Struts1之ActionMapping實例講解
這篇文章主要介紹了Struts1教學之ActionMapping,小編覺得挺不錯的,現在分享給大家,也給大家做個參考。一起跟著小編過來看看吧
首先斷點走出了processpath方法,
# 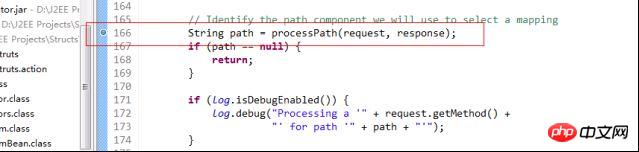
這個方法是用來截取字串的,今天我們來看看怎麼獲得ActionMapping的方法---processMapping。
在此之前簡單說一下ActionMapping,它的原始程式碼中可以看出,其中最重要的屬性和我們的mvc小實例中的ActionMapping類似,都是有path、type還有forwardMap,主要是對應的struts-config設定檔而來,這個就是保存這個設定檔的資訊到記憶體中。
具體的mvc小實例的ActionMapping程式碼如下:
package com.cjq.servlet;
import java.util.Map;
public class ActionMapping {
private String path;
private Object type;
private Map forwardMap;
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
public Object getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(Object type) {
this.type = type;
}
public Map getForwardMap() {
return forwardMap;
}
public void setForwardMap(Map forwardMap) {
this.forwardMap = forwardMap;
}
}而Struts中的Actionconfig(因為ActionMapping是繼承這個ActionConfig的,所以我們來看ActionConfig比較直接)的程式碼如下:
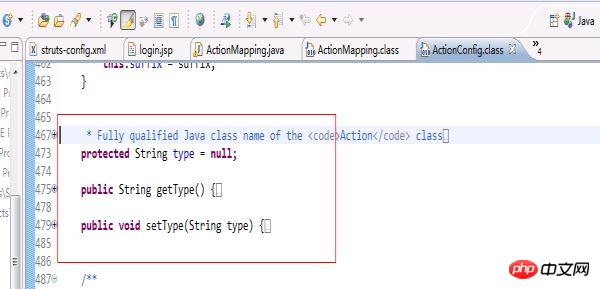
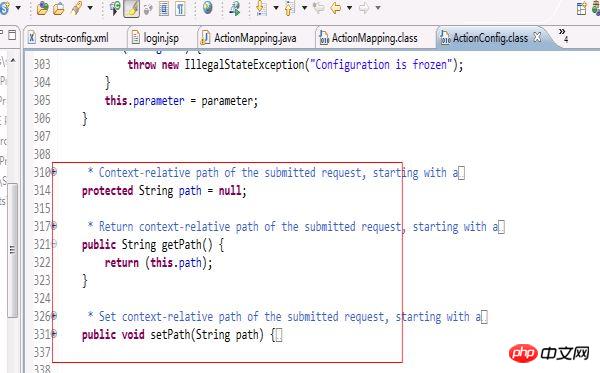
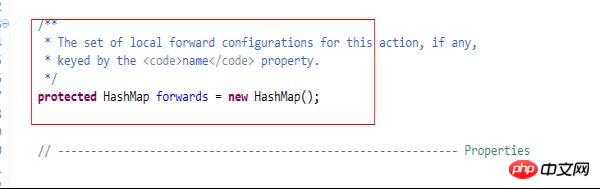
從這兩部分程式碼來看,更印證了我在開篇寫的mvc小實例是一個struts框架的雛形。
講完ActionMapping的一些內容後,相信對ActionMapping有所了解,那麼系統是如何產生ActionMapping和如何找到ActionMapping的呢?這就是今天要說的整體:
我們看下web.xml中有一個
進入斷點偵錯,先在processMapping方法上設定斷點。
進入原始程式碼中:
/**
* <p>Select the mapping used to process theselection path for this request
* If no mapping can be identified, createan error response and return
* <code>null</code>.</p>
*
* @param request The servlet request weare processing
* @param response The servlet response weare creating
* @param path The portion of the requestURI for selecting a mapping
*
* @exception IOException if an input/outputerror occurs
*/
protectedActionMapping processMapping(HttpServletRequestrequest,
HttpServletResponse response,
String path)
throws IOException {
// Is there a mapping for this path?
