Python守護程式和腳本單例運行詳解
本篇文章主要介紹了Python守護程序和腳本單例運行,小編覺得挺不錯的,現在分享給大家,也給大家做個參考。一起跟著小編過來看看吧
一、簡介
守護程序最重要的特性是後台運行;它必須與其運行前的環境隔離開來,這些環境包括未關閉的文件描述符、控制終端、會話和進程組、工作目錄以及檔案建立遮罩等;它可以在系統啟動時從啟動腳本/etc/rc.d中啟動,可以由inetd守護程序啟動,也可以有作業規劃程序crond啟動,還可以由使用者終端(通常是shell)執行。
Python有時需要確保只執行一個腳本實例,以避免資料的衝突。
二、Python守護程式
1、函數實作
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf-8
import sys, os
'''将当前进程fork为一个守护进程
注意:如果你的守护进程是由inetd启动的,不要这样做!inetd完成了
所有需要做的事情,包括重定向标准文件描述符,需要做的事情只有chdir()和umask()了
'''
def daemonize (stdin='/dev/null', stdout='/dev/null', stderr='/dev/null'):
#重定向标准文件描述符(默认情况下定向到/dev/null)
try:
pid = os.fork()
#父进程(会话组头领进程)退出,这意味着一个非会话组头领进程永远不能重新获得控制终端。
if pid > 0:
sys.exit(0) #父进程退出
except OSError, e:
sys.stderr.write ("fork #1 failed: (%d) %s\n" % (e.errno, e.strerror) )
sys.exit(1)
#从母体环境脱离
os.chdir("/") #chdir确认进程不保持任何目录于使用状态,否则不能umount一个文件系统。也可以改变到对于守护程序运行重要的文件所在目录
os.umask(0) #调用umask(0)以便拥有对于写的任何东西的完全控制,因为有时不知道继承了什么样的umask。
os.setsid() #setsid调用成功后,进程成为新的会话组长和新的进程组长,并与原来的登录会话和进程组脱离。
#执行第二次fork
try:
pid = os.fork()
if pid > 0:
sys.exit(0) #第二个父进程退出
except OSError, e:
sys.stderr.write ("fork #2 failed: (%d) %s\n" % (e.errno, e.strerror) )
sys.exit(1)
#进程已经是守护进程了,重定向标准文件描述符
for f in sys.stdout, sys.stderr: f.flush()
si = open(stdin, 'r')
so = open(stdout, 'a+')
se = open(stderr, 'a+', 0)
os.dup2(si.fileno(), sys.stdin.fileno()) #dup2函数原子化关闭和复制文件描述符
os.dup2(so.fileno(), sys.stdout.fileno())
os.dup2(se.fileno(), sys.stderr.fileno())
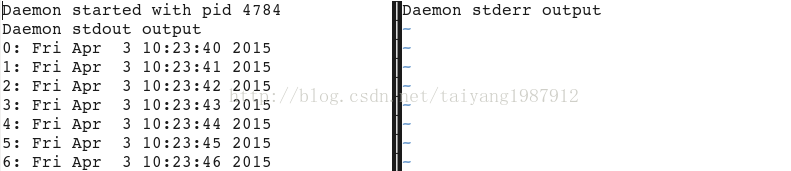
#示例函数:每秒打印一个数字和时间戳
def main():
import time
sys.stdout.write('Daemon started with pid %d\n' % os.getpid())
sys.stdout.write('Daemon stdout output\n')
sys.stderr.write('Daemon stderr output\n')
c = 0
while True:
sys.stdout.write('%d: %s\n' %(c, time.ctime()))
sys.stdout.flush()
c = c+1
time.sleep(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
daemonize('/dev/null','/tmp/daemon_stdout.log','/tmp/daemon_error.log')
main()可以透過指令ps -ef | grep daemon.py檢視後台執行的繼承,在/tmp/daemon_error.log會記錄錯誤執行日誌,在/tmp /daemon_stdout.log會記錄標準輸出日誌。
2、類別實作
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf-8
#python模拟linux的守护进程
import sys, os, time, atexit, string
from signal import SIGTERM
class Daemon:
def __init__(self, pidfile, stdin='/dev/null', stdout='/dev/null', stderr='/dev/null'):
#需要获取调试信息,改为stdin='/dev/stdin', stdout='/dev/stdout', stderr='/dev/stderr',以root身份运行。
self.stdin = stdin
self.stdout = stdout
self.stderr = stderr
self.pidfile = pidfile
def _daemonize(self):
try:
pid = os.fork() #第一次fork,生成子进程,脱离父进程
if pid > 0:
sys.exit(0) #退出主进程
except OSError, e:
sys.stderr.write('fork #1 failed: %d (%s)\n' % (e.errno, e.strerror))
sys.exit(1)
os.chdir("/") #修改工作目录
os.setsid() #设置新的会话连接
os.umask(0) #重新设置文件创建权限
try:
pid = os.fork() #第二次fork,禁止进程打开终端
if pid > 0:
sys.exit(0)
except OSError, e:
sys.stderr.write('fork #2 failed: %d (%s)\n' % (e.errno, e.strerror))
