Java的Hibernate框架資料庫操作中鎖的使用與查詢類型
Hibernate與資料庫鎖定
一、為什麼要使用鎖定?
要想弄清楚鎖機制存在的原因,首先要了解事務的概念。
事務是對資料庫一系列相關的操作,它必須具備ACID特徵:
A(原子性):要麼全部成功,要麼全部撤銷。
C(一致性):要保持資料庫的一致性。
I(隔離性):不同事務操作相同資料時,要有各自的資料空間。
D(持久性):一旦交易成功結束,它對資料庫所做的更新必須永久保持。
我們常用的關係型資料庫RDBMS實現了事務的這些特性。其中,原子性、
一致性和持久性都是採用日誌來保證的。而隔離性就是由今天我們關注的
鎖機制來實現的,這就是為什麼我們需要鎖機制。
如果沒有鎖,對隔離性不加控制,可能會造成哪些後果?
更新遺失:事務1提交的資料被事務2覆蓋。
臟讀:事務2查詢到了事務1未提交的資料。
虛讀:事務2查詢到了事務1提交的新建資料。
不可重複讀取:事務2查詢到了事務1提交的更新資料。
下面來看Hibernate的例子,兩個執行緒分別開啟兩個事務操作tb_account表中
的同一行資料col_id=1。
package com.cdai.orm.hibernate.annotation;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "tb_account")
public class Account implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5018821760412231859L;
@Id
@Column(name = "col_id")
private long id;
@Column(name = "col_balance")
private long balance;
public Account() {
}
public Account(long id, long balance) {
this.id = id;
this.balance = balance;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public long getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(long balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account [id=" + id + ", balance=" + balance + "]";
}
}package com.cdai.orm.hibernate.transaction;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration;
import com.cdai.orm.hibernate.annotation.Account;
public class DirtyRead {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final SessionFactory sessionFactory = new AnnotationConfiguration().
addFile("hibernate/hibernate.cfg.xml").
configure().
addPackage("com.cdai.orm.hibernate.annotation").
addAnnotatedClass(Account.class).
buildSessionFactory();
Thread t1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
Session session1 = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx1 = null;
try {
tx1 = session1.beginTransaction();
System.out.println("T1 - Begin trasaction");
Thread.sleep(500);
Account account = (Account)
session1.get(Account.class, new Long(1));
System.out.println("T1 - balance=" + account.getBalance());
Thread.sleep(500);
account.setBalance(account.getBalance() + 100);
System.out.println("T1 - Change balance:" + account.getBalance());
tx1.commit();
System.out.println("T1 - Commit transaction");
Thread.sleep(500);
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if (tx1 != null)
tx1.rollback();
}
finally {
session1.close();
}
}
};
// 3.Run transaction 2
Thread t2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
Session session2 = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx2 = null;
try {
tx2 = session2.beginTransaction();
System.out.println("T2 - Begin trasaction");
Thread.sleep(500);
Account account = (Account)
session2.get(Account.class, new Long(1));
System.out.println("T2 - balance=" + account.getBalance());
Thread.sleep(500);
account.setBalance(account.getBalance() - 100);
System.out.println("T2 - Change balance:" + account.getBalance());
tx2.commit();
System.out.println("T2 - Commit transaction");
Thread.sleep(500);
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if (tx2 != null)
tx2.rollback();
}
finally {
session2.close();
}
}
};
t1.start();
t2.start();
while (t1.isAlive() || t2.isAlive()) {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
System.out.println("Both T1 and T2 are dead.");
sessionFactory.close();
}
}事務1將col_balance減小100,而事務2將其減少100,最終結果可能是0,也
可能是200,事務1或2的更新可能會遺失。 log輸出也印證了這一點,事務1和2
的log交叉列印。
T1 - Begin trasaction T2 - Begin trasaction Hibernate: select account0_.col_id as col1_0_0_, account0_.col_balance as col2_0_0_ from tb_account account0_ where account0_.col_id=? Hibernate: select account0_.col_id as col1_0_0_, account0_.col_balance as col2_0_0_ from tb_account account0_ where account0_.col_id=? T1 - balance=100 T2 - balance=100 T2 - Change balance:0 T1 - Change balance:200 Hibernate: update tb_account set col_balance=? where col_id=? Hibernate: update tb_account set col_balance=? where col_id=? T1 - Commit transaction T2 - Commit transaction Both T1 and T2 are dead.
