js的簡寫寫法介紹
最近很火的一篇來自國外的文章,js的簡寫寫法一定程度上可以提高你的js書寫水平對於js的理解也會更近一步
原文鏈接,最近很火的一篇文章
This really is a must read for any JavaScript-based developer. I have written this article as a vital source of reference for learning shorthand JavaScript coding techniques that I have picked upearning shorthand JavaScript coding techniques that I have picked up over the years. To help you understand what is going on I have included the longhand versions to give some coding perspective.
#這篇文章對於任何基於javascript開發人員是必須要看的文章了,我寫這文章是學習多年來我所熟悉的JavaScript 簡寫方法,為幫助大家學習理解特整理了一些非簡寫的寫法。
June 14th, 2017: This article was updated to add new shorthand tips based on ES6. If you want to learn more about the changes in ES6, sign up for SitePoint Lookmium and check out Look the changes in ES6, sign up for SitePoint Lookmium and check out Lookmium and checkto inmourium and check out Lookm ESs
1.三元運算子
當想寫if...else語句時,使用三元運算子來取代。
普通寫法:
const x = 20;
let answer;
if (x > 10) {
answer = 'is greater';
} else {
answer = 'is lesser';
}簡寫:
const answer = x > 10 ? 'is greater' : 'is lesser';
也可以嵌套if語句:
const big = x > 10 ? " greater 10" : x
2.短路求值簡寫方式
當給一個變數分配另一個值時,想確定來源始值不是null,undefined或空值。可以寫出寫一個多重條件的if語句。
if (variable1 !== null || variable1 !== undefined || variable1 !== '') {
let variable2 = variable1;
}或可以使用短路求值方法:
const variable2 = variable1 || 'new';
3.宣告變數簡寫方法
let x; let y; let z = 3;
簡寫方法:
let x, y, z=3;
4.if存在條件簡寫方法
if (likeJavaScript === true)
簡寫:
if (likeJavaScript)
只有likeJavaScript是真值時,二者語句才相等
如果判斷值不是真值,可以這樣:
##
let a;
if ( a !== true ) {
// do something...
}let a;
if ( !a ) {
// do something...
}5.JavaScript循環簡寫方法
for (let i = 0; i < allImgs.length; i++)
for (let index in allImgs)
Array .forEach:
function logArrayElements(element, index, array) {
console.log("a[" + index + "] = " + element);
}
[2, 5, 9].forEach(logArrayElements);
// logs:
// a[0] = 2
// a[1] = 5
// a[2] = 96.短路評估
給一個變數分配的值是透過判斷其值是否為null或undefined,則可以:
#
let dbHost;
if (process.env.DB_HOST) {
dbHost = process.env.DB_HOST;
} else {
dbHost = 'localhost';
}##
const dbHost = process.env.DB_HOST || 'localhost';
for (let i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) {}for (let i = 0; i < 1e7; i++) {}
// 下面都是返回true
1e0 === 1;
1e1 === 10;
1e2 === 100;
1e3 === 1000;
1e4 === 10000;
1e5 === 100000;const obj = { x:x, y:y };const obj = { x, y };#9.箭頭函數簡寫傳統函數編寫方法很容易讓人理解和編寫,但是當嵌套在另一個函數中,則這些優勢就蕩然無存。
function sayHello(name) {
console.log('Hello', name);
}
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('Loaded')
}, 2000);
list.forEach(function(item) {
console.log(item);
});
#
sayHello = name => console.log('Hello', name); setTimeout(() => console.log('Loaded'), 2000); list.forEach(item => console.log(item));
10.隱含回傳值簡寫
#經常使用return語句來傳回函數最終結果,一個單獨語句的箭頭函數能隱含回傳其值(函數必須省略
{}為了省略
return關鍵字)
表達式),則需要使用()包圍函數體。
function calcCircumference(diameter) {
return Math.PI * diameter
}
var func = function func() {
return { foo: 1 };
};#
calcCircumference = diameter => (
Math.PI * diameter;
)
var func = () => ({ foo: 1 });function volume(l, w, h) {
if (w === undefined)
w = 3;
if (h === undefined)
h = 4;
return l * w * h;
}volume = (l, w = 3, h = 4 ) => (l * w * h); volume(2) //output: 24
