詳解JavaScript基於物件導向之繼承_javascript技巧
1. Object inheritance mechanism
This example uses UML to explain the inheritance mechanism very well.
The simplest way to illustrate the inheritance mechanism is to use a classic example of geometric shapes. In fact, there are only two types of geometric shapes, ellipses (which are circular) and polygons (which have a certain number of sides). A circle is a type of ellipse that has only one focus. Triangles, rectangles, and pentagons are all types of polygons with varying numbers of sides. A square is a type of rectangle with all sides of the same length. This constitutes a perfect inheritance relationship and explains the object-oriented inheritance mechanism well.
In this example, the shape is the base class of ellipse and polygon (usually we can also call it the parent class, and all classes inherit from it). The ellipse has a foci, which indicates the number of foci the ellipse has. Circle inherits from ellipse, so circle is a subclass of ellipse and ellipse is the superclass of circle. Likewise, triangles, rectangles, and pentagons are all subclasses of polygon, which is their superclass. Finally, the square inherits the rectangle.
It is best to use a diagram to explain this inheritance relationship, which is where UML (Unified Modeling Language) comes in. One of the main uses of UML is to visually represent complex object relationships like inheritance. The following diagram is a UML diagram explaining the relationship between a shape and its subclasses:
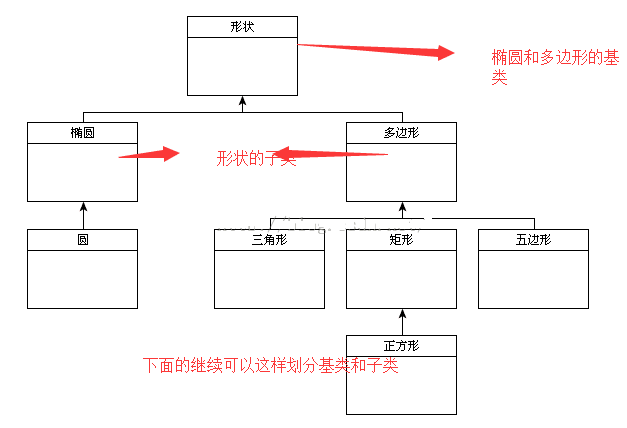
In UML, each box represents a class, described by the class name. The line segments at the top of triangles, rectangles, and pentagons come together to point to shapes, indicating that these classes inherit from shapes. Likewise, the arrow pointing from the square to the rectangle illustrates the inheritance relationship between them.
2. Implementation of ECMAScript inheritance mechanism
To implement the inheritance mechanism with ECMAScript, you can start with the base class you want to inherit from. All developer-defined classes can serve as base classes. For security reasons, native and host classes cannot serve as base classes. This prevents public access to compiled browser-level code that could be used for malicious attacks.
After selecting the base class, you can create its subclasses. It's entirely up to you whether to use a base class or not. Sometimes, you may want to create a base class that cannot be used directly, but is only used to provide common functions to subclasses. In this case, the base class is considered an abstract class. Although ECMAScript does not define abstract classes as strictly as other languages, it does sometimes create classes that are not allowed to be used. Usually, we call this class an abstract class.
The created subclass will inherit all properties and methods of the superclass, including the implementation of constructors and methods. Remember, all properties and methods are public, so subclasses can access these methods directly. Subclasses can also add new properties and methods that are not found in the superclass, or they can override properties and methods of the superclass. Since JS is not an orthodox object-oriented language, some nouns also need to be changed.
3. ECMAScript inheritance methods
In the ECMAScript language, the inherited class (base class) is called a supertype, and the subclass (or derived class) is called a subtype. As with other features, ECMAScript implements inheritance in more than one way. This is because the inheritance mechanism in JavaScript is not explicitly specified, but implemented through imitation. This means that not all inheritance details are entirely handled by the interpreter. As the developer, you have the right to decide the inheritance method that works best for you. Here are some specific inheritance methods for you.