由此可見,隔離性是一個需要慎重考慮的問題,理解鎖很有必要。
二、有多少種鎖?
常見的有共享鎖、更新鎖和獨佔鎖。
1.共享鎖定:用於讀取資料操作,允許其他事務同時讀取。當交易執行select語句時,
資料庫會自動為交易分配一把共享鎖定來鎖定讀取的資料。
2.獨佔鎖:用於修改數據,其他事務不能讀取也不能修改。當交易執行insert、
update和delete時,資料庫會自動分配。
3.更新鎖:用於避免更新操作時共享鎖造成的死鎖,例如事務1和2同時持有
共享鎖並等待獲得獨佔鎖。執行update時,事務先獲得更新鎖,然後將
更新鎖升級成獨佔鎖,這樣就避免了死鎖。
此外,這些鎖都可以施加到資料庫中不同的物件上,即這些鎖可以有不同的粒度。
如資料庫級鎖、表級鎖、頁面級鎖、鍵級鎖和行級鎖。
所以鎖是有很多種的,這麼多鎖要想完全掌握靈活使用太難了,我們又不是DBA。
怎麼辦?還好,鎖機制對我們一般用戶來說是透明的,資料庫會自動添加合適的
鎖,並在適當的時機自動升級、降級各種鎖,真是太周到了!我們只需要做的就是
學會根據不同的業務需求,設定好隔離等級就可以了。
三、怎樣設定隔離等級?
一般來說,資料庫系統會提供四種事務隔離等級供使用者選擇:
1.Serializable(串列化):當兩個事務同時操縱相同資料時,事務2只能停下來等。
2.Repeatable Read(可重複讀):事務1能看到事務2新插入的數據,不能看到對
已有數據的更新。
3.Read Commited(讀取已提交資料):事務1能看到事務2新插入和更新的資料。
4.Read Uncommited(讀未提交資料):事務1能看到事務2沒有提交的插入和更新
資料。
四、應用程式中的鎖定
當資料庫採用Read Commited隔離等級時,可以在應用程式中採用悲觀鎖定或樂觀鎖定。
1.悲觀鎖:假定當前事務操作的資料肯定還會有其他事務訪問,因此悲觀地在應用
程式中明確指定採用獨佔鎖來鎖定資料資源。在MySQL、Oracle中支援以下形式:
select ... for update
明確地讓select採用獨佔鎖定鎖定查詢的記錄,其他事務要查詢、更新或刪除這些被
鎖定的數據,都要等到該事務結束後才行。
在Hibernate中,可以在load時傳入LockMode.UPGRADE來採用悲觀鎖定。修改前面的例子,
在事務1和2的get方法呼叫處,多傳入一個LockMode參數。從log可以看出,事務1和2
不再是交叉運行,事務2等待事務1結束後才可以讀取數據,所以最終col_balance值是正確
的100。
package com.cdai.orm.hibernate.transaction;
import org.hibernate.LockMode;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import com.cdai.orm.hibernate.annotation.Account;
import com.cdai.orm.hibernate.annotation.AnnotationHibernate;
public class UpgradeLock {
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static void main(String[] args) {
final SessionFactory sessionFactory = AnnotationHibernate.createSessionFactory();
// Run transaction 1
Thread t1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
Session session1 = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx1 = null;
try {
tx1 = session1.beginTransaction();
System.out.println("T1 - Begin trasaction");
Thread.sleep(500);
Account account = (Account)
session1.get(Account.class, new Long(1), LockMode.UPGRADE);
System.out.println("T1 - balance=" + account.getBalance());
Thread.sleep(500);
account.setBalance(account.getBalance() + 100);
System.out.println("T1 - Change balance:" + account.getBalance());
tx1.commit();
System.out.println("T1 - Commit transaction");
Thread.sleep(500);
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if (tx1 != null)
tx1.rollback();
}
finally {
session1.close();
}
}
};
// Run transaction 2
Thread t2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
Session session2 = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx2 = null;
try {
tx2 = session2.beginTransaction();
System.out.println("T2 - Begin trasaction");
Thread.sleep(500);
Account account = (Account)
session2.get(Account.class, new Long(1), LockMode.UPGRADE);
System.out.println("T2 - balance=" + account.getBalance());
Thread.sleep(500);
account.setBalance(account.getBalance() - 100);
System.out.println("T2 - Change balance:" + account.getBalance());
tx2.commit();
System.out.println("T2 - Commit transaction");
Thread.sleep(500);
