sql映射檔的實例教程
Sql映射檔案
MyBatis 真正的力量是在映射語句中。和對等功能的jdbc來比價,映射文件節省很多的代碼量。 MyBatis的建構就是聚焦在sql的。
sql映射檔有以下幾個頂層元素:(依序)
cache配置給定命名空間的快取。
cache-ref從其他命名空間引用快取配置。
resultMap最複雜,也是最有力量的元素,用來描述如何從資料庫結果集中來載入你的物件。
parameterMap已經被廢棄了!老式風格的參數映射。內聯參數是首選,這個元素可能在將來被移除。
sql可以重複使用的SQL區塊,也可以被其他語句引用。
insert映射插入語句。
update映射更新語句。
delete映射刪除語句。
select映射查詢語句。
MyBatis的建構就是聚焦在SQL的,使其遠離於普通的方式。
SQL映射檔案有很少的幾個頂層元素(按照它們應該被定義的順序):
>mapper:映射檔案的根元素節點,只有一個屬性namespace命名空間,用於區分不同的mapper,全域唯一,namespace綁定的DAO介面全名稱,即面向介面程式設計。這裡的mapper就相當於介面的實作類別。
cache - 設定給定命名空間的快取。
cache-ref – 從其他命名空間引用快取配置。
resultMap – 最複雜,也是最有力量的元素,用來描述如何從資料庫結果集中來載入你的物件。
parameterMap – 已經被廢棄了!老式風格的參數映射。內聯參數是首選,這個元素可能在將來被移除。這裡不會記錄。
sql – 可以重複使用的SQL區塊,也可以被其他語句引用。
insert – 映射插入語句
update – 映射更新語句
delete – 映射刪除語句
select – 映射查詢語句
一:使用select完成但條件查詢
使用工具idea和mysql資料庫
建立實體類別
public class student {private int stuId;private String stuName;private grade getGrade;private int stuAge;public grade getGetGrade() {return getGrade;
}public void setGetGrade(grade getGrade) {this.getGrade = getGrade;
}public int getStuAge() {return stuAge;
} public student(int id,String name){
} public student(){}public void setStuAge(int stuAge) {this.stuAge = stuAge;
}public int getStuId() {return stuId;
}public void setStuId(int stuId) {this.stuId = stuId;
}public String getStuName() {return stuName;
}public void setStuName(String stuName) {this.stuName = stuName;
}
}使用select完成條件查詢
一:先設定mapper使用resultType
<!--模糊查询 使用resultType返回结果集-->
<select id="getAllStudentByLike" parameterType="String" resultType="stu">* from student where stuName like CONCAT('%',#{stuName},'%'</select>
測試類別
public void Test() throws IOException {
studentDao dao = MyBatis.getSessionTwo().getMapper(studentDao.class);
List<student> list = dao.getAllStudentByLike("z");for (student item:list) {
System.out.println("----------"+item.getStuName());
}
}#另外parameterType支援的複雜型別除了javaBean之外,還包括Map類型
即修改Mapper
<!--模糊查询-->
<select id="getAllStudentByLike" parameterType="Map" resultType="stu">select * from student where stuName like CONCAT('%',#{stuName},'%')</select>
然後再測試類別裡建立一個HashMap集合直接作為方法參數即可
studentDao dao = MyBatis.getSessionTwo().getMapper(studentDao.class);
Map<String,String> userMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
userMap.put("stuName","z");
List<student> list = dao.getAllStudentByLike(userMap);for (student item:list) {
System.out.println("----------"+item.getStuName());
}不過map集合的key值必須和類別中的欄位名稱相同。
二:使用resultMap完成兩表查詢
例如學生表裡關聯班級表的主鍵id,如果使用resultType只能展示其id但在實際中往往關注的是班級名稱,所有需要使用resultMap映射自訂結果。
<resultMap id="studentMap" type="entity.student"> <id property="stuId" column="stuId"></id> <result property="stuName" column="stuName"></result> <result property="gradeName" column="gradeName"> </resultMap> //sql语句
select * from student,grade
resultType直接表示傳回類型,包含基礎型別和複雜資料型別
resultMap則是對外部resultMap的引用,對應resultMap的id 表示回傳結果對應到哪一個resultMap。 :他的應用場景是:資料庫欄位資訊與物件屬性不一致或需要做複雜的聯合查詢以便自由控制映射結果 。