(1) Prototype chain method
This form of inheritance was originally used for the prototype chain in ECMAScript. The previous blog post has introduced the prototype method of creating objects. Prototype chains extend this approach to implement the inheritance mechanism in an interesting way. The prototype object is a template, and the objects to be instantiated are based on this template. In summary, any properties and methods of the prototype object are passed to all instances of that class. The prototype chain utilizes this functionality to implement the inheritance mechanism. Let’s look at an example:
function A() {//超类型A中必须没有参数
this.color = "red";
this.showColor = function () {
return this.color;
};
};
function B() {//子类型B
this.name = "John";
this.showName = function () {
return this.name;
};
};
B.prototype = new A();//子类型B继承了超类型A,通过原型,形成链条
var a = new A();
var b = new B();
document.write(a.showColor());//输出:blue
document.write(b.showColor());//输出:red
document.write(b.showName());//输出:John
In the prototype chain, the instanceof operator also operates in a unique way. For all instances of B, instanceof returns true for both A and B. This is an extremely useful tool in the weakly typed world of ECMAScript, but it cannot be used when using object impersonation. For example:
var b = new B(); document.write(b instanceof A);//输出:true document.write(b instanceof B);//输出:true
使用原型链方式实现了继承,但是这种方式无法共享和子类型给超类型传递参数。我们可以借用构造函数方式(也就是对像冒充)的方式来解决这两个问题。
(2)对象冒充方式
对象冒充方式的其原理如下:构造函数使用this关键字给所有属性和方法赋值(即采用对象声明的构造函数方式)。因为构造函数只是一个函数,所以可使A构造函数成为B的方法,然后调用它。B就会收到A的构造函数中定义的属性和方法。例如,用下面的方式改写上面的例子创建对象A和B:
call()方法
function A(Color) {//创建超类型A
this.color = Color;
this.showColor = function () {
return this.color;
};
};
function B(Color,Name) {//创建子类型B
A.call(this, Color);//对象冒充,给超类型传参
this.name = Name;//新添加的属性
this.showName =
};
var a = new A("blue");
var b = new B("red", "John");
document.write(a.showColor());//输出:blue
document.write(b.showColor());//输出:red
document.write(b.showName());//输出:John
apply()方法
和上面call()方法唯一的区别就是在子类型B中的代码:
A.call(this,arguments);//对象冒充,给超类型传参
当然,只有超类型中的参数顺序与子类型中的参数顺序完全一致时才可以传递参数对象。如果不是,就必须创建一个单独的数组,按照正确的顺序放置参数。
使用对象冒充方式虽然解决了共享和传参的问题,但是没有原型,复用就更不可能了,所以我们组合上述的两种方式,即原型链方式和对象冒充的方式实现JS的继承。
(3)混合方式
这种继承方式使用构造函数定义类,并非使用任何原型。对象冒充的主要问题是必须使用构造函数方式,这不是最好的选择。不过如果使用原型链,就无法使用带参数的构造函数了。开发者如何选择呢?答案很简单,两者都用。由于这种混合方式使用了原型链,所以instanceof运算符仍能正确运行。
在上一篇文章,创建对象的最好方式是用构造函数定义属性,用原型定义方法。这种方式同样适用于继承机制,用对象冒充继承构造函数的属性,用原型链继承prototype对象的方法。用这两种方式重写前面的例子,代码如下:
function A(Color) {
this.color = Color;
};
A.prototype.showColor = function () {
return this.color;
};
function B(Color, Name) {
A.call(this, Color);//对象冒充
this.name = Name;
};
B.prototype = new A();//使用原型链继承
B.prototype.showName = function () {
return this.name;
};
var a = new A("blue");
var b = new B("red", "John");
document.write(a.showColor());//输出:blue
document.write(b.showColor());//输出:red
document.write(b.showName());//输出:John
继承的方式和创建对象的方式有一定的联系,推荐使用的继承方式还时原型链和对象冒充的混合方式。使用这种混合方式可以避免一些不必要的问题。
看这篇文章的时候,必须看一下前面的创建对象的方式:详解JavaScript基于面向对象之创建对象(1)和详解JavaScript基于面向对象之创建对象(2)。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助。

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

AI Hentai Generator
免費產生 AI 無盡。

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)

熱門話題
 C++ 函式繼承詳解:如何在繼承中使用「基底類別指標」和「衍生類別指標」?
May 01, 2024 pm 10:27 PM
C++ 函式繼承詳解:如何在繼承中使用「基底類別指標」和「衍生類別指標」?
