詳解Python使用PDFMiner解析PDF實例
本篇主要介紹了Python使用PDFMiner解析PDF程式碼實例,小編覺得蠻不錯的,現在分享給大家,也給大家做個參考。一起跟著小編過來看看吧
近期在做爬蟲時有時會遇到網站只提供pdf的情況,這樣就不能使用scrapy直接抓取頁面內容了,只能透過解析PDF的方式處理,目前的解決方案大致只有pyPDF和PDFMiner。因為據說PDFMiner更適合文本的解析,而我需要解析的正是文本,因此最後選擇使用PDFMiner(這也就意味著我對pyPDF一無所知了)。
首先說明的是解析PDF是非常蛋痛的事,即使是PDFMiner對於格式不工整的PDF解析效果也不怎麼樣,所以連PDFMiner的開發者都吐槽PDF is evil. 不過這些並不重要。
一.安裝:
1.先下載原始檔包pypi.python.org/pypi/pdfminer/,解壓,然後命令列安裝即可:python setup.py install
2.安裝完成後使用此命令列測試:pdf2txt.py samples/simple1.pdf,如果顯示以下內容則表示安裝成功:
Hello World Hello World H e l l o W o r l d H e l l o W o r l d
3.如果要使用中日韓文字則需要先編譯再安裝:
# make cmap python tools/conv_cmap.py pdfminer/cmap Adobe-CNS1 cmaprsrc/cid2code_Adobe_CNS1.txtreading 'cmaprsrc/cid2code_Adobe_CNS1.txt'...writing 'CNS1_H.py'......(this may take several minutes) # python setup.py install
二.使用
由於解析PDF是一件非常耗時且記憶體的工作,因此PDFMiner使用了一種稱作lazy parsing的策略,只在需要的時候才去解析,以減少時間和記憶體的使用。要解析PDF至少需要兩個類別:PDFParser 和 PDFDocument,PDFParser 從文件中提取數據,PDFDocument保存數據。另外還需要PDFPageInterpreter去處理頁面內容,PDFDevice將其轉換為我們所需要的。 PDFResourceManager用於保存共享內容例如字體或圖片。
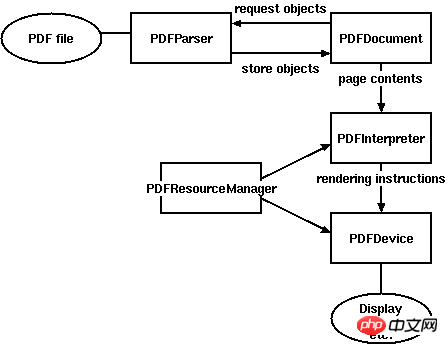
Figure 1. Relationships between PDFMiner classes
比較重要的是Layout,主要包含以下這些元件:
LTPage
Represents an entire page. May contain child objects like LTTextBox, LTFigure, LTImage, LTRect, LTCurve and LTLine.
LTTextBox
Represents a group of text chunks that can be contained rectangular area. Note that this box is created by geometric analysis and does not necessarily represents a logical boundary of the text. It contains a list of LTTextLine objects. get_text() methodcontents the text methodcontent#.
#Contains a list of LTChar objects that represent a single text line. The characters are aligned either horizontaly or vertically, depending on the text's writing mode. get_text() method returns the##LTAnno
Represent an actual letter in the text as a Unicode string. Note that, while a LTChar object has actual boundaries, LTAnno objects does not, as these are "virtual inacters, are "virtual" charby, are "virtual injjers, are" a layout analyzer according to the relationship between two characters (e.g. a space).
LTFigure
Represents an area used by PDF Form objects. PDF Forms can be . yet another PDF document within a page. Note that LTFigure objects can appear recursively.
LTImage
Represents an image object. Embedded images can be in JPEG ora curats Snats, 50,000 much attention to graphical objects.
LTLine
Represents a single straight line. Could be used for separating text or figures.
