開始學習AngularJS表單驗證:
常用的表單驗證指令
1. 必填項驗證
某個表單輸入是否已填寫,只要在輸入欄位元素上新增HTML5標記required即可:
驗證表單輸入的文字長度是否大於某個最小值,在輸入欄位上使用指令ng-minleng= "{number}":
驗證表單輸入的文字長度是否小於或等於某個最大值,在輸入欄位上使用指令ng-maxlength="{number}":
使用ng-pattern="/PATTERN/"來確保輸入能夠符合指定的正規表示式:
驗證輸入內容是否為電子郵件,只要像下面這樣將input的類型設定為email即可:
驗證輸入內容是否為URL,將input的類型設定為 url:
在测试中我们发现,只有当表达式满足验证,才会实时进行双向绑定。同时我们也发现,效果图如下:
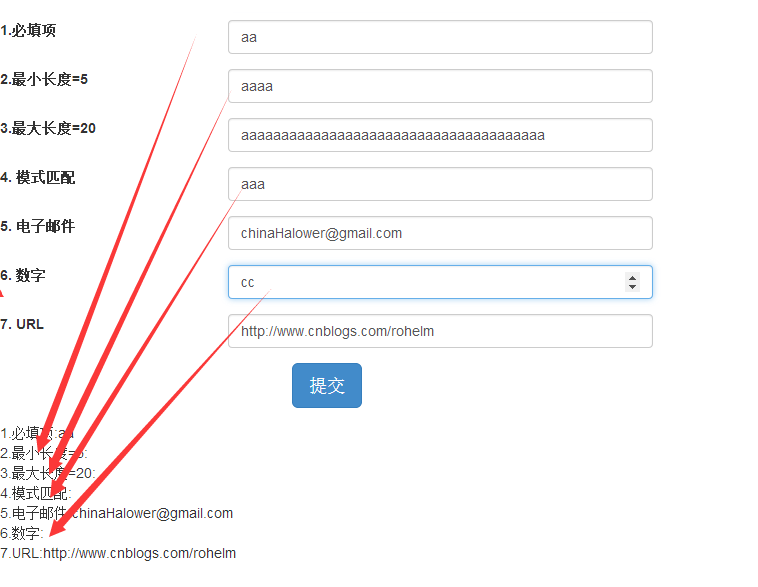
似乎并没有发生什么问题,但是如果我们将其移植到一个队HTML5验证不怎么好的浏览器再来测试一下【本例IE9】,问题来了,某些字段完全没得验证
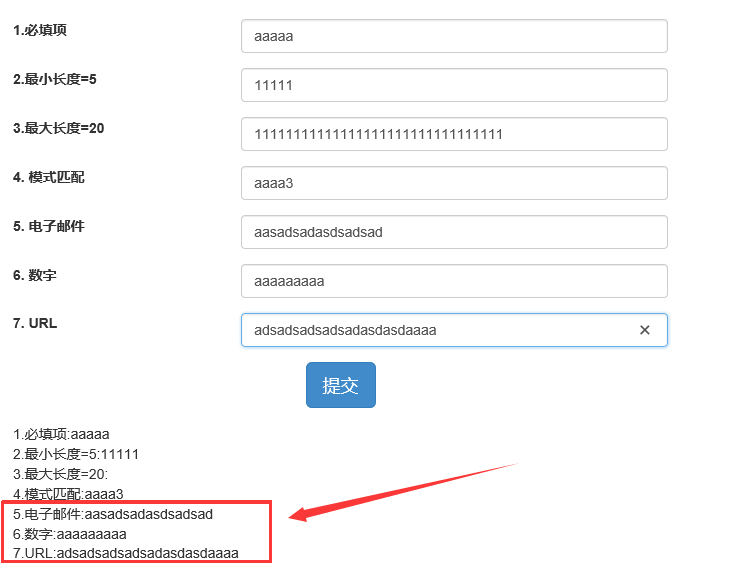
其实,上面的例子,我们利用了HTML5的验证与ng自有的验证进行了结合,不支持HTML5验证,但ng自由验证运行良好。解决方案很简单,可以使用模式匹配的方式解决这几种情况,也可以自定义验证指令来复写或者重定义验证规则。
屏蔽浏览器对表单的默认验证行为
在表单元素上添加novalidate标记即可,问题是我们怎么知道我们的表单有哪些字段是有效的,那些事非法或者无效的?ng对此也提供了非常棒的解决方案,表单的属性可以在其所属的$scope对象中访问到,而我们又可以访问$scope对象,因此JavaScript可以间接地访问DOM中的表单属性。借助这些属性,我们可以对表单做出实时响应。
可以使用formName.inputFieldName.property的格式访问这些属性。
未修改过的表单
布尔值属性,表示用户是否修改了表单。如果为ture,表示没有修改过;false表示修改过formName.inputFieldName.$pristine;
修改的表单
布尔型属性,当且仅当用户实际已经修改的表单。不管表单是否通过验证:formName.inputFieldName.$dirty
经过验证的表单
布尔型属性,它指示表单是否通过验证。如果表单当前通过验证,他将为true:formName.inputFieldName.$valid
未通过验证的表单:formName.inputFieldName.$invalid
最后两个属性在用于DOM元素的显示或隐藏时是特别有用的。同时,如果要设置特定的class时,他们也非常有用的。
错误
这是AngularJS提供的另外一个非常有用的属性:$error对象。它包含当前表单的所有验证内容,以及它们是否合法的信息。用下面的语法访问这个属性
formName.inputfieldName.$error
如果验证失败,这个属性的值为true;如果值为false,说明输入字段的值通过了验证。
下面我们对这些验证指令进行测试:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html ng-app="myTest">
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
<title>Index</title>
<link href="~/Content/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<script src="~/Javascript/angular.min.js"> </script>
<style type="text/css">
body { padding-top: 30px; }
</style>
</head>
<body ng-Controller="MyController">
<div class="col-md-6">
<form role="form" name="myForm" ng-submit="submitForm(myForm.$valid)" class="form-horizontal" novalidate>
<div class="form-group has-feedback">
<div class="col-md-4">
<label for="name">1.必填项</label>
</div>
<div class="col-md-8">
<input class="form-control" id="name" name="name" type="text" required ng-model='user.name' />
<span class="glyphicon glyphicon-ok form-control-feedback"
ng-show="myForm.name.$dirty && myForm.name.$valid"></span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-feedback">
<div class="col-md-4">