sys.exit(1)
#重定向文件描述符
sys.stdout.flush()
sys.stderr.flush()
si = file(self.stdin, 'r')
so = file(self.stdout, 'a+')
se = file(self.stderr, 'a+', 0)
os.dup2(si.fileno(), sys.stdin.fileno())
os.dup2(so.fileno(), sys.stdout.fileno())
os.dup2(se.fileno(), sys.stderr.fileno())
#注册退出函数,根据文件pid判断是否存在进程
atexit.register(self.delpid)
pid = str(os.getpid())
file(self.pidfile,'w+').write('%s\n' % pid)
def delpid(self):
os.remove(self.pidfile)
def start(self):
#检查pid文件是否存在以探测是否存在进程
try:
pf = file(self.pidfile,'r')
pid = int(pf.read().strip())
pf.close()
except IOError:
pid = None
if pid:
message = 'pidfile %s already exist. Daemon already running!\n'
sys.stderr.write(message % self.pidfile)
sys.exit(1)
#启动监控
self._daemonize()
self._run()
def stop(self):
#从pid文件中获取pid
try:
pf = file(self.pidfile,'r')
pid = int(pf.read().strip())
pf.close()
except IOError:
pid = None
if not pid: #重启不报错
message = 'pidfile %s does not exist. Daemon not running!\n'
sys.stderr.write(message % self.pidfile)
return
#杀进程
try:
while 1:
os.kill(pid, SIGTERM)
time.sleep(0.1)
#os.system('hadoop-daemon.sh stop datanode')
#os.system('hadoop-daemon.sh stop tasktracker')
#os.remove(self.pidfile)
except OSError, err:
err = str(err)
if err.find('No such process') > 0:
if os.path.exists(self.pidfile):
os.remove(self.pidfile)
else:
print str(err)
sys.exit(1)
def restart(self):
self.stop()
self.start()
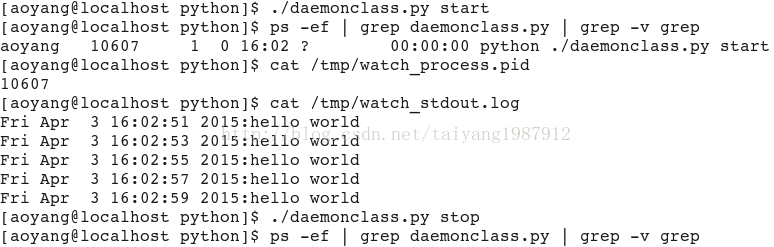
def _run(self):
""" run your fun"""
while True:
#fp=open('/tmp/result','a+')
#fp.write('Hello World\n')
sys.stdout.write('%s:hello world\n' % (time.ctime(),))
sys.stdout.flush()
time.sleep(2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
daemon = Daemon('/tmp/watch_process.pid', stdout = '/tmp/watch_stdout.log')
if len(sys.argv) == 2:
if 'start' == sys.argv[1]:
daemon.start()
elif 'stop' == sys.argv[1]:
daemon.stop()
elif 'restart' == sys.argv[1]:
daemon.restart()
else:
print 'unknown command'
sys.exit(2)
sys.exit(0)
else:
print 'usage: %s start|stop|restart' % sys.argv[0]
sys.exit(2)運作結果:
它是當Daemon設計成一個模板,在其他檔案中from daemon
它是當Daemon設計成一個模板,在其他檔案中from daemon import Daemon,然後定義子類自己的功能。class MyDaemon(Daemon):
def run(self):
while True:
fp=open('/tmp/run.log','a+')
fp.write('Hello World\n')
time.sleep(1)
不足:訊號處理signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, cleanup_handler)暫時沒有安裝,註冊程式退出時的回呼函數delpid()沒有被呼叫。
#/bin/sh while true do count=`ps -ef | grep "daemonclass.py" | grep -v "grep"` if [ "$?" != "0" ]; then daemonclass.py start fi sleep 2 done
三、python保證只能運行一個腳本實例
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf-8
import fcntl, sys, time, os
pidfile = 0
def ApplicationInstance():
global pidfile
pidfile = open(os.path.realpath(__file__), "r")
try:
fcntl.flock(pidfile, fcntl.LOCK_EX | fcntl.LOCK_NB) #创建一个排他锁,并且所被锁住其他进程不会阻塞
except:
print "another instance is running..."