LTRect
##Represents a rectangle . Could be used for framing another pictures or figures.#LTCurveRepresents a generic Bezier curve.官方文档给了几个Demo但是都过于简略,虽然给了一个详细一些的Demo,但链接地址是旧的现在已经失效,不过最终还是找到了新的地址:denis.papathanasiou.org/posts/2010.08.04.post.html
这个Demo就比较详细了,源码如下:
#!/usr/bin/python
import sys
import os
from binascii import b2a_hex
###
### pdf-miner requirements
###
from pdfminer.pdfparser import PDFParser
from pdfminer.pdfdocument import PDFDocument, PDFNoOutlines
from pdfminer.pdfpage import PDFPage
from pdfminer.pdfinterp import PDFResourceManager, PDFPageInterpreter
from pdfminer.converter import PDFPageAggregator
from pdfminer.layout import LAParams, LTTextBox, LTTextLine, LTFigure, LTImage, LTChar
def with_pdf (pdf_doc, fn, pdf_pwd, *args):
"""Open the pdf document, and apply the function, returning the results"""
result = None
try:
# open the pdf file
fp = open(pdf_doc, 'rb')
# create a parser object associated with the file object
parser = PDFParser(fp)
# create a PDFDocument object that stores the document structure
doc = PDFDocument(parser, pdf_pwd)
# connect the parser and document objects
parser.set_document(doc)
# supply the password for initialization
if doc.is_extractable:
# apply the function and return the result
result = fn(doc, *args)
# close the pdf file
fp.close()
except IOError:
# the file doesn't exist or similar problem
pass
return result
###
### Table of Contents
###
def _parse_toc (doc):
"""With an open PDFDocument object, get the table of contents (toc) data
[this is a higher-order function to be passed to with_pdf()]"""
toc = []
try:
outlines = doc.get_outlines()
for (level,title,dest,a,se) in outlines:
toc.append( (level, title) )
except PDFNoOutlines:
pass
return toc
def get_toc (pdf_doc, pdf_pwd=''):
"""Return the table of contents (toc), if any, for this pdf file"""
return with_pdf(pdf_doc, _parse_toc, pdf_pwd)
###
### Extracting Images
###
def write_file (folder, filename, filedata, flags='w'):
"""Write the file data to the folder and filename combination
(flags: 'w' for write text, 'wb' for write binary, use 'a' instead of 'w' for append)"""
result = False
if os.path.isdir(folder):
try:
file_obj = open(os.path.join(folder, filename), flags)
file_obj.write(filedata)
file_obj.close()
result = True
except IOError:
pass
return result
def determine_image_type (stream_first_4_bytes):
"""Find out the image file type based on the magic number comparison of the first 4 (or 2) bytes"""
file_type = None
bytes_as_hex = b2a_hex(stream_first_4_bytes)
if bytes_as_hex.startswith('ffd8'):
file_type = '.jpeg'
elif bytes_as_hex == '89504e47':
file_type = '.png'
elif bytes_as_hex == '47494638':
file_type = '.gif'
elif bytes_as_hex.startswith('424d'):
file_type = '.bmp'
return file_type
def save_image (lt_image, page_number, images_folder):
"""Try to save the image data from this LTImage object, and return the file name, if successful"""
result = None
if lt_image.stream:
file_stream = lt_image.stream.get_rawdata()
if file_stream:
file_ext = determine_image_type(file_stream[0:4])
if file_ext:
file_name = ''.join([str(page_number), '_', lt_image.name, file_ext])
if write_file(images_folder, file_name, file_stream, flags='wb'):
result = file_name
return result
###
### Extracting Text
###
def to_bytestring (s, enc='utf-8'):
"""Convert the given unicode string to a bytestring, using the standard encoding,
unless it's already a bytestring"""