<label for="minlength">2.最小长度=5</label>
</div>
<div class="col-md-8">
<input type="text" id="minlength" name="minlength" ng-minlength="5" ng-model="user.minlength" class="form-control" />
<span class="glyphicon glyphicon-ok form-control-feedback"
ng-show="myForm.minlength.$dirty && myForm.minlength.$valid"></span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-feedback">
<div class="col-md-4">
<label for="maxlength">3.最大长度=20</label>
</div>
<div class="col-md-8">
<input type="text" id="maxlength" name="maxlength" ng-model="user.maxlength" ng-maxlength="20" class="form-control" />
<span class="glyphicon glyphicon-ok form-control-feedback"
ng-show="myForm.maxlength.$dirty && myForm.maxlength.$valid"></span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-feedback">
<div class="col-md-4">
<label for="pattern">4. 模式匹配</label>
</div>
<div class="col-md-8">
<input type="text" id="pattern" name="pattern" ng-model="user.pattern" ng-pattern="/^[a-zA-Z]*\d$/" class="form-control" />
<span class="glyphicon glyphicon-ok form-control-feedback"
ng-show="myForm.pattern.$dirty && myForm.pattern.$valid"></span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-feedback">
<div class="col-md-4">
<label for="email">5. 电子邮件</label>
</div>
<div class="col-md-8">
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" ng-model="user.email" class="form-control" />
<span class="glyphicon glyphicon-ok form-control-feedback"
ng-show="myForm.email.$dirty && myForm.email.$valid"></span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-feedback">
<div class="col-md-4">
<label for="age">6. 数字</label>
</div>
<div class="col-md-8">
<input type="number" id="age" name="age" ng-model="user.age" class="form-control" />
<span class="glyphicon glyphicon-ok form-control-feedback"
ng-show="myForm.age.$dirty && myForm.age.$valid"></span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-feedback">
<div class="col-md-4">
<label for="url"> 7. URL</label>
</div>
<div class="col-md-8">
<input type="url" id="url" name="url" ng-model="user.url" class="form-control" />
<span class="glyphicon glyphicon-ok form-control-feedback"
ng-show="myForm.url.$dirty && myForm.url.$valid"></span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group text-center">
