解析MySQL快取啟動方法及參數(query_cache_size)
MySQL query cache從4.1版本開始提供了,不過值今天本人才對其進行研究。預設設定下,MySQL的該功能是沒有啟動的,可能你透過show variables like '%query_cache%';會發現其變數have_query_cache的值是yes,MYSQL初學者很容易以為這個參數為YES就代表開啟了查詢快取#,實際上是不對的,該參數表示目前版本的MYSQL是否支援Query Cache,實際上是否開啟查詢快取是看另一個參數的值:query_cache_size ,值為0,表示停用query cache,而預設配置正是配置為0。
設定方法:
在MYSQL的設定檔my.ini或my.cnf中找到如下內容:
# Query cache is used to cache SELECT results and later return them
# without actual executing the same query once again. Having the query
# cache enabled may result in significant speed , if your
# have a lot of identical queries and rarely changing tables. See the
# “Qcache_lowmem_prunes” status variable to check if the current value
是 is high
#1110 71700 enough for your load.
# Note: In case your tables change very often or if your queries are
# textually different every time, the query cache may result in a
# slowdown instead of a performance improvement.
query_cache_size=0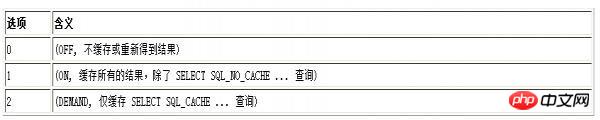
以上資訊是預設配置,其
註解
意思是說,MYSQL的查詢快取用於快取select查詢結果,並下次接收到同樣的查詢請求時,不再執行實際查詢處理而直接返回結果,有這樣的查詢快取能提高查詢的速度,使查詢效能得到最佳化,前提條件是你有大量的相同或相似的查詢,而很少改變表裡的數據,否則沒有必要使用此功能。可以透過Qcache_lowmem_prunes變數的值來檢查是否目前的值滿足你目前系統的負載。注意:如果你查詢的表格
更新
比較頻繁,而且很少有相同的查詢,最好不要使用查詢快取。
具體配置方法:
1.將query_cache_size設定為具體的大小,具體大小是多少取決於查詢的實際情況,但最好設定為1024的倍數,參考值32M。
2.增加一行:query_cache_type=1
query_cache_type參數用來控制快取的類型,注意這個值不能隨便設置,必須設定為數字,可選項目以及說明如下:
#如果設定為0,那麼可以說,你的快取根本就沒有用,相當於禁用了。但是這種情況下query_cache_size設定的大小系統是否要為其分配呢,這個問題有待測試?
如果設定為1,將會快取所有的結果,除非你的select語句使用SQL_NO_CACHE停用了查詢快取。
如果設定為2,則只快取在select語句中透過SQL_CACHE指定需要快取的查詢。
OK,配置完後的部分文件如下:
query_cache_size=128M
mysql> show variables like ‘%query_cache%'; +——————————+———–+ | Variable_name | Value | +——————————+———–+ | have_query_cache | YES | | query_cache_limit | 1048576 | | query_cache_min_res_unit | 4096 | | query_cache_size | 134217728 | | query_cache_type | ON | | query_cache_wlock_invalidate | OFF | +——————————+———–+ 6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show status like ‘%Qcache%'; +————————-+———–+ | Variable_name | Value | +————————-+———–+ | Qcache_free_blocks | 1 | | Qcache_free_memory | 134208800 | | Qcache_hits | 0 | | Qcache_inserts | 0 | | Qcache_lowmem_prunes | 0 | | Qcache_not_cached | 2 | | Qcache_queries_in_cache | 0 | | Qcache_total_blocks | 1 | +————————-+———–+ 8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
这里顺便解释下这个几个参数的作用:
Qcache_free_blocks:表示查询缓存中目前还有多少剩余的blocks,如果该值显示较大,则说明查询缓存中的内存碎片过多了,可能在一定的时间进行整理。
Qcache_free_memory:查询缓存的内存大小,通过这个参数可以很清晰的知道当前系统的查询内存是否够用,是多了,还是不够用,DBA可以根据实际情况做出调整。
Qcache_hits:表示有多少次命中缓存。我们主要可以通过该值来验证我们的查询缓存的效果。数字越大,缓存效果越理想。
Qcache_inserts: 表示多少次未命中然后插入,意思是新来的SQL请求在缓存中未找到,不得不执行查询处理,执行查询处理后把结果insert到查询缓存中。这样的情况的次数,次数越多,表示查询缓存应用到的比较少,效果也就不理想。当然系统刚启动后,查询缓存是空的,这很正常。
Qcache_lowmem_prunes:该参数记录有多少条查询因为内存不足而被移除出查询缓存。通过这个值,用户可以适当的调整缓存大小。
Qcache_not_cached: 表示因为query_cache_type的设置而没有被缓存的查询数量。
Qcache_queries_in_cache:当前缓存中缓存的查询数量。
Qcache_total_blocks:当前缓存的block数量。
下边我们测试下:
比如执行如下查询语句
mysql> select * from user where id = 2; +—-+——-+ | id | name | +—-+——-+ | 2 | test2 | +—-+——-+ 1 row in set (0.02 sec)
然后执行show status like ‘%Qcache%',看看有什么变化:
