一、struts2是什麼
1.概念
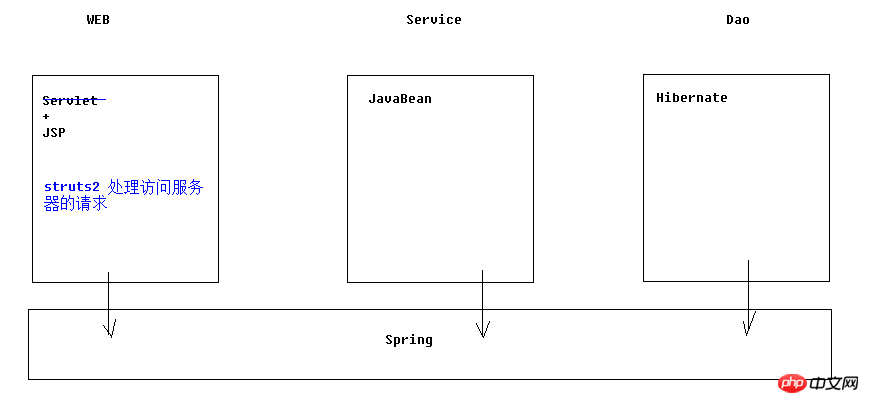
# 2.struts2使用優勢以及歷史
# 
二、建造struts2框架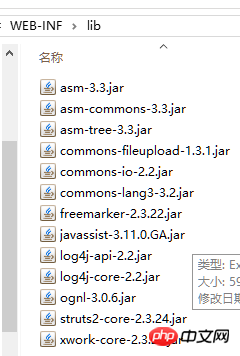
1.導包

 (解壓縮)struts2-blank.war就會看到
(解壓縮)struts2-blank.war就會看到
2.書寫Action類別
 #
#public class HelloAction {public String hello(){
System.out.println("hello world!"); return "success";
}
}3.書寫src/struts.xml (記得加上dtd約束)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd"><struts><package name="hello" namespace="/hello" extends="struts-default" ><action name="HelloAction" class="cn.itheima.a_hello.HelloAction" method="hello" ><result name="success" type="dispatcher" >/hello.jsp</result></action></package></struts>
filter-class記不住可以ctrl+shift+t 輸入strutsPre來找出全類別名稱
#
<!-- struts2核心过滤器 --> <filter> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping>
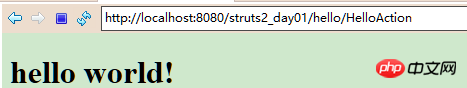
View Code# 5.測試
#
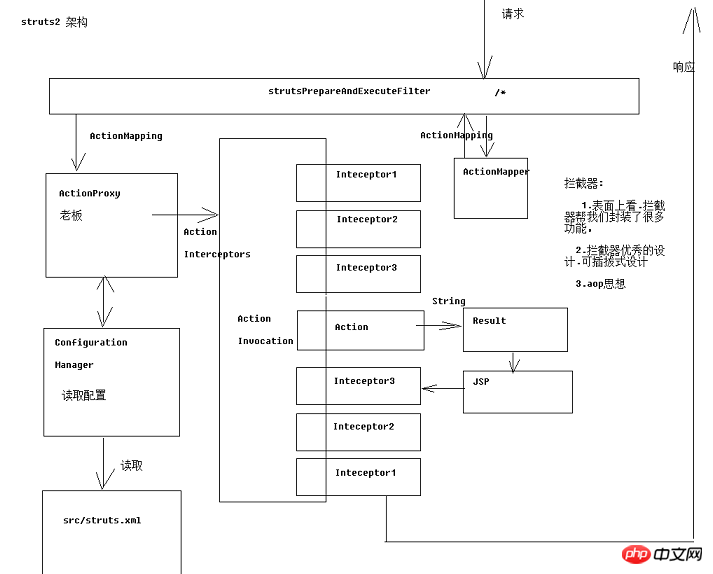
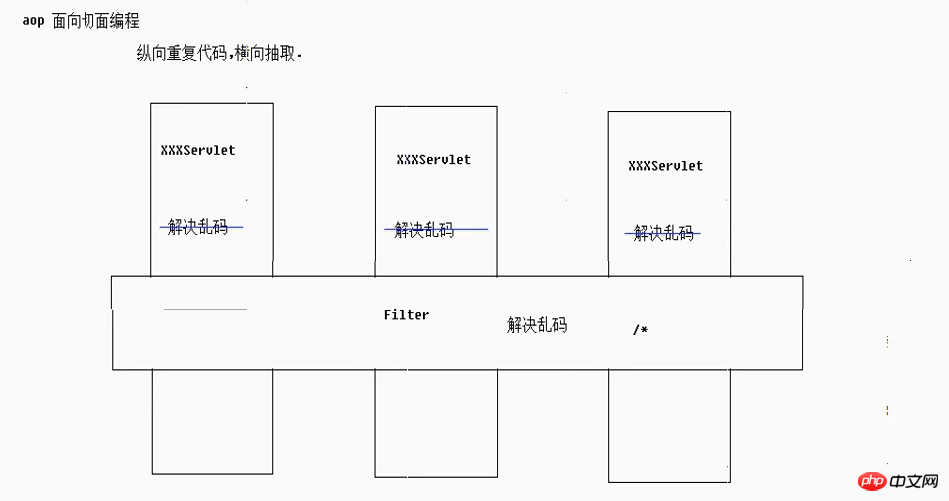
1.struts2架構
#
2.Aop程式設計(面向切面)
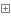
 #
四、設定詳解
#
四、設定詳解