<input class="btn btn-primary btn-lg" ng-disabled="myForm.$invalid" type="submit" value="提交" />
</div>
</form>
</div>
<div class="col-md-12">
1.必填项:{{user.name}}
$pristine 【没修改】:{{myForm.name.$pristine }}
$dirty【修改过】:{{myForm.name.$dirty}}
$invalid【验证失败】:{{myForm.name.$invalid}}
$invalid【验证成功】:{{myForm.name.$valid}}
required:{{myForm.name.$error.required}}
<br>
2.最小长度=5:{{user.minlength}}
$pristine 【没修改】:{{myForm.minlength.$pristine }}
$dirty【修改过】:{{myForm.minlength.$dirty}}
$invalid【验证失败】:{{myForm.minlength.$invalid}}
$invalid【验证成功】:{{myForm.minlength.$valid}}
$error【错误详情】:{{myForm.minlength.$error}} <br>
3.最大长度=20:{{user.maxlength}}
$pristine 【没修改】:{{myForm.maxlength.$pristine }}
$dirty【修改过】:{{myForm.maxlength.$dirty}}
$invalid【验证失败】:{{myForm.maxlength.$invalid}}
$invalid【验证成功】:{{myForm.maxlength.$valid}}
$error【错误详情】:{{myForm.maxlength.$error}} <br>
4.模式匹配:{{user.pattern}}
$pristine 【没修改】:{{myForm.pattern.$pristine }}
$dirty【修改过】:{{myForm.pattern.$dirty}}
$invalid【验证失败】:{{myForm.pattern.$invalid}}
$invalid【验证成功】:{{myForm.pattern.$valid}}
$error【错误详情】:{{myForm.pattern.$error}} <br>
5.电子邮件:{{user.email}}
$pristine 【没修改】:{{myForm.email.$pristine }}
$dirty【修改过】:{{myForm.email.$dirty}}
$invalid【验证失败】:{{myForm.email.$invalid}}
$invalid【验证成功】:{{myForm.email.$valid}}
$error【错误详情】:{{myForm.email.$error}} <br>
6.数字:{{user.age}}
$pristine 【没修改】:{{myForm.age.$pristine }}
$dirty【修改过】:{{myForm.age.$dirty}}
$invalid【验证失败】:{{myForm.age.$invalid}}
$invalid【验证成功】:{{myForm.age.$valid}}
$error【错误详情】:{{myForm.age.$error}} <br>
7.URL:{{user.url}}
$pristine 【没修改】:{{myForm.url.$pristine }}
$dirty【修改过】:{{myForm.url.$dirty}}
$invalid【验证失败】:{{myForm.url.$invalid}}
$invalid【验证成功】:{{myForm.url.$valid}}
$error【错误详情】:{{myForm.url.$error}} <br>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<script type="text/javascript">
angular.module('myTest', [])
.controller('myController', function($scope) {
$scope.submitForm = function(isValid) {
if (!isValid) {
alert('验证失败');
}
};
}
);
</script>
效果如下:

同时,ng针对这几种验证指令,针对性的设置了一些css样式
它们包括:
.ng-valid { }
.ng-invalid { }
.ng-pristine { }
.ng-dirty { }
/* really specific css rules applied by angular */
.ng-invalid-required { }
.ng-invalid-minlength { }
.ng-valid-max-length { }
它们对应着表单输入字段的特定状态。
例如当某个字段中的输入非法时,.ng-invlid类会被添加到这个字段上。 你可以编辑自己喜欢的CSS . 你可以私有定制化这些类来实现特定的场景应用.