if s:
if isinstance(s, str):
return s
else:
return s.encode(enc)
def update_page_text_hash (h, lt_obj, pct=0.2):
"""Use the bbox x0,x1 values within pct% to produce lists of associated text within the hash"""
x0 = lt_obj.bbox[0]
x1 = lt_obj.bbox[2]
key_found = False
for k, v in h.items():
hash_x0 = k[0]
if x0 >= (hash_x0 * (1.0-pct)) and (hash_x0 * (1.0+pct)) >= x0:
hash_x1 = k[1]
if x1 >= (hash_x1 * (1.0-pct)) and (hash_x1 * (1.0+pct)) >= x1:
# the text inside this LT* object was positioned at the same
# width as a prior series of text, so it belongs together
key_found = True
v.append(to_bytestring(lt_obj.get_text()))
h[k] = v
if not key_found:
# the text, based on width, is a new series,
# so it gets its own series (entry in the hash)
h[(x0,x1)] = [to_bytestring(lt_obj.get_text())]
return h
def parse_lt_objs (lt_objs, page_number, images_folder, text=[]):
"""Iterate through the list of LT* objects and capture the text or image data contained in each"""
text_content = []
page_text = {} # k=(x0, x1) of the bbox, v=list of text strings within that bbox width (physical column)
for lt_obj in lt_objs:
if isinstance(lt_obj, LTTextBox) or isinstance(lt_obj, LTTextLine):
# text, so arrange is logically based on its column width
page_text = update_page_text_hash(page_text, lt_obj)
elif isinstance(lt_obj, LTImage):
# an image, so save it to the designated folder, and note its place in the text
saved_file = save_image(lt_obj, page_number, images_folder)
if saved_file:
# use html style <img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="'+os.path.join(images_folder, saved_file)+'" class="lazy" alt="詳解Python使用PDFMiner解析PDF實例" > tag to mark the position of the image within the text
text_content.append('<img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="'+os.path.join(images_folder, saved_file)+'" class="lazy" alt="詳解Python使用PDFMiner解析PDF實例" >')
else:
print >> sys.stderr, "error saving image on page", page_number, lt_obj.__repr__
elif isinstance(lt_obj, LTFigure):
# LTFigure objects are containers for other LT* objects, so recurse through the children
text_content.append(parse_lt_objs(lt_obj, page_number, images_folder, text_content))
for k, v in sorted([(key,value) for (key,value) in page_text.items()]):
# sort the page_text hash by the keys (x0,x1 values of the bbox),
# which produces a top-down, left-to-right sequence of related columns
text_content.append(''.join(v))
return '\n'.join(text_content)
###
### Processing Pages
###
def _parse_pages (doc, images_folder):
"""With an open PDFDocument object, get the pages and parse each one
[this is a higher-order function to be passed to with_pdf()]"""
rsrcmgr = PDFResourceManager()
laparams = LAParams()
device = PDFPageAggregator(rsrcmgr, laparams=laparams)
interpreter = PDFPageInterpreter(rsrcmgr, device)
text_content = []
for i, page in enumerate(PDFPage.create_pages(doc)):
interpreter.process_page(page)
# receive the LTPage object for this page
layout = device.get_result()
# layout is an LTPage object which may contain child objects like LTTextBox, LTFigure, LTImage, etc.
text_content.append(parse_lt_objs(layout, (i+1), images_folder))
return text_content
def get_pages (pdf_doc, pdf_pwd='', images_folder='/tmp'):
"""Process each of the pages in this pdf file and return a list of strings representing the text found in each page"""
return with_pdf(pdf_doc, _parse_pages, pdf_pwd, *tuple([images_folder]))
