在 Web 應用程式中,JavaScript 透過 XMLHttpRequest (XHR)來執行非同步請求,這是一種有效改進頁面通訊的技術,當我們談及Ajax技術的時候,通常意思就是基於 XMLHttpRequest 的 Ajax。雖說 Ajax 很有用,但它不是最佳 API,它在設計上不符合職責分離原則,將輸入、輸出和用事件來追蹤的狀態混雜在一個物件裡。而且,基於事件的模型與現在 JavaScript 流行的 Promise 以及基於生成器的非同步程式設計模型相背道而馳。本文將要介紹的內容則是XMLHttpRequest 的最新替代技術— Fetch API, 它是 W3C 的正式標準。
相容性
在介紹之前,先看看目前主流瀏覽器對Fetch API 的支援情況:
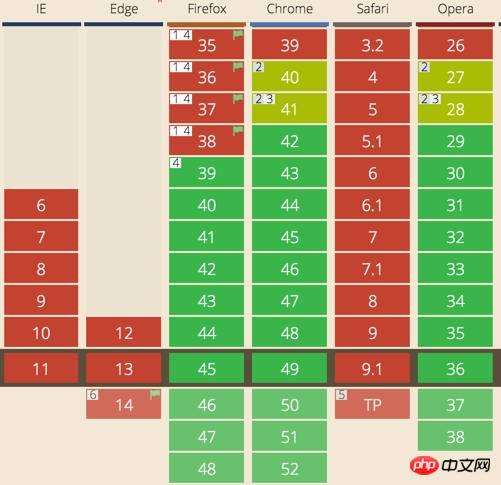
Fetch 的支持目前還處於早期的階段,在Firefox 39 以上,和Chrome 42 以上都被支持了。
如果你現在就想使用它,你還可以用 Fetch Polyfil,用來支援那些還未支援 Fetch 的瀏覽器。
在使用Fetch 之前,也可以對其進行功能性偵測:
if(self.fetch) {
// run my fetch request here
} else {
// do something with
XMLHttpRequest?
}簡單的fetching範例
在Fetch API 中,最常用的就是fetch() 函數。它接收一個URL參數,回傳一個 promise 來處理 response。 response 是 Response 物件:
fetch("/data.json").then(function(res)
{
// res instanceof Response ==
true.
if (res.ok) {
res.json().then(function(data) {
console.log(data.entries);
});
} else {
console.log("Looks like the response wasn't
perfect, got status", res.status);
}
}, function(e) {
console.log("Fetch failed!", e);
});fetch() 接受第二個可選參數,一個可以控制不同配置的 init 物件。如果是提交一個 POST 請求,程式碼如下:
fetch("http://www.example.org/submit.php",
{
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type":
"application/x-www-form-urlencoded"
},
body:
"firstName=Nikhil&favColor=blue&password=easytoguess"
}).then(function(res) {
if (res.ok) {
//res.ok用于检测请求是否成功
console.log("Perfect! Your settings are
saved.");
} else if (res.status == 401) {
console.log("Oops! You are not
authorized.");
}
}, function(e) {
console.log("Error submitting
form!");
});如果遇到網路故障,fetch() promise 將會 reject,帶一個 TypeError 物件。想要精確的判斷 fetch() 是否成功,需要包含 promise resolved 的情況,此時再判斷 Response.ok 是不是為 true。
Fetch 實作了四個介面:GlobalFetch、Headers、Request 和 Response。 GloabaFetch 只包含了一個 fetch 方法用來取得網路資源,其它三個直接對應了對應的 HTTP 概念。此外,在 request/reponse 中,也混淆了 Body。
Headers
Headers 介面允許定義 HTTP 的請求頭(Request.headers)和回應頭(Response.headers)。一個Headers 物件是一個簡單的多名值對:
var content = "Hello World";
var myHeaders = new Headers();
myHeaders.append("Content-Type",
"text/plain");
myHeaders.append("Content-Length",
content.length.toString());
myHeaders.append("X-Custom-Header",
"ProcessThisImmediately");也可以傳一個多維數組或物件字面量:
myHeaders = new Headers({
"Content-Type": "text/plain",
"Content-Length":
content.length.toString(),
"X-Custom-Header":
"ProcessThisImmediately",
});此外,Headers 接口提供了set ,delete 等API 用於檢索其內容:
console.log(reqHeaders.has("Content-Type")); //
true
console.log(reqHeaders.has("Set-Cookie")); //
false
reqHeaders.set("Content-Type",
"text/html");
reqHeaders.append("X-Custom-Header",
"AnotherValue");
console.log(reqHeaders.get("Content-Length"));
// 11
console.log(reqHeaders.getAll("X-Custom-Header")); //
["ProcessThisImmediately", "AnotherValue"]
reqHeaders.delete("X-Custom-Header");
console.log(reqHeaders.getAll("X-Custom-Header")); //
[]雖然有些操作僅在 ServiceWorkers 中使用,但相對於 XHR,其本身提供了非常方便的操作 Headers 的 API。
