tomcat-dbcp資料庫連線池配置以及使用時候的一些坑
一、資料庫連線池
開發的時候常常會需要對資料庫進行一些操作,比如說常見的增刪改查之類的,當資料量小的時候,可以直接進行操作,但是當資料量增多的時候,每一次連接以及釋放資料庫都會耗費一定的時間,這個時候,可以採用資料庫連接池來保持資料庫的鏈接,減少連接資料庫對程式帶來的開銷,並且可以減少資料庫的壓力,那麼資料庫連結池是一個什麼樣的東西呢?顧名思義,它是一個池子,池子裡放的是對數據庫的鏈接,打個比方魚塘,就是養魚的池子,想要吃魚可以直接去撈,不用自己去親自的買魚苗等,數據庫連接池就是放的對於數據庫的鏈接,統一的把所有的鏈接都給建立好了,用的時候就可以直接的從裡面去取,用完了之後放回池子裡就可以,既然用這個東西,那麼我們也沒必要完全自己去寫程式碼實現,有些開源的可以直接用,常見的有三種開源的連接池,c3p0,dbcp,proxool這三種,對於c3p0、proxool這兩種沒用過,只是簡單的用過dbcp的池子,在此講下如何使用dbcp資料庫連接池,以及使用的時候遇到的一些坑
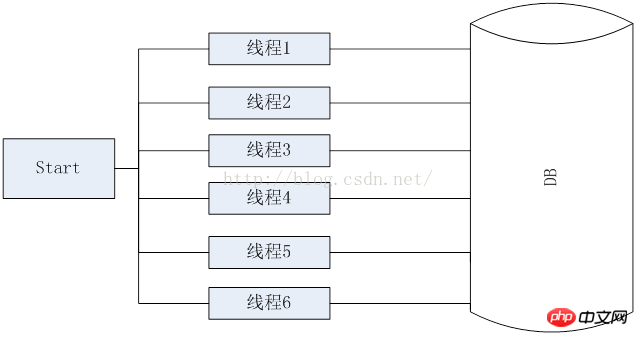
圖1、使用連接池之前
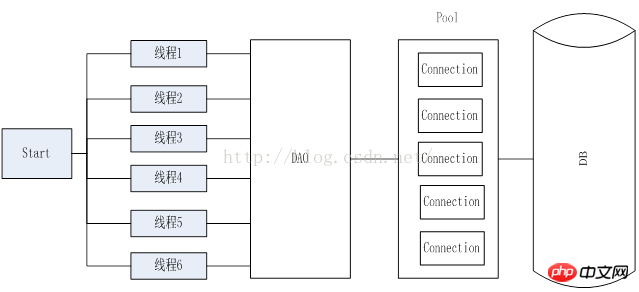
圖2 使用連線池之後
如上圖1所示,在使用連線池之前,需要每次都對資料庫建立鏈接,並且需要隨時進行釋放,在資料量大的情況下,需要很大的連接資料庫的開銷,並且頻繁的對資料庫進行訪問以及釋放,也會對資料庫造成很大的壓力,圖2為使用資料庫連接池之後,將所有的鏈接放在池子裡,不進行釋放,當用的時候直接從池子裡去取,用完之後放回池子裡,池子保持對數據庫的長鏈接,連結斷開會進行自動重連,如果連接不夠那麼對應後來的用戶就需要進行等待
二、使用tomcat-dbcp所使用的jar包
包含tomcat-dbcp.jar即可,剩下的都是一些基礎包
三、所使用的配置
dbname.Driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver dbname.Url=jdbc:mysql://<your ip>/<your dbname>?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8 &autoReconnect=true&failOverReadOnly=false&maxReconnects=10&autoReconnectForPools=true&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&connectTimeout=3000 dbname.Username=<your username> dbname.Password=<your password> dbname.InitialSize=15 dbname.MinIdle=10 dbname.MaxIdle=20 dbname.MaxWait=5000 dbname.MaxActive=20 dbname.validationQuery=select 1
其中這些配置只需要放在
其中driver,url,username,password為常見的資料庫連接的配置
##
InitialSize为初始化建立的连接数
minidle为数据库连接池中保持的最少的空闲的链接数
maxidle数据库连接池中保持的最大的连接数
maxwait等待数据库连接池分配连接的最长时间,超出之后报错
maxactivite最大的活动链接数,如果是多线程可以设置为超出多线程个数个链接数
<pre name="code" class="java">validationQuery测试是否连接是有效的sql语句
public abstract class DB {
private static HashMap<String, DataSource> dsTable = new HashMap<String, DataSource>();//此处记得用static
private BasicDataSource ds;
private PreparedStatement stmt = null;
private DataSource getDataSource(String n) {
if (dsTable.containsKey(n)) {
return dsTable.get(n);//如果不同的数据库,多个连接池
} else {
synchronized (dsTable) {
ds = new BasicDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName(DBConfig.getString("db", n.concat(".Driver")));//将<yourname>.properties的值读进来
ds.setUrl(DBConfig.getString("db", n.concat(".Url")));
ds.setUsername(DBConfig.getString("db", n.concat(".Username")));
ds.setPassword(DBConfig.getString("db", n.concat(".Password")));
ds.setInitialSize(DBConfig.getInteger("db", n.concat(".InitialSize")));
ds.setMinIdle(DBConfig.getInteger("db", n.concat(".MinIdle")));
ds.setMaxIdle(DBConfig.getInteger("db", n.concat(".MaxIdle")));
ds.setMaxWait(DBConfig.getInteger("db", n.concat(".MaxWait")));
ds.setMaxActive(DBConfig.getInteger("db", n.concat(".MaxActive")));
ds.setValidationQuery(DBConfig.getString("db", n.concat(".validationQuery")));
dsTable.put(n, ds);
return ds;
}
}
}
protected Connection conn;