但是,默认的验证指令不一定能够,完全满足我们的真实应用场景,ng同样提供的自定义验证指令的功能。
首先我们来看一个简单的例子:
angular.module("myTest", [])
.directive('multipleEmail', [function () {
return {
require: "ngModel",
link: function (scope, element, attr, ngModel) {
if (ngModel) {
var emailsRegexp = /^([a-z0-9!#$%&'*+\/=?^_`{|}~.-]+@[a-z0-9-]+(\.[a-z0-9-]+)*[;;]?)+$/i;
}
var customValidator = function (value) {
var validity = ngModel.$isEmpty(value) || emailsRegexp.test(value);
ngModel.$setValidity("multipleEmail", validity);
return validity ? value : undefined;
};
ngModel.$formatters.push(customValidator);
ngModel.$parsers.push(customValidator);
}
};
}])页面Html部分代码如下:
<form class="form-horizontal" role="form" id="custom_form" name="custom_form" novalidate>
<div class="form-group">
<label class="col-sm-2 control-label">多个email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input multiple-email name="user_email" ng-model="user.email" required class="form-control" placeholder="自定义验证,多个邮箱地址,以“;”或者“;”分割" />
验证通过:{{custom_form.user_email.$valid}}
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group text-center">
<input class="btn btn-primary btn-lg" ng-disabled="custom_form.$invalid" type="submit" value="提交" />
</div>
</form>
The code is very simple, and the effect is as follows:

This code is very simple, but it involves several important attributes of ngModelController
$viewValue
$viewValue property holds the actual string required to update the view.
$modelValue
$modelValue is held by the data model. $modelValue and $viewValue may be different depending on whether the $parser pipeline operates on them.
$parsers
The value of$parsers is an array of functions. When the user interacts with the controller and the $setViewValue() method in ngModelController is called, the value of When the user interacts with the controller, the function will be called one by one in the form of a pipeline when the $setViewValue() method in ngModelController is called. The value read by ngModel from the DOM will be passed into the function in $parsers and processed by the parser in it. This is for processing and modifying values.
Note: The ngModel.$setViewValue() function is used to set the view value in the scope.
ngModel.$set ViewValue() function can accept one parameter.
value (string): The value parameter is the actual value we want to assign to the ngModel instance.
This method will update the local $viewValue on the controller and then pass the value to every $parser function (including validators). When the value is parsed and all functions in the $parser pipeline have been called, the value is assigned to the $modelValue attribute and passed to the expression provided by the ng-model attribute in the directive. Finally, after all steps are completed, all listeners in $viewChangeListeners will be called. Note that calling $setViewValue() alone will not trigger a new digest loop, so if you want to update the directive, you need to manually trigger digest after setting $viewValue. The $setViewValue() method is suitable for listening to custom events in custom instructions (such as using a jQuery plug-in with a callback function). We will want to set $viewValue and execute the digest loop during the callback.
$formatters
The value of$formatters is an array of functions, in which the functions will be called one by one in the form of a pipeline when the value of the data model changes. It has no influence on the $parser pipeline and is used to format and convert values so that they can be displayed in the control bound to this value.
$viewChangeListeners
The value of$viewChangeListeners is an array of functions, the functions of which will be called one by one in the form of a pipeline when the value in the view changes. Similar behavior can be achieved without using $watch via $viewChangeListeners. These functions do not require a return value because the return value is ignored.
$error
The$error object stores the name of the validator that failed verification and the corresponding error message.
$pristine
The value of$pristine is Boolean and can tell us whether the user has modified the control.
$dirty
The value of$dirty is opposite to $pristine and can tell us whether the user has interacted with the control.
$valid
The$valid value can tell us whether there is an error in the current control. The value is false when there is an error and true when there is no error.
$invalid
The$invalid value can tell us whether there is at least one error in the current control, and its value is opposite to $valid.
The above is the entire content of this article. I hope it will be helpful to everyone in implementing AngularJS form verification.




