="helloworld");
System.out.println(s3.equals("helloworld"));
}
}登入後複製
public boolean stratsWith(String str) 判斷字串是否以某個指定的字串開頭pubilc booelan endsWithd(String str) 判斷字串是否以某個指定的字串結尾public boolean isEmpty() 字元判斷字串的內容是否為空
package cn;
/**
* String类的判断功能
* public boolean equals(Object obj) 判断字符串的内容是否相等,区分大小写
* public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str) 判断字符串的内容是否相等,不区分大小写
* public contains(String str) 判断大的字符串中是否包含小的字符串
* public boolean startsWith(String str) 判断是否以某种字符串开开头
* public boolean endsWith(String str) 判断是否以某种字符串结尾
* public boolean isEmpty() 判断字符串的内容是否为空
*
*/
public class StringDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建字符串对象
String s1 = "helloworld";
String s2 = "helloworld";
String s3 = "helloWorld";
//public boolean equals(Object obj) 判断字符串的内容是否相等,区分大小写
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));//false
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
//public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str) 判断字符串的内容是否相等,不区分大小写
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3));//true
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2));//true
//public contains(String str) 判断大的字符串中是否包含小的字符串
System.out.println(s1.contains("hello"));//true
System.out.println(s1.contains("hw"));//false
//public boolean startsWith(String str) 判断是否以某种字符串开开头
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("hello"));//true
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("h"));//true
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("world"));//false
//public boolean endsWith(String str) 判断是否以某种字符串结尾
System.out.println(s1.endsWith("world"));//true
//public boolean isEmpty() 判断字符串是否为空
System.out.println(s1.isEmpty());//false
String s4 = "";
System.out.println(s4.isEmpty());//true
String s5 = null;
/**
* Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
* 因为s5的对象不存在,它怎么可以调用方法呢??
*/
//System.out.println(s5.isEmpty());
}
}登入後複製
package cn;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*
* 模拟登录,给三次机会,并提示还有几次机会
*
* 分析:
* 1.定义用户名和密码,已经存在的
* 2.键盘录入用户名和密码。
* 3.比较用户名和密码,如果都相同,则登录成功,如果有一个不同,则登录失败
* 4.给三次机会,用循环改进,用for循环
*/
public class StringDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义用户名和密码,已经存在的
String username = "admin";
String password = "admin";
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
//键盘录入用户名和密码
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String name = sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String pwd = sc.next();
//比较用户名和密码,如果都相同,则登录成功,如果有一个不同,则登录失败
if(username.equals(name) && password.equals(pwd)){
//如果都相同,则登录成功
System.out.println("登录成功");
break;
}else{
//如果有一个不同,则登录失败
if((2-i) == 0){//如果是第0次,那么就
System.out.println("抱歉,帐号被锁定。");
}else{
System.out.println("登录失败,你还有"+(2-i)+"次机会");
}
}
}
}
}登入後複製
package cn;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*
* 模拟登录,给三次机会,并提示还有几次机会,如果登录成功,就可以玩猜数字了
*
* 分析:
* 1.定义用户名和密码,已经存在的
* 2.键盘录入用户名和密码。
* 3.比较用户名和密码,如果都相同,则登录成功,如果有一个不同,则登录失败
* 4.给三次机会,用循环改进,用for循环
*/
public class StringDemo1 {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义用户名和密码,已经存在的
String username = "admin";
String password = "admin";
boolean flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
//键盘录入用户名和密码
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String name = sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String pwd = sc.next();
//比较用户名和密码,如果都相同,则登录成功,如果有一个不同,则登录失败
if(username.equals(name) && password.equals(pwd)){
flag = true;
//如果都相同,则登录成功
System.out.println("登录成功");
break;
}else{
//如果有一个不同,则登录失败
if((2-i) == 0){//如果是第0次,那么就
System.out.println("抱歉,帐号被锁定。");
}else{
System.out.println("登录失败,你还有"+(2-i)+"次机会");
}
}
}
if(flag){
GuessNumberGame.start();
}
}
}
package cn;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 创建猜数字的小游戏
*/
public class GuessNumberGame {
private GuessNumberGame(){}
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void start(){
//产生一个随机数
int number = (int)(Math.random() * 100 ) + 1 ;
System.out.println(number);
while(true){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你要猜的数据(1-100):");
int guessNumber = sc.nextInt();
//判断
if(guessNumber > number){
System.out.println("你猜的数据"+guessNumber+"大了");
}else if (guessNumber < number){
System.out.println("你猜的数据"+guessNumber+"小了");
}else{
System.out.println("恭喜你,猜中了");
break;
}
}
}
}登入後複製
package cn;
/**
* String类的获取功能
* public int length() 获取字符串的长度
* public char charAt(int index) 获取指定索引位置上的字符
* 为什么这里是int类型,而不是char类型?
