使用遊標資料
在一個遊標被開啟後,可以使用 FETCH 語句分別存取它的每一行。 FETCH 指定要檢索什麼資料(所需的欄位),檢索出來的資料儲存在什麼地方。它也會向前移動遊標中的內部行指針,使下一個 FETCH 語句檢索下一行(不重複讀取同一行)。
第一個範例從遊標中檢索單一行(第一行):
輸入:
create procedure processorders() BEGIN -- declare local variables declare o int; -- declare the cursor declare ordernumbers cursor for select order_num from orders: -- open the cursor open ordernumbers; -- get order number fetch ordernumbers into o; -- close the cursor close ordernumbers; end;
分析:其中FETCH 用來檢索目前行的order_num 欄位(將自動從第一行開始)到一個名為o 的局部宣告的變數。對檢索出的資料不做任何處理。
在下一個例子中,循環檢索數據,從第一行到最後一行:
輸入:
create procedure processorders() BEGIN -- declare local variables declare done boolean default 0; declare o int; -- declare the cursor declare ordernumbers cursor for select order_num from orders: --declare continue handler declare continue handler for sqlstate '02000' set done = 1; -- open the cursor open ordernumbers; --loop through all rows repeat -- get order number fetch ordernumbers into o; -- end of loop until done end repeat; -- close the cursor close ordernumbers; end;
分析:與前一個例子一樣,這個例子使用FETCH檢索目前order_num到宣告的名為o 的變數中。但與前一個例子不一樣的是,這個例子中的 FETCH 是在 REPEAT 內,因此它反覆執行直到 done 為真(由 UNTILdone END REPEAT; 規定)。為使它起作用,用一個 DEFAULT 0 (假,不結束)定義變數 done 。那麼, done 怎樣才能在結束時被設定為真呢?答案是用以下語句:
declare continue handler for sqlstate '02000' set done = 1;
這條語句定義了一個 CONTINUE HANDLER ,它是在條件出現時被執行的程式碼。這裡,它指出當 SQLSTATE '02000' 出現時, SET done=1。 SQLSTATE '02000' 是一個找不到條件,當 REPEAT 因為沒有更多的行供循環而不能繼續時,就會出現這個條件。
MySQL的錯誤代碼 關於MySQL 5所使用的MySQL錯誤代碼列表,請參考http://dev.mysql.com/doc/mysql/en/error-handling.html。
DECLARE 語句的次序 DECLARE 語句的發布存在特定的次序。用 DECLARE 語句定義的局部變數必須在定義任意遊標或句柄之前定義,而句柄必須在遊標之後定義。不遵守此順序將產生錯誤訊息。
如果呼叫這個預存程序,它將定義幾個變數和一個 CONTINUE HANDLER ,定義並開啟一個遊標,重複讀取所有行,然後關閉遊標。如果一切正常,你可以在迴圈內放入任意需要的處理(在 FETCH 語句之後,迴圈結束前)。
重複或循環? 除這裡使用的 REPEAT 語句外,MySQL還支援循環語句,它可用來重複執行程式碼,直到使用 LEAVE 語句手動退出為止。通常 REPEAT 語句的語法使它更適合於對遊標進行循環。
為了把這些內容組織起來,下面給出我們的遊標儲存過程範例的更進一步修改的版本,這次對取出的資料進行某種實際的處理:
輸入:
create procedure processorders() BEGIN -- declare local variables declare done boolean default 0; declare o int; declare t decimal(8,2); -- declare the cursor declare ordernumbers cursor for select order_num from orders; -- declare continue handler declare continue handler for sqlstate '02000' set done = 1; -- create a table to store the results create table if not exists ordertotals (order_num int, total decimal(8,2)); -- open the cursor open ordernumbers; -- loop through all rows repeat -- get order number fetch ordernumbers into o; -- get the total for this order call ordertotal(o,1,t); -- insert order and total into ordertotals insert into ordertotals(order_num,total) values(o,t); -- end of loop until done end repeat; -- close the cursor close ordernumbers; END;
分析:在這個例子中,我們增加了另一個名為t 的變數(儲存每個訂單的總和)。此預存程序還在運行中建立了一個新表(如果它不存在的話),名為 ordertotals 。這個表將保存儲存過程產生的結果。 FETCH像以前一樣取每個 order_num ,然後用 CALL 執行另一個預存程序(我們在前一章中建立)來計算每個訂單的帶稅的合計(結果儲存到 t )。最後,用 INSERT 保存每個訂單的訂單號碼和總和。
此預存程序不會傳回數據,但它能夠建立和填入另一個表,可以用一條簡單的SELECT 語句查看該表:
輸入:
select * from ordertotals;
輸出:
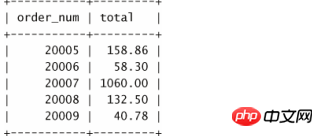
這樣,我們就得到了預存程序、遊標、逐行處理以及預存程序呼叫其他預存程序的一個完整的工作範例。
以上是MySQL使用遊標資料實例教程的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