public boolean open() throws SQLException {
BasicDataSource bds=(BasicDataSource)this.getDataSource(this.getConnectionName());
System.out.println("connection_number:"+bds.getNumActive()+"dsTable:"+dsTable);
this.conn = this.getDataSource(this.getConnectionName()).getConnection();
return true;
}
public void close() throws SQLException {
if (this.conn != null)
this.conn.close();
}
protected abstract String getConnectionName();//此函数可以根据自己的需求,将数据库的名字传进来即可
public void prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {
this.stmt = this.conn.prepareStatement(sql);
}
public void setObject(int index, Object value, int type) throws SQLException {
this.stmt.setObject(index, value, type);
}
public void setObject(int index, Object value) throws SQLException {
this.stmt.setObject(index, value);
}
public int execute() throws SQLException {
return this.stmt.executeUpdate();
}
}登入後複製
上述是線程池使用的時候所用到的代碼,只是給出了大概的寫法,具體的DBDAO部分需要根據自己的需求去自己實現,比如批處理,查詢,更新等函數,可以根據個人的需求去進行修改,那麼如何判斷你所創建的連結是你想要的呢?有兩種辦法可以檢驗1、建立一個空的資料庫,查看連結個數2、在linux下面查看連結個數得到processidpublic abstract class DB {
private static HashMap<String, DataSource> dsTable = new HashMap<String, DataSource>();//此处记得用static
private BasicDataSource ds;
private PreparedStatement stmt = null;
private DataSource getDataSource(String n) {
if (dsTable.containsKey(n)) {
return dsTable.get(n);//如果不同的数据库,多个连接池
} else {
synchronized (dsTable) {
ds = new BasicDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName(DBConfig.getString("db", n.concat(".Driver")));//将<yourname>.properties的值读进来
ds.setUrl(DBConfig.getString("db", n.concat(".Url")));
ds.setUsername(DBConfig.getString("db", n.concat(".Username")));
ds.setPassword(DBConfig.getString("db", n.concat(".Password")));
ds.setInitialSize(DBConfig.getInteger("db", n.concat(".InitialSize")));
ds.setMinIdle(DBConfig.getInteger("db", n.concat(".MinIdle")));
ds.setMaxIdle(DBConfig.getInteger("db", n.concat(".MaxIdle")));
ds.setMaxWait(DBConfig.getInteger("db", n.concat(".MaxWait")));
ds.setMaxActive(DBConfig.getInteger("db", n.concat(".MaxActive")));
ds.setValidationQuery(DBConfig.getString("db", n.concat(".validationQuery")));
dsTable.put(n, ds);
return ds;
}
}
}
protected Connection conn;
public boolean open() throws SQLException {
BasicDataSource bds=(BasicDataSource)this.getDataSource(this.getConnectionName());
System.out.println("connection_number:"+bds.getNumActive()+"dsTable:"+dsTable);
this.conn = this.getDataSource(this.getConnectionName()).getConnection();
return true;
}
public void close() throws SQLException {
if (this.conn != null)
this.conn.close();
}
protected abstract String getConnectionName();//此函数可以根据自己的需求,将数据库的名字传进来即可
public void prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {
this.stmt = this.conn.prepareStatement(sql);
}