May 01, 2024 pm 10:27 PM
在函數繼承中,使用「基底類別指標」和「衍生類別指標」來理解繼承機制:基底類別指標指向派生類別物件時,執行向上轉型,只存取基底類別成員。派生類別指標指向基底類別物件時,執行向下轉型(不安全),必須謹慎使用。
 C++ 中繼承和多態性如何影響類別的耦合度?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 02:33 PM
C++ 中繼承和多態性如何影響類別的耦合度?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 02:33 PM
繼承和多態性會影響類別的耦合度:繼承會增加耦合度,因為衍生類別依賴基底類別。多態性可以降低耦合度,因為物件可以透過虛擬函數和基底類別指標以一致的方式回應訊息。最佳實踐包括謹慎使用繼承、定義公共介面、避免在基底類別中新增資料成員,以及透過依賴注入解耦類別。實戰案例顯示如何使用多態性和依賴注入來降低銀行帳戶應用程式中的耦合度。
 探索Go語言中的物件導向編程
Apr 04, 2024 am 10:39 AM
探索Go語言中的物件導向編程
Apr 04, 2024 am 10:39 AM
Go語言支援物件導向編程,透過型別定義和方法關聯實作。它不支援傳統繼承,而是透過組合實現。介面提供了類型間的一致性,允許定義抽象方法。實戰案例展示如何使用OOP管理客戶訊息,包括建立、取得、更新和刪除客戶操作。
 C++ 函式繼承詳解:如何偵錯繼承中出現的錯誤?
May 02, 2024 am 09:54 AM
C++ 函式繼承詳解:如何偵錯繼承中出現的錯誤?
May 02, 2024 am 09:54 AM
繼承錯誤調試技巧:確保正確的繼承關係。使用偵錯器逐步執行程式碼,檢查變數值。確保正確使用virtual修飾符。檢查隱藏的繼承帶來的菱形繼承問題。檢查抽象類別中未實現的純虛函數。
 PHP高階特性:物件導向程式設計的最佳實踐
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:39 PM
PHP高階特性:物件導向程式設計的最佳實踐
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:39 PM
PHP中OOP最佳實務包括命名約定、介面與抽象類別、繼承與多型、依賴注入。實戰案例包括:使用倉庫模式管理數據,使用策略模式實現排序。
 Go語言的物件導向特性解析
Apr 04, 2024 am 11:18 AM
Go語言的物件導向特性解析
Apr 04, 2024 am 11:18 AM
Go語言支援物件導向編程,透過struct定義對象,使用指標接收器定義方法,並透過介面實現多態。物件導向特性在Go語言中提供了程式碼重用、可維護性和封裝,但也存在缺乏傳統類別和繼承的概念以及方法簽章強制型別轉換的限制。
 C++ 函式繼承詳解:如何理解繼承中的「is-a」與「has-a」關係?
May 02, 2024 am 08:18 AM
C++ 函式繼承詳解:如何理解繼承中的「is-a」與「has-a」關係?
May 02, 2024 am 08:18 AM
C++函式繼承詳解:掌握「is-a」和「has-a」關係什麼是函式繼承?函數繼承是C++中一種將衍生類別中定義的方法與基底類別中定義的方法關聯起來的技術。它允許衍生類別存取和重寫基底類別的方法,從而擴展了基底類別的功能。 「is-a」和「has-a」關係在函數繼承中,「is-a」關係指派生類別是基底類別的子類型,也就是說,衍生類別「繼承」了基底類別的特性和行為。 「has-a」關係指派生類別包含對基底類別物件的參考或指針,也就是說,衍生類別「擁有」了基底類別物件。語法以下是如何實作函數繼承的語法:classDerivedClass:pu
 Golang中有類似類別的物件導向特性嗎?
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:51 PM
Golang中有類似類別的物件導向特性嗎?
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:51 PM
在Golang(Go語言)中並沒有傳統意義上的類別的概念,但它提供了一種稱為結構體的資料類型,透過結構體可以實現類似類別的物件導向特性。在本文中,我們將介紹如何使用結構體實現物件導向的特性,並提供具體的程式碼範例。結構體的定義和使用首先,讓我們來看看結構體的定義和使用方式。在Golang中,結構體可以透過type關鍵字定義,然後在需要的地方使用。結構體中可以包含屬