sys.exit(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
ApplicationInstance()
while True:
print 'running...'
time.sleep(1)2、開啟自訂檔案並加鎖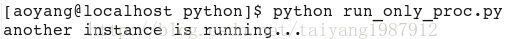
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf-8
import fcntl, sys, time
pidfile = 0
def ApplicationInstance():
global pidfile
pidfile = open("instance.pid", "w")
try:
fcntl.lockf(pidfile, fcntl.LOCK_EX | fcntl.LOCK_NB) #创建一个排他锁,并且所被锁住其他进程不会阻塞
except IOError:
print "another instance is running..."
sys.exit(0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
ApplicationInstance()
while True:
print 'running...'
time.sleep(1)#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf-8
import time, os, sys
import signal
pidfile = '/tmp/process.pid'
def sig_handler(sig, frame):
if os.path.exists(pidfile):
os.remove(pidfile)
sys.exit(0)
def ApplicationInstance():
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, sig_handler)
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, sig_handler)
signal.signal(signal.SIGQUIT, sig_handler)
try:
pf = file(pidfile, 'r')
pid = int(pf.read().strip())
pf.close()
except IOError:
pid = None
if pid:
sys.stdout.write('instance is running...\n')
sys.exit(0)
file(pidfile, 'w+').write('%s\n' % os.getpid())
if __name__ == "__main__":
ApplicationInstance()
while True:
print 'running...'
time.sleep(1)4、偵測特定資料夾或檔案
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf-8
import time, commands, signal, sys
def sig_handler(sig, frame):
if os.path.exists("/tmp/test"):
os.rmdir("/tmp/test")
sys.exit(0)
def ApplicationInstance():
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, sig_handler)
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, sig_handler)
signal.signal(signal.SIGQUIT, sig_handler)
if commands.getstatusoutput("mkdir /tmp/test")[0]:
print "instance is running..."
sys.exit(0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
ApplicationInstance()
while True:
print 'running...'
time.sleep(1)
也可以偵測某一個特定的文件,判斷文件是否存在:
import os
import os.path
import time
#class used to handle one application instance mechanism
class ApplicationInstance:
#specify the file used to save the application instance pid
def __init__( self, pid_file ):
self.pid_file = pid_file
self.check()
self.startApplication()
#check if the current application is already running
def check( self ):
#check if the pidfile exists
if not os.path.isfile( self.pid_file ):
return
#read the pid from the file
pid = 0
try:
file = open( self.pid_file, 'rt' )
data = file.read()
file.close()
pid = int( data )
except:
pass
#check if the process with specified by pid exists
if 0 == pid:
return
try:
os.kill( pid, 0 ) #this will raise an exception if the pid is not valid
except:
return
#exit the application
print "The application is already running..."