出於安全性原因,有些 header 欄位的設定只能透過 User Agent 實現,不能透過程式設定:請求頭禁置欄位 和 回應頭禁置欄位。
如果使用了一個不合法的 HTTP Header 屬性名稱或寫入一個不可寫的屬性,Headers 的方法通常都會拋出TypeError 例外:
var myResponse = Response.error();
try {
myResponse.headers.set("Origin",
"http://mybank.com");
} catch(e) {
console.log("Cannot pretend to be a
bank!");
}最佳實踐是在使用之前檢查content type 是否正確,例如:
fetch(myRequest).then(function(response)
{
if(response.headers.get("content-type") ===
"application/json") {
return response.json().then(function(json)
{
// process your JSON further
});
} else {
console.log("Oops, we haven't got
JSON!");
}
});由於Headers 可以在request 請求中被傳送或在response 請求中被接收,並且規定了哪些參數是可寫的,Headers 物件有一個特殊的 guard 屬性。這個屬性沒有暴露給 Web,但是它影響到哪些內容可以在 Headers 物件中被改變。
可能的值如下:
#none:預設的
r
equest:从 request 中获得的 headers(Request.headers)只读 request-no-cors:从不同域(Request.mode no-cors)的 request 中获得的 headers 只读 response:从 response 中获得的 headers(Response.headers)只读 immutable:在 ServiceWorkers 中最常用的,所有的 headers 都只读
Request
Request 介面定義了透過HTTP請求資源的request格式,一個簡單請求建構如下:
var req = new
Request("/index.html");
console.log(req.method); // "GET"
console.log(req.url); //
"http://example.com/index.html"
console.log(req.headers);
//请求头和 fetch() 一樣,Request 接受第二個可選參數,一個可以控制不同配置的 init 物件:
var myHeaders = new Headers();
var myInit = { method: 'GET',
headers: myHeaders,
mode: 'cors',
cache: 'default' ,
credentials: true,
body: "image data"};
var myRequest = new
Request('flowers.jpg',myInit);
fetch(myRequest,myInit)
.then(function(response) {
return response.blob();
})
.then(function(myBlob) {
var objectURL =
URL.createObjectURL(myBlob);
myImage.src = objectURL;
});mode 屬性用來決定是否允許跨域請求,以及哪些response 屬性可讀。 mode 可選的屬性值:
same-origin:請求遵循同源策略
no-cors: 預設值,允許來自CDN的腳本、其他域的圖片和其他一些跨域資源(前提條件是 method 只能是HEAD,GET或POST)
cors :允許跨域,請求遵循 CROS協定
credentials 枚舉屬性決定了cookies 是否能跨域得到,這與 XHR 的 withCredentials 標誌相同,但只有三個值,分別是omit(預設),same-origin以及include。
Response
Response 實例是在 fentch() 處理完 promises 之後傳回的,它的實例也可用透過 JavaScript 來建立, 但只有在 ServiceWorkers 中才真正有用。當使用 respondWith() 方法並提供了一個自訂的response來接受request時:
var myBody = new Blob();
addEventListener('fetch', function(event)
{
event.respondWith(new Response(myBody,
{
headers: { "Content-Type" : "text/plain"
}
});
});#Response() 建構方法接受兩個可選參數—response的資料體和一個初始化對象(與 Request() 所接受的init參數類似.)
最常見的response屬性有:
Response.status — 整数(默认值为200) 为response的状态码. Response.statusText — 字符串(默认值为OK),该值与HTTP状态码消息对应. Response.ok — 如上所示, 该属性是来检查response的状态是否在200-299(包括200,299)这个范围内.该属性返回一个Boolean值. Response.headers — 响应头 Response.type — 响应类型,如:basic/ cors /error
Body
Request 和Response 都實作了Body 接口,在請求過程中,二者都會攜帶 Body,其可以是以下任何一種類型的實例:
ArrayBuffer ArrayBufferView Blob/file URLSearchParams FormData
此外,Request 和 Response 都为他们的body提供了以下方法,这些方法都返回一个Promise对象:
arrayBuffer() blob() json() text() formData()
以上就是XML Http Request最新替代技术—— Fetch 的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!