12.模板字串
#傳統的JavaScript語言,輸出模板通常是這樣寫的。const welcome = 'You have logged in as ' + first + ' ' + last + '.' const db = 'http://' + host + ':' + port + '/' + database;
${}
簡寫:const welcome = `You have logged in as ${first} ${last}`;
const db = `http://${host}:${port}/${database}`;const observable = require('mobx/observable'); const action = require('mobx/action'); const runInAction = require('mobx/runInAction'); const store = this.props.store; const form = this.props.form; const loading = this.props.loading; const errors = this.props.errors; const entity = this.props.entity;
import { observable, action, runInAction } from 'mobx';
const { store, form, loading, errors, entity } = this.props;const { store, form, loading, errors, entity:contact } = this.props;
//最后一个变量名为contactconst lorem = 'Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur\n\t' + 'adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt\n\t' + 'ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim\n\t' + 'veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris\n\t' + 'nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute\n\t' + 'irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse.\n\t'
const lorem = `Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse.`
15.扩展运算符简写
扩展运算符有几种用例让JavaScript代码更加有效使用,可以用来代替某个数组函数。
// joining arrays const odd = [1, 3, 5]; const nums = [2 ,4 , 6].concat(odd); // cloning arrays const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]; const arr2 = arr.slice()
简写:
// joining arrays const odd = [1, 3, 5 ]; const nums = [2 ,4 , 6, ...odd]; console.log(nums); // [ 2, 4, 6, 1, 3, 5 ] // cloning arrays const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]; const arr2 = [...arr];
不像concat()函数,可以使用扩展运算符来在一个数组中任意处插入另一个数组。
const odd = [1, 3, 5 ]; const nums = [2, ...odd, 4 , 6];
也可以使用扩展运算符解构:
const { a, b, ...z } = { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3, d: 4 };
console.log(a) // 1
console.log(b) // 2
console.log(z) // { c: 3, d: 4 }16.强制参数简写
JavaScript中如果没有向函数参数传递值,则参数为undefined。为了增强参数赋值,可以使用if语句来抛出异常,或使用强制参数简写方法。
function foo(bar) {
if(bar === undefined) {
throw new Error('Missing parameter!');
}
return bar;
}简写:
mandatory = () => {
throw new Error('Missing parameter!');
}
foo = (bar = mandatory()) => {
return bar;
}17.Array.find简写
想从数组中查找某个值,则需要循环。在ES6中,find()函数能实现同样效果。
const pets = [
{ type: 'Dog', name: 'Max'},
{ type: 'Cat', name: 'Karl'},
{ type: 'Dog', name: 'Tommy'},
]
function findDog(name) {
for(let i = 0; i<pets.length; ++i) {
if(pets[i].type === 'Dog' && pets[i].name === name) {
return pets[i];
}
}
}简写:
pet = pets.find(pet => pet.type ==='Dog' && pet.name === 'Tommy');
console.log(pet); // { type: 'Dog', name: 'Tommy' }18.Object[key]简写
考虑一个验证函数
function validate(values) {
if(!values.first)
return false;
if(!values.last)
return false;
return true;
}
console.log(validate({first:'Bruce',last:'Wayne'})); // true假设当需要不同域和规则来验证,能否编写一个通用函数在运行时确认?
// 对象验证规则
const schema = {
first: {
required:true
},
last: {
required:true
}
}
// 通用验证函数
const validate = (schema, values) => {
for(field in schema) {
if(schema[field].required) {