mysql> show status like ‘%Qcache%'; +————————-+———–+ | Variable_name | Value | +————————-+———–+ | Qcache_free_blocks | 1 | | Qcache_free_memory | 134207264 | | Qcache_hits | 0 | | Qcache_inserts | 1 | | Qcache_lowmem_prunes | 0 | | Qcache_not_cached | 3 | | Qcache_queries_in_cache | 1 | | Qcache_total_blocks | 4 | +————————-+———–+ 8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
对比前面的参数值,我们发现Qcache_inserts变化了。Qcache_hits没有变,下边我们在执行同样的查询
select * from user where id = 2,按照前面的理论分析:Qcache_hits应该等于1,而Qcache_inserts应该值不变(其他参数的值变化暂时不关注,读者可以自行测试),再次执行:
show status like ‘%Qcache%',看看有什么变化:
mysql> show status like ‘%Qcache%'; +————————-+———–+ | Variable_name | Value | +————————-+———–+ | Qcache_free_blocks | 1 | | Qcache_free_memory | 134207264 | | Qcache_hits | 1 | | Qcache_inserts | 1 | | Qcache_lowmem_prunes | 0 | | Qcache_not_cached | 4 | | Qcache_queries_in_cache | 1 | | Qcache_total_blocks | 4 | +————————-+———–+ 8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
OK,果然跟我们分析的完全一致。
以上是解析MySQL快取啟動方法及參數(query_cache_size)的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 MySQL:世界上最受歡迎的數據庫的簡介
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL:世界上最受歡迎的數據庫的簡介
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL是一種開源的關係型數據庫管理系統,主要用於快速、可靠地存儲和檢索數據。其工作原理包括客戶端請求、查詢解析、執行查詢和返回結果。使用示例包括創建表、插入和查詢數據,以及高級功能如JOIN操作。常見錯誤涉及SQL語法、數據類型和權限問題,優化建議包括使用索引、優化查詢和分錶分區。
 apache怎麼連接數據庫
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
apache怎麼連接數據庫
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Apache 連接數據庫需要以下步驟:安裝數據庫驅動程序。配置 web.xml 文件以創建連接池。創建 JDBC 數據源,指定連接設置。從 Java 代碼中使用 JDBC API 訪問數據庫,包括獲取連接、創建語句、綁定參數、執行查詢或更新以及處理結果。
 MySQL的位置:數據庫和編程
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL的位置:數據庫和編程
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL在數據庫和編程中的地位非常重要,它是一個開源的關係型數據庫管理系統,廣泛應用於各種應用場景。 1)MySQL提供高效的數據存儲、組織和檢索功能,支持Web、移動和企業級系統。 2)它使用客戶端-服務器架構,支持多種存儲引擎和索引優化。 3)基本用法包括創建表和插入數據,高級用法涉及多表JOIN和復雜查詢。 4)常見問題如SQL語法錯誤和性能問題可以通過EXPLAIN命令和慢查詢日誌調試。 5)性能優化方法包括合理使用索引、優化查詢和使用緩存,最佳實踐包括使用事務和PreparedStatemen
 為什麼要使用mysql?利益和優勢
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
為什麼要使用mysql?利益和優勢
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
選擇MySQL的原因是其性能、可靠性、易用性和社區支持。 1.MySQL提供高效的數據存儲和檢索功能,支持多種數據類型和高級查詢操作。 2.採用客戶端-服務器架構和多種存儲引擎,支持事務和查詢優化。 3.易於使用,支持多種操作系統和編程語言。 4.擁有強大的社區支持,提供豐富的資源和解決方案。
 MySQL的角色:Web應用程序中的數據庫
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
MySQL的角色:Web應用程序中的數據庫
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
MySQL在Web應用中的主要作用是存儲和管理數據。 1.MySQL高效處理用戶信息、產品目錄和交易記錄等數據。 2.通過SQL查詢,開發者能從數據庫提取信息生成動態內容。 3.MySQL基於客戶端-服務器模型工作,確保查詢速度可接受。
 docker怎麼啟動mysql
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
docker怎麼啟動mysql
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
在 Docker 中啟動 MySQL 的過程包含以下步驟:拉取 MySQL 鏡像創建並啟動容器,設置根用戶密碼並映射端口驗證連接創建數據庫和用戶授予對數據庫的所有權限
 laravel入門實例
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
laravel入門實例
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel 是一款 PHP 框架,用於輕鬆構建 Web 應用程序。它提供一系列強大的功能,包括:安裝: 使用 Composer 全局安裝 Laravel CLI,並在項目目錄中創建應用程序。路由: 在 routes/web.php 中定義 URL 和處理函數之間的關係。視圖: 在 resources/views 中創建視圖以呈現應用程序的界面。數據庫集成: 提供與 MySQL 等數據庫的開箱即用集成,並使用遷移來創建和修改表。模型和控制器: 模型表示數據庫實體,控制器處理 HTTP 請求。
 解決數據庫連接問題:使用minii/db庫的實際案例
Apr 18, 2025 am 07:09 AM
解決數據庫連接問題:使用minii/db庫的實際案例
Apr 18, 2025 am 07:09 AM
在開發一個小型應用時,我遇到了一個棘手的問題:需要快速集成一個輕量級的數據庫操作庫。嘗試了多個庫後,我發現它們要么功能過多,要么兼容性不佳。最終,我找到了minii/db,這是一個基於Yii2的簡化版本,完美地解決了我的問題。