ActionMapping mapping = (ActionMapping)
moduleConfig.findActionConfig(path);
// If a mapping is found, put it in the request and return it
if (mapping != null) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}
// Locate the mapping for unknown paths (if any)
ActionConfig configs[] = moduleConfig.findActionConfigs();
for (int i = 0; i < configs.length; i++) {
if (configs[i].getUnknown()) {
mapping = (ActionMapping)configs[i];
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}
}
// No mapping can be found to process this request
String msg = getInternal().getMessage("processInvalid");
log.error(msg + " " + path);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, msg);
return null;
}首先我們傳入我們在上一步所截取的路徑,透過moduleConfig的findAction方法來找出ActionConfig,並且傳回ActionMapping。具體程式碼是:
ActionMapping mapping =(ActionMapping) moduleConfig.findActionConfig(path);
如果找到,那就講ActionMapping存放到request的context中。程式碼:
if (mapping != null) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}如果沒有透過path找到mapping,則在Actionconfig中遍歷為未知路徑尋找mapping,如果找到則存放到request中,如果沒有找到,則回傳錯誤訊息,具體程式碼如下:
// Locate the mapping for unknownpaths (if any)
ActionConfig configs[] = moduleConfigfindActionConfigs();
for (int i = 0; i < configslength; i++) {
if (configs[i].getUnknown()) {
mapping = (ActionMapping)configs[i];
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}
}
// No mapping can be found to process this request
String msg = getInternal().getMessage("processInvalid");
log.error(msg + " " + path);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, msg);
return null;來看下ActionServlet中的一個方法processActionForm,當我們在截取字串,再根據字串在取得ActionMapping(這是前兩篇文章中介紹的)之後,我們就要用利用ActionMapping來建立ActionForm了,並且把ActionForm放到request或session中管理。
先來看看特定struts中processActionForm方法的具體實作:
/**
* <p>Retrieve and return the <code>ActionForm</code> associatedwith
* this mapping, creating and retaining oneif necessary. If there is no
* <code>ActionForm</code> associated with this mapping,return
* <code>null</code>.</p>
*
* @param request The servlet request weare processing
* @param response The servlet response weare creating
* @param mapping The mapping we are using
*/
protectedActionForm processActionForm(HttpServletRequestrequest,
HttpServletResponse response,
ActionMapping mapping) {
// Create (if necessary) a form bean to use
ActionForm instance = RequestUtilscreateActionForm
(request, mapping, moduleConfig, servlet);
if (instance == null) {
return (null);
}
// Store the new instance in the appropriate scope
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(" Storing ActionForm bean instance in scope '" +
mapping.getScope() + "' under attribute key '" +
mapping.getAttribute() + "'");
}
if ("request".equals(mapping.getScope())) {
request.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
} else {
HttpSession session =requestgetSession();
session.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
}
return (instance);
}這個方法的大體流程是:根據ActionMapping中的name名稱查找ActionForm,如果配置了ActionForm,那麼就到request或session中查找,如果在request或session中存在已經建立的ActionForm,那麼將會回傳。如果不存在那麼會根據ActionForm的完成路徑採用反射進行創建,再將創建好的ActionForm放到request或session中,之後再傳回ActionForm。
#具體我們可以跟隨斷點偵錯來看看這個方法是如何運作的。
先設定斷點,之後再進入processActionForm方法。
第一個步驟就是建立ActionForm:
// Create (if necessary) a formbean to use
ActionForm instance = RequestUtils.createActionForm
(request, mapping, moduleConfig, servlet);
if (instance == null) {
return (null);
}透過呼叫RequestUtils.createActionForm的方法把ActionMapping中的ActionForm字串產生對象,並且返回。進入這段程式碼:
publicstaticActionForm createActionForm(
HttpServletRequest request,
ActionMapping mapping,
ModuleConfig moduleConfig,
ActionServlet servlet) {
// Is there a form bean associated with this mapping?