###1.struts.xml設定詳解###################
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd"><struts><!-- i18n:国际化. 解决post提交乱码 --><constant name="struts.i18n.encoding" value="UTF-8"></constant><!-- 指定反问action时的后缀名
http://localhost:8080/struts2_day01/hello/HelloAction.do--><constant name="struts.action.extension" value="action"></constant><!-- 指定struts2是否以开发模式运行
1.热加载主配置.(不需要重启即可生效)
2.提供更多错误信息输出,方便开发时的调试 --><constant name="struts.devMode" value="true"></constant><!-- package:将Action配置封装.就是可以在Package中配置很多action.
name属性: 给包起个名字,起到标识作用.随便起.不能其他包名重复.
namespace属性:给action的访问路径中定义一个命名空间
extends属性: 继承一个 指定包
abstract属性:包是否为抽象的; 标识性属性.标识该包不能独立运行.专门被继承 --><package name="hello" namespace="/hello" extends="struts-default" ><!-- action元素:配置action类
name属性: 决定了Action访问资源名.
class属性: action的完整类名
method属性: 指定调用Action中的哪个方法来处理请求 --><action name="HelloAction" class="cn.itheima.a_hello.HelloAction" method="hello" ><!-- result元素:结果配置
name属性: 标识结果处理的名称.与action方法的返回值对应.
type属性: 指定调用哪一个result类来处理结果,默认使用转发.
标签体:填写页面的相对路径--><result name="success" type="dispatcher" >/hello.jsp</result></action></package><!-- 引入其他struts配置文件 --><include file="cn/itheima/b_dynamic/struts.xml"></include><include file="cn/itheima/c_default/struts.xml"></include></struts><!-- i18n:国际化. 解决post提交乱码 --> <constant name="struts.i18n.encoding" value="UTF-8"></constant>
struts.i18n.encoding=UTF8
<context-param> <param-name>struts.i18n.encoding</param-name> <param-value>UTF-8</param-value> </context-param>
顺序:

2.3 常量配置
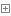
<!-- i18n:国际化. 解决post提交乱码 --><constant name="struts.i18n.encoding" value="UTF-8"></constant><!-- 指定反问action时的后缀名
http://localhost:8080/struts2_day01/hello/HelloAction.do--><constant name="struts.action.extension" value="action"></constant><!-- 指定struts2是否以开发模式运行
1.热加载主配置.(不需要重启即可生效)
2.提供更多错误信息输出,方便开发时的调试 --><constant name="struts.devMode" value="true"></constant>3.struts2配置的进阶
3.1动态方法调用(重要)
<!-- 配置动态方法调用是否开启常量
默认是关闭的,需要开启 --><constant name="struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation" value="true"></constant>
<!-- 动态方法调用方式2:通配符方式
使用{1} 取出第一个星号通配的内容 --><action name="Demo1Action_*" class="cn.itheima.b_dynamic.Demo1Action" method="{1}" ><result name="success" >/hello.jsp</result></action>3.2struts2中的默认配置(了解)
<package name="default" namespace="/default" extends="struts-default" ><!-- 找不到包下的action,会使用Demo2Action作为默认action处理请求 --><default-action-ref name="Demo2Action"></default-action-ref><!-- method属性:execute --><!-- result的name属性:success --><!-- result的type属性:dispatcher 转发 --><!-- class属性:com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport --><action name="Demo2Action" ><result >/hello.jsp</result></action></package>
五、action类详解
Action类的书写方式
//方式1: 创建一个类.可以是POJO//POJO:不用继承任何父类.也不需要实现任何接口.//使struts2框架的代码侵入性更低.public class Demo3Action {
}
//方式2: 实现一个接口Action// 里面有execute方法,提供action方法的规范.// Action接口预置了一些字符串.可以在返回结果时使用.为了方便public class Demo4Action implements Action {
@Overridepublic String execute() throws Exception {return null;
}
}
//方式3: 继承一个类.ActionSupport// 帮我们实现了 Validateable, ValidationAware, TextProvider, LocaleProvider .//如果我们需要用到这些接口的实现时,不需要自己来实现了.public class Demo5Action extends ActionSupport{
}
六、练习:客户列表
图解:

实现:
public class CustomerAction extends ActionSupport {private CustomerService cs = new CustomerServiceImpl(); public String list() throws Exception {//1 接受参数String cust_name = ServletActionContext.getRequest().getParameter("cust_name");//2 创建离线查询对象DetachedCriteria dc =DetachedCriteria.forClass(Customer.class);//3 判断参数拼装条件if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(cust_name)){
dc.add(Restrictions.like("cust_name", "%"+cust_name+"%"));
}//4 调用Service将离线对象传递List<Customer> list = cs.getAll(dc);//5 将返回的list放入request域.转发到list.jsp显示ServletActionContext.getRequest().setAttribute("list", list);return "list";
}
}

public List<Customer> getAll(DetachedCriteria dc) {
Session session = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession();//打开事务Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
List<Customer> list = customerDao.getAll(dc); //关闭事务 tx.commit();return list;
}
public List<Customer> getAll(DetachedCriteria dc) {//1 获得sessionSession session = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession();//2 将离线对象关联到sessionCriteria c = dc.getExecutableCriteria(session);//3 执行查询并返回return c.list();
}
以上是struts2是什麼?如何使用?的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