if(!values[field]) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
console.log(validate(schema, {first:'Bruce'})); // false
console.log(validate(schema, {first:'Bruce',last:'Wayne'})); // true现在可以有适用于各种情况的验证函数,不需要为了每个而编写自定义验证函数了
19.双重非位运算简写
有一个有效用例用于双重非运算操作符。可以用来代替Math.floor(),其优势在于运行更快,可以阅读此文章了解更多位运算。
Math.floor(4.9) === 4 //true
简写
~~4.9 === 4 //true
到此就完成了相关的介绍,推荐大家继续看下面的相关文章
以上是js的簡寫寫法介紹的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 wapi是什麼東西詳細介紹
Jan 07, 2024 pm 09:14 PM
wapi是什麼東西詳細介紹
Jan 07, 2024 pm 09:14 PM
wapi這個名詞使用者可能在使用網路得時候見過過,但是對於一部分人來說肯定都不知道wapi是什麼,下面就帶來了詳細介紹,幫助不知道小伙伴去了解。 wapi是什麼東西:答:wapi是無線區域網路鑑別和保密的基礎架構。這就像紅外線和藍牙等功能一樣,一般都覆蓋在辦公大樓等地方的附近。基本上都是為一個小部門所有的,所以這個功能涉及的範圍只有幾公里。 wapi相關介紹:1、wapi是無線區域網路裡面的一種傳輸協定。 2.這款技術是可以去避免窄頻帶通訊的問題,可以更好的去進行傳播。 3.只要只需要一個代碼就可以去傳送訊號了
 詳解win11能否運行PUBG遊戲
Jan 06, 2024 pm 07:17 PM
詳解win11能否運行PUBG遊戲
Jan 06, 2024 pm 07:17 PM
pubg又稱絕地求生,是一款非常經典的射擊大逃殺類型遊戲,從2016年火爆以來一直擁有非常多的玩家。在最近的win11系統推出後,就有不少玩家想要在win11上游玩它,下面就跟著小編來看看win11是否可以玩pubg吧。 win11能玩pubg嗎:答:win11可以玩pubg。 1.在win11推出之初,因為win11需要開啟tpm的緣故,所以導致很多玩家被pubg封號處理了。 2.不過後來根據玩家的回饋,藍洞方面已經解決了這個問題,目前已經可以在win11中正常玩pubg了。 3.如果大家遇到了pub
 i5處理器是否能裝win11詳細介紹
Dec 27, 2023 pm 05:03 PM
i5處理器是否能裝win11詳細介紹
Dec 27, 2023 pm 05:03 PM
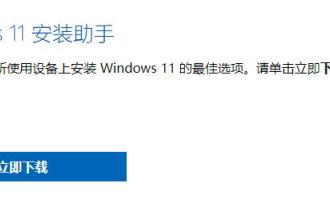
i5是英特爾旗下的一系列處理器,擁有到現在11代i5的各種不同版本,每一代都有不同效能。因此對於i5處理器是否能夠安裝win11,還要看是第幾代的處理器,下面就跟著小編一起來分別了解一下吧。 i5處理器能裝win11嗎:答:i5處理器能裝win11。一、第八代及之後的i51、第八代及後續的i5處理器是能夠滿足微軟的最低配置需求的。 2.因此我們只需要進入微軟網站,下載一個「win11安裝助手」3、下載完成後,運行該安裝助手,根據提示進行操作就可以安裝win11了。二、第八代之前的i51、第八代之
 介紹最新的Win 11聲音調法方法
Jan 08, 2024 pm 06:41 PM
介紹最新的Win 11聲音調法方法
Jan 08, 2024 pm 06:41 PM
很多用戶更新了最新的win11之後發現自己系統的聲音有了些許的變化,但是又不知道該怎麼去進行調整,所以今天本站就給你們帶來了電腦最新win11聲音調法介紹,操作不難而且選擇多樣,快來一起下載試試吧。電腦最新系統windows11聲音如何調1、先右鍵點選桌面右下角的聲音圖標,並選擇「播放設定」。 2、然後進入設定中點選播放列中的「揚聲器」。 3、隨後點選右下方的「屬性」。 4.點選屬性中的「增強」選項列。 5.此時如果「禁用所有聲音效果」前的√勾上了就把他取消。 6、之後就可以選擇下面的聲音效果來進行設定並點
 簡易JavaScript教學:取得HTTP狀態碼的方法
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
簡易JavaScript教學:取得HTTP狀態碼的方法
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript教學:如何取得HTTP狀態碼,需要具體程式碼範例前言:在Web開發中,經常會涉及到與伺服器進行資料互動的場景。在與伺服器進行通訊時,我們經常需要取得傳回的HTTP狀態碼來判斷操作是否成功,並根據不同的狀態碼來進行對應的處理。本篇文章將教你如何使用JavaScript來取得HTTP狀態碼,並提供一些實用的程式碼範例。使用XMLHttpRequest
 什麼是狗狗幣
Apr 01, 2024 pm 04:46 PM
什麼是狗狗幣
Apr 01, 2024 pm 04:46 PM
狗狗幣是一種基於網路迷因創建的加密貨幣,沒有固定的供應上限,交易時間快速,交易費用低,擁有龐大的迷因社群。用途包括小額交易、打賞和慈善捐贈。然而,其無限供應量、市場波動和作為笑話幣的地位也帶來風險和擔憂。什麼是狗狗幣?狗狗幣是一種基於網路迷因和笑話創建的加密貨幣。起源與歷史:2013年12月,兩位軟體工程師BillyMarkus和JacksonPalmer創立狗狗幣。靈感來自於當時流行的"Doge"模因,一個以一隻柴犬為特徵的滑稽照片加上破碎英語。特徵與優勢:無限供應量:與比特幣等其他加密貨
 PyCharm新手指南:取代功能全面解析
Feb 25, 2024 am 11:15 AM
PyCharm新手指南:取代功能全面解析
Feb 25, 2024 am 11:15 AM
PyCharm是一款功能強大的Python整合開發環境,具有豐富的功能與工具,能夠大幅提升開發效率。其中,替換功能是開發過程中常用的功能之一,能夠幫助開發者快速修改程式碼並提高程式碼品質。本文將詳細介紹PyCharm的替換功能,並結合具體的程式碼範例,幫助新手更好地掌握和使用該功能。替換功能簡介PyCharm的替換功能可以幫助開發者在程式碼中快速替換指定的文本
 詳細介紹電腦中的印表機驅動程式位置
Jan 08, 2024 pm 03:29 PM
詳細介紹電腦中的印表機驅動程式位置
Jan 08, 2024 pm 03:29 PM
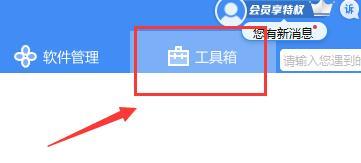
許多用戶在電腦上安裝了印表機驅動程序,但卻不知道如何找到它們。因此,今天我為大家帶來了詳細介紹印表機驅動程式在電腦中的位置,對於還不了解的用戶,快來看看吧印表機驅動在電腦哪裡找重新撰寫內容而不改變原義時,需要將語言改寫為中文,不需要出現原句首先,建議使用第三方軟體進行搜尋2、在右上角找到"工具箱"3、在下方找到並點選「裝置管理員」。改寫後的句子:3、在底部找到並點擊“裝置管理員”4、然後打開“列印佇列”,然後找到你的印表機裝置。此次是你的印表機名稱型號。 5.右鍵印表機設備,就能夠去更新或卸載我