* 因为:'a'和97是可以相互转换的,即97就是代表'a'
* public int indexOf(int ch) 返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现的位置
* public int indexOf(String str) 返回指定字符串在此字符串中第一次出现的位置
* public int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex)返回指定字符在此支付串从指定位置中第一次出现的位置
* public int indexOf(Sring str,itn fromIndex) 返回指定字符串在此字符串从指定位置中第一次出现的位置
* public String subString(int start) 从指定位置开始截取的字符串
* public String subString(int strat,int end) 从指定位置开始到指定位置结束时截取的字符串
*/
public class StringDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义一个字符串
String s = "helloworld";
//public int length() 获取字符串的长度
System.out.println("s的长度是:"+s.length());//s的长度是:10
//public char charAt(int index) 获取指定索引位置上的字符
System.out.println(s.charAt(0));//h
//public int indexOf(int ch) 返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现的位置
System.out.println("l出现第一次的索引"+s.indexOf('l'));//l出现第一次的索引2
//public int indexOf(String str) 返回指定字符串在此字符串中第一次出现的位置
System.out.println("hello第一次出现的索引"+s.indexOf("hello"));//hello第一次出现的索引0
//public int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex)返回指定字符在此支付串从指定位置中第一次出现的位置
System.out.println("l从索引为4开始出现d的第一次索引位置:"+s.indexOf('l', 4));//l从索引为4开始出现d的第一次索引位置:8
System.out.println("l从索引为4开始出现d的第一次索引位置:"+s.indexOf('k', 4));//l从索引为4开始出现d的第一次索引位置:-1
System.out.println("l从索引为4开始出现d的第一次索引位置:"+s.indexOf('l', 40));//l从索引为4开始出现d的第一次索引位置:-1
//public int indexOf(Sring str,itn fromIndex) 返回指定字符串在此字符串从指定位置中第一次出现的位置
System.out.println("or从第2个索引位置开始出现的第一个索引位置:"+s.indexOf("or", 2));//or从第2个索引位置开始出现的第一个索引位置:6
//public String subString(int start) 从指定位置开始截取的字符串
System.out.println("截取world:"+s.substring(5));//截取world:world
System.out.println("截取helloworld:"+s.substring(0));//截取helloworld:helloworld
//public String subString(int strat,int end) 从指定位置开始到指定位置结束时截取的字符串
System.out.println("截取wo:"+s.substring(5, 7));//截取wo:wo
}
}登入後複製
package cn;
/**
* 需求:遍历获取字符串中的每一个字符
*
*/
public class StringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "helloworld";
//第一种实现方法
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char ch = s.charAt(i);
System.out.print(ch+" ");
}
System.out.println();
//第二种实现方法
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) {
System.out.print(ch[i]+" ");
}
}
}登入後複製
package cn;
/**
* 需求:统计一个字符串中大写字母字符、小写字母字符,数字字符出现的次数(不考虑其他字符)
* 举例:
* "Hello123World"
* 结果:
* 大写字符 2个
* 小写字符 8个
* 数字字符 3个
*
*
*/
public class StringTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "Hello123World";
int maxCharacterSum = 0;
int minCharacterSum = 0;
int numSum = 0;
//方法一:将字符串转换为字符数组
char[] chs = str.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {
if(chs[i] >= 'a' && chs[i] <= 'z'){
minCharacterSum ++;
}else if(chs[i] >= 'A' && chs[i] <= 'Z'){
maxCharacterSum ++;
}else if(chs[i] >= '0' && chs[i] <= '9'){
numSum ++;
}
}
System.out.println("大写字符的总数:"+maxCharacterSum);
System.out.println("小写字符的总数:"+minCharacterSum);