public void setObject(int index, Object value, int type) throws SQLException {
this.stmt.setObject(index, value, type);
}
public void setObject(int index, Object value) throws SQLException {
this.stmt.setObject(index, value);
}
public int execute() throws SQLException {
return this.stmt.executeUpdate();
}
}
ps aux|grep <your java name>
netstat -apn|grep <your processid>
#

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 iOS 18 新增「已復原」相簿功能 可找回遺失或損壞的照片
Jul 18, 2024 am 05:48 AM
iOS 18 新增「已復原」相簿功能 可找回遺失或損壞的照片
Jul 18, 2024 am 05:48 AM
蘋果公司最新發布的iOS18、iPadOS18以及macOSSequoia系統為Photos應用程式增添了一項重要功能,旨在幫助用戶輕鬆恢復因各種原因遺失或損壞的照片和影片。這項新功能在Photos應用的"工具"部分引入了一個名為"已恢復"的相冊,當用戶設備中存在未納入其照片庫的圖片或影片時,該相冊將自動顯示。 "已恢復"相簿的出現為因資料庫損壞、相機應用未正確保存至照片庫或第三方應用管理照片庫時照片和視頻丟失提供了解決方案。使用者只需簡單幾步
 Hibernate 如何實作多型映射?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
Hibernate 如何實作多型映射?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
Hibernate多態映射可映射繼承類別到資料庫,提供以下映射類型:joined-subclass:為子類別建立單獨表,包含父類別所有欄位。 table-per-class:為子類別建立單獨資料表,僅包含子類別特有列。 union-subclass:類似joined-subclass,但父類別表聯合所有子類別列。
 在PHP中使用MySQLi建立資料庫連線的詳盡教學
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:42 PM
在PHP中使用MySQLi建立資料庫連線的詳盡教學
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:42 PM
如何在PHP中使用MySQLi建立資料庫連線:包含MySQLi擴充(require_once)建立連線函數(functionconnect_to_db)呼叫連線函數($conn=connect_to_db())執行查詢($result=$conn->query())關閉連線( $conn->close())
 如何在PHP中處理資料庫連線錯誤
Jun 05, 2024 pm 02:16 PM
如何在PHP中處理資料庫連線錯誤
Jun 05, 2024 pm 02:16 PM
PHP處理資料庫連線報錯,可以使用下列步驟:使用mysqli_connect_errno()取得錯誤代碼。使用mysqli_connect_error()取得錯誤訊息。透過擷取並記錄這些錯誤訊息,可以輕鬆識別並解決資料庫連接問題,確保應用程式的順暢運作。
 如何在 Golang 中使用資料庫回呼函數?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 02:20 PM
如何在 Golang 中使用資料庫回呼函數?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 02:20 PM
在Golang中使用資料庫回呼函數可以實現:在指定資料庫操作完成後執行自訂程式碼。透過單獨的函數新增自訂行為,無需編寫額外程式碼。回調函數可用於插入、更新、刪除和查詢操作。必須使用sql.Exec、sql.QueryRow或sql.Query函數才能使用回呼函數。
 如何用 Golang 連接遠端資料庫?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 08:31 PM
如何用 Golang 連接遠端資料庫?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 08:31 PM
透過Go標準庫database/sql包,可以連接到MySQL、PostgreSQL或SQLite等遠端資料庫:建立包含資料庫連接資訊的連接字串。使用sql.Open()函數開啟資料庫連線。執行SQL查詢和插入操作等資料庫操作。使用defer關閉資料庫連線以釋放資源。
 如何在 Golang 中將 JSON 資料保存到資料庫中?
Jun 06, 2024 am 11:24 AM
如何在 Golang 中將 JSON 資料保存到資料庫中?
Jun 06, 2024 am 11:24 AM
可以透過使用gjson函式庫或json.Unmarshal函數將JSON資料儲存到MySQL資料庫中。 gjson函式庫提供了方便的方法來解析JSON字段,而json.Unmarshal函數需要一個目標類型指標來解組JSON資料。這兩種方法都需要準備SQL語句和執行插入操作來將資料持久化到資料庫中。
 如何使用C++處理資料庫連線和操作?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 07:24 PM
如何使用C++處理資料庫連線和操作?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 07:24 PM
在C++中使用DataAccessObjects(DAO)函式庫連接和操作資料庫,包括建立資料庫連線、執行SQL查詢、插入新記錄和更新現有記錄。具體步驟為:1.包含必要的函式庫語句;2.開啟資料庫檔案;3.建立Recordset物件執行SQL查詢或操作資料;4.遍歷結果或依照特定需求更新記錄。