a = open('a.txt','a')
for i in get_pages('/home/jamespei/nova.pdf'):
a.write(i)
a.close()这段代码重点在于第128行,可以看到PDFMiner是一种基于坐标来解析的框架,PDF中能解析的组件全都包括上下左右边缘的坐标,如x0 = lt_obj.bbox[0]就是lt_obj元素的左边缘的坐标,同理x1则为右边缘。以上代码的意思就是把所有x0且x1的坐标相差在20%以内的元素分成一组,这样就实现了从PDF文件中定向抽取内容。
----------------补充--------------------
有一个需要注意的地方,在解析有些PDF的时候会报这样的异常:pdfminer.pdfdocument.PDFEncryptionError: Unknown algorithm: param={'CF': {'StdCF': {'Length': 16, 'CFM': /AESV2, 'AuthEvent': /DocOpen}}, 'O': '\xe4\xe74\xb86/\xa8)\xa6x\xe6\xa3/U\xdf\x0fWR\x9cPh\xac\xae\x88B\x06_\xb0\x93@\x9f\x8d', 'Filter': /Standard, 'P': -1340, 'Length': 128, 'R': 4, 'U': '|UTX#f\xc9V\x18\x87z\x10\xcb\xf5{\xa7\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00', 'V': 4, 'StmF': /StdCF, 'StrF': /StdCF}
从字面意思来看是因为这个PDF是一个加密的PDF,所以无法解析 ,但是如果直接打开PDF却是可以的并没有要求输密码什么的,原因是这个PDF虽然是加过密的,但密码是空,所以就出现了这样的问题。
解决这个的问题的办法是通过qpdf命令来解密文件(要确保已经安装了qpdf),要想在python中调用该命令只需使用call即可:
from subprocess import call
call('qpdf --password=%s --decrypt %s %s' %('', file_path, new_file_path), shell=True)其中参数file_path是要解密的PDF的路径,new_file_path是解密后的PDF文件路径,然后使用解密后的文件去做解析就OK了
以上是詳解Python使用PDFMiner解析PDF實例的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 Python vs.C:申請和用例
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs.C:申請和用例
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python适合数据科学、Web开发和自动化任务,而C 适用于系统编程、游戏开发和嵌入式系统。Python以简洁和强大的生态系统著称,C 则以高性能和底层控制能力闻名。
 Python:遊戲,Guis等
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python:遊戲,Guis等
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python在遊戲和GUI開發中表現出色。 1)遊戲開發使用Pygame,提供繪圖、音頻等功能,適合創建2D遊戲。 2)GUI開發可選擇Tkinter或PyQt,Tkinter簡單易用,PyQt功能豐富,適合專業開發。
 Python與C:學習曲線和易用性
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python與C:學習曲線和易用性
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python更易學且易用,C 則更強大但複雜。 1.Python語法簡潔,適合初學者,動態類型和自動內存管理使其易用,但可能導致運行時錯誤。 2.C 提供低級控制和高級特性,適合高性能應用,但學習門檻高,需手動管理內存和類型安全。
 Python和時間:充分利用您的學習時間
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python和時間:充分利用您的學習時間
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
要在有限的時間內最大化學習Python的效率,可以使用Python的datetime、time和schedule模塊。 1.datetime模塊用於記錄和規劃學習時間。 2.time模塊幫助設置學習和休息時間。 3.schedule模塊自動化安排每週學習任務。
 Python vs.C:探索性能和效率
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs.C:探索性能和效率
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python在開發效率上優於C ,但C 在執行性能上更高。 1.Python的簡潔語法和豐富庫提高開發效率。 2.C 的編譯型特性和硬件控制提升執行性能。選擇時需根據項目需求權衡開發速度與執行效率。
 Python:自動化,腳本和任務管理
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python:自動化,腳本和任務管理
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python在自動化、腳本編寫和任務管理中表現出色。 1)自動化:通過標準庫如os、shutil實現文件備份。 2)腳本編寫:使用psutil庫監控系統資源。 3)任務管理:利用schedule庫調度任務。 Python的易用性和豐富庫支持使其在這些領域中成為首選工具。
 Python標準庫的哪一部分是:列表或數組?
Apr 27, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Python標準庫的哪一部分是:列表或數組?
Apr 27, 2025 am 12:03 AM
pythonlistsarepartofthestAndArdLibrary,herilearRaysarenot.listsarebuilt-In,多功能,和Rused ForStoringCollections,而EasaraySaraySaraySaraysaraySaraySaraysaraySaraysarrayModuleandleandleandlesscommonlyusedDduetolimitedFunctionalityFunctionalityFunctionality。
 學習Python:2小時的每日學習是否足夠?
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
學習Python:2小時的每日學習是否足夠?
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
每天學習Python兩個小時是否足夠?這取決於你的目標和學習方法。 1)制定清晰的學習計劃,2)選擇合適的學習資源和方法,3)動手實踐和復習鞏固,可以在這段時間內逐步掌握Python的基本知識和高級功能。