exit(0) #exit raise an exception so don't put it in a try/except block
#called when the single instance starts to save it's pid
def startApplication( self ):
file = open( self.pid_file, 'wt' )
file.write( str( os.getpid() ) )
file.close()
#called when the single instance exit ( remove pid file )
def exitApplication( self ):
try:
os.remove( self.pid_file )
except:
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
#create application instance
appInstance = ApplicationInstance( '/tmp/myapp.pid' )
#do something here
print "Start MyApp"
time.sleep(5) #sleep 5 seconds
print "End MyApp"
#remove pid file
appInstance.exitApplication()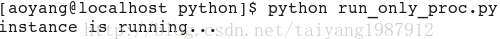
os.kill( pid, 0
os.kill( pid, 0
os.kill( pid, 0 )用於檢測一個為不上的進程的進程已經停止則拋出異常,若正在運行則不發送kill訊號。
5、socket監聽一個特定端口#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf-8
import socket, time, sys
def ApplicationInstance():
try:
global s
s = socket.socket()
host = socket.gethostname()
s.bind((host, 60123))
except:
print "instance is running..."
sys.exit(0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
ApplicationInstance()
while True:
print 'running...'
time.sleep(1)可以將函數使用裝飾器實現,便於重用(效果與上述相同):總結
rereee1 )守護程式和單腳本運行在實際應用中比較重要,方法也比較多,可選擇合適的來進行修改,可以將它們做成一個單獨的類別或模板,然後子類化實現自訂。
(2)daemon監控進程自動恢復避免了nohup和&的使用,並配合shell腳本可以省去很多不定時啟動掛掉伺服器的麻煩。以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持PHP中文網。
更多Python守護程式和腳本單例運行詳解相關文章請關注PHP中文網!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

AI Hentai Generator
免費產生 AI 無盡。

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)

熱門話題
 如何解決Linux終端中查看Python版本時遇到的權限問題?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
如何解決Linux終端中查看Python版本時遇到的權限問題?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
Linux終端中查看Python版本時遇到權限問題的解決方法當你在Linux終端中嘗試查看Python的版本時,輸入python...
 在Python中如何高效地將一個DataFrame的整列複製到另一個結構不同的DataFrame中?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 11:15 PM
在Python中如何高效地將一個DataFrame的整列複製到另一個結構不同的DataFrame中?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 11:15 PM
在使用Python的pandas庫時,如何在兩個結構不同的DataFrame之間進行整列複製是一個常見的問題。假設我們有兩個Dat...
 如何在10小時內通過項目和問題驅動的方式教計算機小白編程基礎?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:18 AM
如何在10小時內通過項目和問題驅動的方式教計算機小白編程基礎?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:18 AM
如何在10小時內教計算機小白編程基礎?如果你只有10個小時來教計算機小白一些編程知識,你會選擇教些什麼�...
 Uvicorn是如何在沒有serve_forever()的情況下持續監聽HTTP請求的?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
Uvicorn是如何在沒有serve_forever()的情況下持續監聽HTTP請求的?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
Uvicorn是如何持續監聽HTTP請求的? Uvicorn是一個基於ASGI的輕量級Web服務器,其核心功能之一便是監聽HTTP請求並進�...
 Python中如何通過字符串動態創建對象並調用其方法?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 11:18 PM
Python中如何通過字符串動態創建對象並調用其方法?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 11:18 PM
在Python中,如何通過字符串動態創建對象並調用其方法?這是一個常見的編程需求,尤其在需要根據配置或運行...
 哪些流行的Python庫及其用途?
Mar 21, 2025 pm 06:46 PM
哪些流行的Python庫及其用途?
Mar 21, 2025 pm 06:46 PM
本文討論了諸如Numpy,Pandas,Matplotlib,Scikit-Learn,Tensorflow,Tensorflow,Django,Blask和請求等流行的Python庫,並詳細介紹了它們在科學計算,數據分析,可視化,機器學習,網絡開發和H中的用途
 如何在使用 Fiddler Everywhere 進行中間人讀取時避免被瀏覽器檢測到?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:15 AM
如何在使用 Fiddler Everywhere 進行中間人讀取時避免被瀏覽器檢測到?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:15 AM
使用FiddlerEverywhere進行中間人讀取時如何避免被檢測到當你使用FiddlerEverywhere...