另外在 MyBatis的select元素中,resultType和resultMap本質上是一樣的,都是Map資料結構。但是 二者不能同時 存在。
三:使用resultMap的自動對映等級
MyBatis中分為三個對應等級
>NONE:禁止自動符合
>PARTIAL;NONE:禁止自動符合
>PARTIAL :(預設):自動符合所有屬性有內部巢狀(association,collection)的除外
>FULL:自動符合所有
<settings> <!--设置resultMap的自动映射级别为Full(自动匹配所有)--><setting name="autoMappingBehavior" value="FULL" /> <!--FULL要大写··--> </settings>
設定autoMappingBehavior的值為FULL時就不需要設定resultMap下的節點,他會根據資料庫自動比對
四:使用update完成修改
<update id="update">update student set stuName=#{0} where stuId=#{1}</update>
這裡使用佔位符比較簡單的一種作為參數,在測試類別中就直接填參就行了
五:使用映射複雜類型的屬性association
前面的result只能對應到javaBean的某個「簡單類型」屬性,基礎資料類型和包裝類別等/
stuAge; 。。。。。省略封装
<resultMap id="studentMap" type="entity.student"> <!-- <id property="stuId" column="stuId"></id> <result property="stuName" column="stuName"></result>--> <!--关联另一个 属性--> <association property="getGrade" javaType="grade"> <!-- <id property="gradeId" javaType="Integer" column="gradeId"></id> <result property="gradeName" javaType="String" column="gradeName"></result>--> </association> </resultMap> <!--这里使用了自动匹配-->
<select id="getAllStudent" resultMap="studentMap"> SELECT * FROM student,grade WHERE student.stuGrade=grade.gradeId</select>
测试类里直接调用即可
六:前面说到association仅处理一对一的管理关系
如果要处理一对多的关系,则需要使用collection,它与 association元素差不多,但它映射的属性是一个集合列表,即javaBean内部嵌套一个复杂数据类型属性。
javaBean
private int gradeId;private String gradeName;private List<student> gatStudent;
<resultMap id="gradeMap" type="grade"> <!--<id property="gradeId" column="gradeId"></id> <result property="gradeName" column="gradeName"></result>--> <collection property="gatStudent" ofType="stu"> <!-- <id property="stuId" column="stuId"></id> <result property="stuName" column="stuName"></result>--> </collection> </resultMap>
<!--查询对应年级的student--> <select id="getAll" resultMap="gradeMap"> select * from student,grade where stuGrade = gradeId and gradeId=1 </select>
以上是sql映射檔的實例教程的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

AI Hentai Generator
免費產生 AI 無盡。

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)

熱門話題
 微信檔案過期怎麼恢復 微信的過期檔案能恢復嗎
Feb 22, 2024 pm 02:46 PM
微信檔案過期怎麼恢復 微信的過期檔案能恢復嗎
Feb 22, 2024 pm 02:46 PM
開啟微信,在我中選擇設置,選擇通用後選擇儲存空間,在儲存空間選擇管理,選擇要恢復檔案的對話選擇感嘆號圖示。教學適用型號:iPhone13系統:iOS15.3版本:微信8.0.24解析1先開啟微信,在我的頁面中點選設定選項。 2接著在設定頁面中找到並點選通用選項。 3然後在通用頁面中點選儲存空間。 4接下來在儲存空間頁面中點選管理。 5最後選擇要恢復檔案的對話,點選右側的感嘆號圖示。補充:微信文件一般幾天過期1要是微信接收的文件並沒有點開過的情況下,那在七十二鐘頭之後微信系統會清除掉,要是己經查看了微信
 照片無法開啟此文件,因為格式不受支援或文件已損壞
Feb 22, 2024 am 09:49 AM
照片無法開啟此文件,因為格式不受支援或文件已損壞
Feb 22, 2024 am 09:49 AM
在Windows系統中,照片應用程式是一個方便的方式來檢視和管理照片和影片。透過這個應用程序,用戶可以輕鬆存取他們的多媒體文件,而無需安裝額外的軟體。然而,有時用戶可能會碰到一些問題,例如在使用照片應用程式時遇到「無法開啟此文件,因為不支援該格式」的錯誤提示,或在嘗試開啟照片或影片時出現文件損壞的問題。這種情況可能會讓使用者感到困惑和不便,需要進行一些調查和修復來解決這些問題。當用戶嘗試在Photos應用程式上開啟照片或影片時,會看到以下錯誤。抱歉,照片無法開啟此文件,因為目前不支援該格式,或該文件
 可以刪除Tmp格式檔案嗎?
Feb 24, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
可以刪除Tmp格式檔案嗎?