System.out.println("数字字符的总数:"+numSum);
//第二中实现
maxCharacterSum = 0;
minCharacterSum = 0;
numSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if(ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z'){
minCharacterSum ++;
}else if(ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z'){
maxCharacterSum ++;
}else if(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'){
numSum ++;
}
}
System.out.println("大写字符的总数:"+maxCharacterSum);
System.out.println("小写字符的总数:"+minCharacterSum);
System.out.println("数字字符的总数:"+numSum);
}
}登入後複製
package cn;
/**
* String类的转换功能
*
* public byte[] getBytes() 字符串转换为字节数组
* public char[] toCharArray() 字符串转换为字符数组
* public static String valueOf(char[] chs) 将字符数组转换为字符串
* public static String valueOf(int i) 将int类型的数值转换为字符串
* public String toLowerCase() 将字符串转换为小写
* public String toUpperCase() 将字符串转换为大写
* public String concat(String str) 字符串的拼接
*
*/
public class StringDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义一个字符串对象
String s = "javaSE";
//public byte[] getBytes() 字符串转换为字节数组
byte[] bytes = s.getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
System.out.print(bytes[i]+" ");//106 97 118 97 83 69
}
System.out.println();
//public char[] toCharArray() 字符串转换为字符数组
char[] chs = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {
System.out.print(chs[i]+" ");//j a v a S E
}
System.out.println();
// public static String valueOf(char[] chs) 将字符数组转换为字符串
String ss = String.valueOf(chs);
System.out.println(ss);//javaSE
System.out.println();
//public static String valueOf(int i) 将int类型的数值转换为字符串
int num = 100;
System.out.println(s.valueOf(num));//100
System.out.println();
System.out.println("转换小写:"+s.toLowerCase());//转换小写:javase
System.out.println("转换大写:"+s.toUpperCase());//转换大写:JAVASE
System.out.println();
System.out.println(s.concat("javaEE"));//javaSEjavaEE
}
}登入後複製
package cn;
/**
* 需求:把一个字符串的首字母转换为大写
* 举例:
* helloWORLD
* 结果
* HelloWORLD
*/
public class StringTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloWORLD";
str = str.substring(0,1).toUpperCase()+str.substring(1);
System.out.println(str);//HelloWORLD
}
}
package cn;
/**
* 需求:把一个字符串的首字母转换为大写,其余为小写
* 举例:
* helloWORLD
* 结果
* Helloworld
*/
public class StringTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloWORLD";
str = str.substring(0,1).toUpperCase()+str.substring(1).toLowerCase();
System.out.println(str);//Helloworld
}
}登入後複製
本文出自“11831428” 博客,請務必保留此出處http://11841428.blog.51cto.com/11831428/1859607
本網站聲明
本文內容由網友自願投稿,版權歸原作者所有。本站不承擔相應的法律責任。如發現涉嫌抄襲或侵權的內容,請聯絡admin@php.cn

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章
Windows 11 KB5054979中的新功能以及如何解決更新問題
3 週前
By DDD
如何修復KB5055523無法在Windows 11中安裝?
2 週前
By DDD
Inzoi:如何申請學校和大學
4 週前
By DDD
如何修復KB5055518無法在Windows 10中安裝?
2 週前
By DDD
Roblox:Dead Rails - 如何召喚和擊敗Nikola Tesla
1 個月前
By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)