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if (tx2 != null)
tx2.rollback();
}
finally {
session2.close();
}
}
};
t1.start();
t2.start();
while (t1.isAlive() || t2.isAlive()) {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
System.out.println("Both T1 and T2 are dead.");
sessionFactory.close();
}
}T1 - Begin trasaction T2 - Begin trasaction Hibernate: select account0_.col_id as col1_0_0_, account0_.col_balance as col2_0_0_ from tb_account account0_ with (updlock, rowlock) where account0_.col_id=? Hibernate: select account0_.col_id as col1_0_0_, account0_.col_balance as col2_0_0_ from tb_account account0_ with (updlock, rowlock) where account0_.col_id=? T2 - balance=100 T2 - Change balance:0 Hibernate: update tb_account set col_balance=? where col_id=? T2 - Commit transaction T1 - balance=0 T1 - Change balance:100 Hibernate: update tb_account set col_balance=? where col_id=? T1 - Commit transaction Both T1 and T2 are dead.
Hibernate對於SQLServer 2005會執行SQL:
select account0_.col_id as col1_0_0_, account0_.col_balance as col2_0_0_ from tb_account account0_ with (updlock, rowlock) where account0_.col_id=?
為選定的col_id為1的資料行加上行鎖和更新鎖定。
2.樂觀鎖:假定當前事務操作的資料不會有其他事務同時訪問,因此完全依靠資料庫
的隔離等級來自動管理鎖的工作。在應用程式中採用版本控制來避免可能低機率出現
的並發問題。
在Hibernate中,使用Version註解來定義版本號欄位。
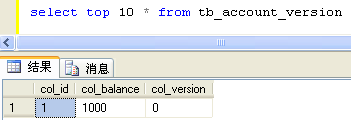
将DirtyLock中的Account对象替换成AccountVersion,其他代码不变,执行出现异常。
package com.cdai.orm.hibernate.transaction;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import javax.persistence.Version;
@Entity
@Table(name = "tb_account_version")
public class AccountVersion {
@Id
@Column(name = "col_id")
private long id;
@Column(name = "col_balance")
private long balance;
@Version
@Column(name = "col_version")
private int version;
public AccountVersion() {
}
public AccountVersion(long id, long balance) {
this.id = id;
this.balance = balance;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public long getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(long balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public int getVersion() {
return version;
}
public void setVersion(int version) {
this.version = version;
}
}log如下:
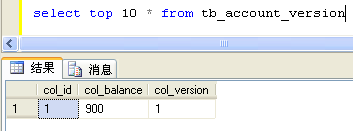
T1 - Begin trasaction T2 - Begin trasaction Hibernate: select accountver0_.col_id as col1_0_0_, accountver0_.col_balance as col2_0_0_, accountver0_.col_version as col3_0_0_ from tb_account_version accountver0_ where accountver0_.col_id=? Hibernate: select accountver0_.col_id as col1_0_0_, accountver0_.col_balance as col2_0_0_, accountver0_.col_version as col3_0_0_ from tb_account_version accountver0_ where accountver0_.col_id=? T1 - balance=1000 T2 - balance=1000 T1 - Change balance:900 T2 - Change balance:1100 Hibernate: update tb_account_version set col_balance=?, col_version=? where col_id=? and col_version=? Hibernate: update tb_account_version set col_balance=?, col_version=? where col_id=? and col_version=? T1 - Commit transaction 2264 [Thread-2] ERROR org.hibernate.event.def.AbstractFlushingEventListener - Could not synchronize database state with session org.hibernate.StaleObjectStateException: Row was updated or deleted by another transaction (or unsaved-value mapping was incorrect): [com.cdai.orm.hibernate.transaction.AccountVersion#1] at org.hibernate.persister.entity.AbstractEntityPersister.check(AbstractEntityPersister.java:1934) at org.hibernate.persister.entity.AbstractEntityPersister.update(AbstractEntityPersister.java:2578) at org.hibernate.persister.entity.AbstractEntityPersister.updateOrInsert(AbstractEntityPersister.java:2478) at org.hibernate.persister.entity.AbstractEntityPersister.update(AbstractEntityPersister.java:2805) at org.hibernate.action.EntityUpdateAction.execute(EntityUpdateAction.java:114) at org.hibernate.engine.ActionQueue.execute(ActionQueue.java:268) at org.hibernate.engine.ActionQueue.executeActions(ActionQueue.java:260) at org.hibernate.engine.ActionQueue.executeActions(ActionQueue.java:180) at org.hibernate.event.def.AbstractFlushingEventListener.performExecutions(AbstractFlushingEventListener.java:321) at org.hibernate.event.def.DefaultFlushEventListener.onFlush(DefaultFlushEventListener.java:51) at org.hibernate.impl.SessionImpl.flush(SessionImpl.java:1206) at org.hibernate.impl.SessionImpl.managedFlush(SessionImpl.java:375) at org.hibernate.transaction.JDBCTransaction.commit(JDBCTransaction.java:137) at com.cdai.orm.hibernate.transaction.VersionLock$2.run(VersionLock.java:93) Both T1 and T2 are dead.
由于乐观锁完全将事务隔离交给数据库来控制,所以事务1和2交叉运行了,事务1提交
成功并将col_version改为1,然而事务2提交时已经找不到col_version为0的数据了,所以
抛出了异常。
Hibernate查询方法比较
Hibernate主要有三种查询方法:
1.HQL (Hibernate Query Language)
和SQL很类似,支持分页、连接、分组、聚集函数和子查询等特性,
但HQL是面向对象的,而不是面向关系数据库中的表。正因查询语句
是面向Domain对象的,所以使用HQL可以获得跨平台的好处,Hibernate
会自动帮我们根据不同的数据库翻译成不同的SQL语句。这在需要支持
多种数据库或者数据库迁移的应用中是十分方便的。
但得到方便的同时,由于SQL语句是由Hibernate自动生成的,所以这不
利于SQL语句的效率优化和调试,当数据量很大时可能会有效率问题,
出了问题也不便于排查解决。
2.QBC/QBE (Query by Criteria/Example)
QBC/QBE是通过组装查询条件或者模板对象来执行查询的。这在需要
灵活地支持许多查询条件自由组合的应用中是比较方便的。同样的问题
是由于查询语句是自由组装的,创建一条语句的代码可能很长,并且
包含许多分支条件,很不便于优化和调试。
3.SQL
Hibernate也支持直接执行SQL的查询方式。这种方式牺牲了Hibernate跨
数据库的优点,手工地编写底层SQL语句,从而获得最好的执行效率,
相对前两种方法,优化和调试方便了一些。
下面来看一组简单的例子。
package com.cdai.orm.hibernate.query;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import org.hibernate.Criteria;
import org.hibernate.Query;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration;
import org.hibernate.criterion.Criterion;
import org.hibernate.criterion.Example;
import org.hibernate.criterion.Expression;
import com.cdai.orm.hibernate.annotation.Account;
public class BasicQuery {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SessionFactory sessionFactory = new AnnotationConfiguration().
addFile("hibernate/hibernate.cfg.xml").
configure().
addPackage("com.cdai.orm.hibernate.annotation").
addAnnotatedClass(Account.class).