Feb 24, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
Tmp格式檔案是一種暫存檔案格式,通常由電腦系統或程式在執行過程中產生。這些文件的目的是儲存臨時數據,以幫助程式正常運行或提高效能。一旦程式執行完成或電腦重啟,這些tmp檔案往往就沒有了存在的必要性。所以,對於Tmp格式檔案來說,它們本質上是可以刪除的。而且,刪除這些tmp檔案能夠釋放硬碟空間,確保電腦的正常運作。但是,在刪除Tmp格式檔案之前,我們需
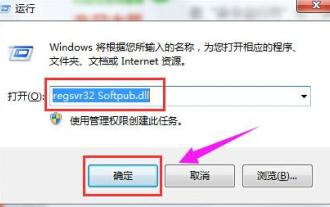 出現0x80004005錯誤代碼怎麼辦 小編教你0x80004005錯誤代碼解決方法
Mar 21, 2024 pm 09:17 PM
出現0x80004005錯誤代碼怎麼辦 小編教你0x80004005錯誤代碼解決方法
Mar 21, 2024 pm 09:17 PM
在電腦中刪除或解壓縮資料夾,時有時會彈出提示對話框“錯誤0x80004005:未指定錯誤”,如果遇到這中情況應該怎麼解決呢?提示錯誤碼0x80004005的原因其實很多,但大部分因為病毒導致,我們可以重新註冊dll來解決問題,下面,小編給大夥講解0x80004005錯誤代碼處理經驗。有使用者在使用電腦時出現錯誤代碼0X80004005的提示,0x80004005錯誤主要是由於電腦沒有正確註冊某些動態連結庫文件,或電腦與Internet之間存在不允許的HTTPS連接防火牆所引起。那麼如何
 夸克網盤的檔案怎麼轉移到百度網盤?
Mar 14, 2024 pm 02:07 PM
夸克網盤的檔案怎麼轉移到百度網盤?
Mar 14, 2024 pm 02:07 PM
夸克網盤和百度網盤都是現在最常用的儲存文件的網盤軟體,如果想要將夸克網盤內的文件保存到百度網盤,要怎麼操作呢?本期小編整理了夸克網盤電腦端的檔案轉移到百度網盤的教學步驟,一起來看看是怎麼操作吧。 夸克網盤的檔案怎麼存到百度網盤?要將夸克網盤的文件轉移到百度網盤,首先需在夸克網盤下載所需文件,然後在百度網盤用戶端中選擇目標資料夾並開啟。接著,將夸克網盤中下載的檔案拖放到百度網盤用戶端開啟的資料夾中,或使用上傳功能將檔案新增至百度網盤。確保上傳完成後在百度網盤中查看檔案是否已成功轉移。這樣就
 如何安裝GHO文件
Feb 19, 2024 pm 10:06 PM
如何安裝GHO文件
Feb 19, 2024 pm 10:06 PM
gho檔案是一種GhostImage影像文件,它通常用於將整個硬碟或分割區的資料備份成一個檔案。在一些特定的情況下,我們需要將這種gho檔案重新安裝回硬碟上,以還原硬碟或分割區到先前的狀態。下面將介紹gho檔案的安裝方法。首先,在安裝之前,我們需要準備以下工具和材料:實體的gho文件:確保你擁有一份完整的gho文件,它通常以.gho為後綴名,並且包含有備份
 hiberfil.sys是什麼檔案? hiberfil.sys可以刪除嗎?
Mar 15, 2024 am 09:49 AM
hiberfil.sys是什麼檔案? hiberfil.sys可以刪除嗎?
Mar 15, 2024 am 09:49 AM
最近有很多網友問小編,hiberfil.sys是什麼文件? hiberfil.sys佔用了大量的C碟空間可以刪除嗎?小編可以告訴大家hiberfil.sys檔是可以刪除的。下面就來看看詳細的內容。 hiberfil.sys是Windows系統中的隱藏文件,也是系統休眠文件。通常儲存在C盤根目錄下,其大小與系統安裝記憶體大小相當。這個檔案在電腦休眠時被使用,其中包含了當前系統的記憶體數據,以便在恢復時快速恢復到先前的狀態。由於其大小與記憶體容量相等,因此它可能會佔用較大的硬碟空間。 hiber
 斜線和反斜線在檔案路徑中的不同使用
Feb 26, 2024 pm 04:36 PM
斜線和反斜線在檔案路徑中的不同使用
Feb 26, 2024 pm 04:36 PM
檔案路徑是作業系統中用於識別和定位檔案或資料夾的字串。在檔案路徑中,常見的有兩種符號分隔路徑,即正斜線(/)和反斜線()。這兩個符號在不同的作業系統中有不同的使用方式和意義。正斜線(/)是Unix和Linux系統中常用的路徑分隔符號。在這些系統中,檔案路徑是以根目錄(/)為起始點,每個目錄之間使用正斜線進行分隔。例如,路徑/home/user/Docume