String attribute = mappinggetAttribute();
if (attribute == null) {
return (null);
}
// Look up the form bean configuration information to use
String name = mapping.getName();
FormBeanConfig config =moduleConfigfindFormBeanConfig(name);
if (config == null) {
log.warn("No FormBeanConfig found under '"+ name + "'");
return (null);
}
ActionForm instance = lookupActionForm(request,attribute, mappinggetScope());
// Can we recycle the existing form bean instance (if there is one)?
try {
if (instance != null && canReuseActionForm(instance,config)) {
return (instance);
}
} catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
log.error(servlet.getInternal().getMessage("formBean",config.getType()), e);
return (null);
}
return createActionForm(config,servlet);
}方法先定義變數name,並且從mapping取得值,String name = mapping.getName();也就是我們實例中的LoginForm字串。之後透過呼叫FormBeanConfig config =moduleConfig.findFormBeanConfig(name);這句話把對應的LoginForm字串產生對應的物件。
這裡要說明的是我們在struts-config設定檔中,配置過這樣一個標籤資訊:
<form-beans>
<form-bean name="loginForm" type=".struts.LoginActionForm"/>
</form-beans>这个标签在服务器一启动的时候就会利用digester读取这里的配置信息,并且放在FormBeanConfig类中,这样我们可以通过上面那一句话就可以把LoginForm字符串生成相应的对象。
之后调用了ActionForm instance = lookupActionForm(request,attribute, mapping.getScope());这个方法,这个方法主要是查找scope属性中有没有存在ActionForm。具体实现:
if ("request".equals(scope)){
instance = (ActionForm)request.getAttribute(attribute);
} else {
session = request.getSession();
instance = (ActionForm)session.getAttribute(attribute);
}这里判断scope属性值是否为request,如果是则从request中读出ActionForm,如果不是则从session中读出。程序如果是第一次执行,那么ActionForm会是为空的。因为这里的ActionForm为空,所以就进入了if判断语句中,最后通过调用return createActionForm(config, servlet);创建ActionForm并且返回。
之后processActionForm就会把返回来的ActionForm放入request或者session中。具体实现就是:
if ("request".equals(mapping.getScope())){
request.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
} else {
HttpSession session =request.getSession();
session.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
}到此为止,ActionForm就创建完成,当ActionForm创建完成之后,就要用其他的方法来往ActionForm中赋值了
以上是Struts1之ActionMapping實例講解的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 公司安全軟件導致應用無法運行?如何排查和解決?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
公司安全軟件導致應用無法運行?如何排查和解決?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
公司安全軟件導致部分應用無法正常運行的排查與解決方法許多公司為了保障內部網絡安全,會部署安全軟件。 ...
 如何將姓名轉換為數字以實現排序並保持群組中的一致性?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
如何將姓名轉換為數字以實現排序並保持群組中的一致性?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
將姓名轉換為數字以實現排序的解決方案在許多應用場景中,用戶可能需要在群組中進行排序,尤其是在一個用...
 IntelliJ IDEA是如何在不輸出日誌的情況下識別Spring Boot項目的端口號的?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
IntelliJ IDEA是如何在不輸出日誌的情況下識別Spring Boot項目的端口號的?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
在使用IntelliJIDEAUltimate版本啟動Spring...
 如何使用MapStruct簡化系統對接中的字段映射問題?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 06:21 PM
如何使用MapStruct簡化系統對接中的字段映射問題?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 06:21 PM
系統對接中的字段映射處理在進行系統對接時,常常會遇到一個棘手的問題:如何將A系統的接口字段有效地映�...
 如何優雅地獲取實體類變量名構建數據庫查詢條件?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:42 PM
如何優雅地獲取實體類變量名構建數據庫查詢條件?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:42 PM
在使用MyBatis-Plus或其他ORM框架進行數據庫操作時,經常需要根據實體類的屬性名構造查詢條件。如果每次都手動...
 Java對像如何安全地轉換為數組?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Java對像如何安全地轉換為數組?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Java對象與數組的轉換:深入探討強制類型轉換的風險與正確方法很多Java初學者會遇到將一個對象轉換成數組的�...
 如何利用Redis緩存方案高效實現產品排行榜列表的需求?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
如何利用Redis緩存方案高效實現產品排行榜列表的需求?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
Redis緩存方案如何實現產品排行榜列表的需求?在開發過程中,我們常常需要處理排行榜的需求,例如展示一個�...
 電商平台SKU和SPU數據庫設計:如何兼顧用戶自定義屬性和無屬性商品?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
電商平台SKU和SPU數據庫設計:如何兼顧用戶自定義屬性和無屬性商品?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
電商平台SKU和SPU表設計詳解本文將探討電商平台中SKU和SPU的數據庫設計問題,特別是如何處理用戶自定義銷售屬...