buildSessionFactory();
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
// 1.HQL
Query query = session.createQuery("from Account as a where a.id=:id");
query.setLong("id", 1);
List result = query.list();
for (Object row : result) {
System.out.println(row);
}
// 2.QBC
Criteria criteria = session.createCriteria(Account.class);
criteria.add(Expression.eq("id", new Long(2)));
result = criteria.list();
for (Object row : result) {
System.out.println(row);
}
// 3.QBE
Account example= new Account();
example.setBalance(100);
result = session.createCriteria(Account.class).
add(Example.create(example)).
list();
for (Object row : result) {
System.out.println(row);
}
// 4.SQL
query = session.createSQLQuery(
" select top 10 * from tb_account order by col_id desc ");
result = query.list();
for (Object row : result) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString((Object[]) row));
}
session.close();
}
}Hibernate: select account0_.col_id as col1_0_, account0_.col_balance as col2_0_ from tb_account account0_ where account0_.col_id=? Account [id=1, balance=100] Hibernate: select this_.col_id as col1_0_0_, this_.col_balance as col2_0_0_ from tb_account this_ where this_.col_id=? Account [id=2, balance=100] Hibernate: select this_.col_id as col1_0_0_, this_.col_balance as col2_0_0_ from tb_account this_ where (this_.col_balance=?) Account [id=1, balance=100] Account [id=2, balance=100] Hibernate: select top 10 * from tb_account order by col_id desc [2, 100] [1, 100]
从log中可以清楚的看到Hibernate对于生成的SQL语句的控制,具体选择
哪种查询方式就要看具体应用了。
更多Java的Hibernate框架数据库操作中锁的使用和查询类型相关文章请关注PHP中文网!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 公司安全軟件導致應用無法運行?如何排查和解決?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
公司安全軟件導致應用無法運行?如何排查和解決?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
公司安全軟件導致部分應用無法正常運行的排查與解決方法許多公司為了保障內部網絡安全,會部署安全軟件。 ...
 如何使用MapStruct簡化系統對接中的字段映射問題?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 06:21 PM
如何使用MapStruct簡化系統對接中的字段映射問題?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 06:21 PM
系統對接中的字段映射處理在進行系統對接時,常常會遇到一個棘手的問題:如何將A系統的接口字段有效地映�...
 如何優雅地獲取實體類變量名構建數據庫查詢條件?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:42 PM
如何優雅地獲取實體類變量名構建數據庫查詢條件?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:42 PM
在使用MyBatis-Plus或其他ORM框架進行數據庫操作時,經常需要根據實體類的屬性名構造查詢條件。如果每次都手動...
 如何將姓名轉換為數字以實現排序並保持群組中的一致性?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
如何將姓名轉換為數字以實現排序並保持群組中的一致性?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
將姓名轉換為數字以實現排序的解決方案在許多應用場景中,用戶可能需要在群組中進行排序,尤其是在一個用...
 IntelliJ IDEA是如何在不輸出日誌的情況下識別Spring Boot項目的端口號的?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
IntelliJ IDEA是如何在不輸出日誌的情況下識別Spring Boot項目的端口號的?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
在使用IntelliJIDEAUltimate版本啟動Spring...
 Java對像如何安全地轉換為數組?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Java對像如何安全地轉換為數組?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Java對象與數組的轉換:深入探討強制類型轉換的風險與正確方法很多Java初學者會遇到將一個對象轉換成數組的�...
 電商平台SKU和SPU數據庫設計:如何兼顧用戶自定義屬性和無屬性商品?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
電商平台SKU和SPU數據庫設計:如何兼顧用戶自定義屬性和無屬性商品?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
電商平台SKU和SPU表設計詳解本文將探討電商平台中SKU和SPU的數據庫設計問題,特別是如何處理用戶自定義銷售屬...
 使用TKMyBatis進行數據庫查詢時,如何優雅地獲取實體類變量名構建查詢條件?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 09:51 PM
使用TKMyBatis進行數據庫查詢時,如何優雅地獲取實體類變量名構建查詢條件?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 09:51 PM
在使用TKMyBatis進行數據庫查詢時,如何優雅地獲取實體類變量名以構建查詢條件,是一個常見的難題。本文將針...






