這篇文章主要介紹了java LRU演算法,簡單介紹了LRU演算法的概念並結合實例形式分析了LRU演算法的具體使用方法,需要的朋友可以參考下
本文實例講述了java LRU演算法介紹與用法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:
1.前言
在用戶使用聯網的軟體的時候,總是會從網絡上取得數據,當在一段時間內要多次使用同一個數據的時候,用戶不可能每次用的時候都去聯網進行請求,既浪費時間又浪費網絡
這時就可以將使用者請求過的資料進行保存,但不是任意資料都進行保存,這樣會造成記憶體浪費的。 LRU演算法的想法就可以運用了。
2.LRU簡介
LRU是Least Recently Used 近期最少使用演算法,它可以將長時間沒有被利用的資料進行刪除。
LRU在人們一些情感中也體現的得很好的。當你和一群朋友接觸的時候,經常聯絡的人關係是很好的,若很久沒有聯絡到最後估計都不會再有聯絡了,也就會是失去這位朋友了。
3.以下透過程式碼展現LRU演算法:
最簡單的一種方法是利用LinkHashMap,因為它本身就有一個方法就是在所設定的快取範圍內,去移除額外的舊資料
public class LRUByHashMap<K, V> {
/*
* 通过LinkHashMap简单实现LRU算法
*/
/**
* 缓存大小
*/
private int cacheSize;
/**
* 当前缓存数目
*/
private int currentSize;
private LinkedHashMap<K, V> maps;
public LRUByHashMap(int cacheSize1) {
this.cacheSize = cacheSize1;
maps = new LinkedHashMap<K, V>() {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1;
// 这里移除旧的缓存数据
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(java.util.Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) {
// 当超过缓存数量的时候就将旧的数据移除
return getCurrentSize() > LRUByHashMap.this.cacheSize;
}
};
}
public synchronized int getCurrentSize() {
return maps.size();
}
public synchronized void put(K k, V v) {
if (k == null) {
throw new Error("存入的键值不能为空");
}
maps.put(k, v);
}
public synchronized void remove(K k) {
if (k == null) {
throw new Error("移除的键值不能为空");
}
maps.remove(k);
}
public synchronized void clear() {
maps = null;
}
// 获取集合
public synchronized Collection<V> getCollection() {
if (maps != null) {
return maps.values();
} else {
return null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试
LRUByHashMap<Integer, String> maps = new LRUByHashMap<Integer, String>(
3);
maps.put(1, "1");
maps.put(2, "2");
maps.put(3, "3");
maps.put(4, "4");
maps.put(5, "5");
maps.put(6, "6");
Collection<String> col = maps.getCollection();
System.out.println("存入缓存中的数据是--->>" + col.toString());
}
}運行後的效果:
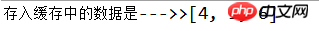
程式碼明明是put了6個Entry但最後只顯示了三個,之間的三個是舊的所以直接被咔嚓掉了
第二種方法是利用雙向鍊錶+ HashTable
雙向鍊錶的作用是用來記錄位置的,而HashTable則是作為容器來儲存資料的
為什麼用HashTable不用HashMap呢?
1.HashTable的鍵和值都不能為null;
2.上面用LinkHashMap實作的LRU,有用到synchronized , 讓執行緒同步去處理,這樣就避免在多執行緒處理統一資料時造成問題
而HashTable自帶同步機制的,所以多執行緒就能對HashTable進行正確的處理了。
Cache的所都用有位置雙連錶連接起來,當一個位置被命中之後,就將透過調整鍊錶的指向,將該位置調整到鍊錶頭的位置,新加入的Cache直接加到鍊錶頭中。這樣,在進行多次Cache操作後,
最近被命中的,就會被向鍊錶頭方向移動,而沒有命中的,而想鍊錶後面移動,鍊錶尾則表示最近最少使用的Cache 。當需要替換內容時候,鍊錶的最後位置就是最少被命中的位置,我們只需要淘
汰鍊錶最後的部分即可
public class LRUCache {
private int cacheSize;
private Hashtable<Object, Entry> nodes;//缓存容器
private int currentSize;
private Entry first;//链表头
private Entry last;//链表尾
public LRUCache(int i) {
currentSize = 0;
cacheSize = i;
nodes = new Hashtable<Object, Entry>(i);//缓存容器
}
/**
* 获取缓存中对象,并把它放在最前面
*/
public Entry get(Object key) {
Entry node = nodes.get(key);
if (node != null) {
moveToHead(node);
return node;
} else {
return null;
}
}
/**
* 添加 entry到hashtable, 并把entry
*/
public void put(Object key, Object value) {
//先查看hashtable是否存在该entry, 如果存在,则只更新其value
Entry node = nodes.get(key);
if (node == null) {
//缓存容器是否已经超过大小.
if (currentSize >= cacheSize) {
nodes.remove(last.key);
removeLast();
} else {
currentSize++;
}
node = new Entry();
}
node.value = value;
//将最新使用的节点放到链表头,表示最新使用的.
node.key = key
moveToHead(node);
nodes.put(key, node);
}
/**
* 将entry删除, 注意:删除操作只有在cache满了才会被执行
*/
public void remove(Object key) {
Entry node = nodes.get(key);
//在链表中删除
if (node != null) {
if (node.prev != null) {
node.prev.next = node.next;
}
if (node.next != null) {
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
if (last == node)
last = node.prev;
if (first == node)
first = node.next;
}
//在hashtable中删除
nodes.remove(key);
}
/**
* 删除链表尾部节点,即使用最后 使用的entry
*/
private void removeLast() {
//链表尾不为空,则将链表尾指向null. 删除连表尾(删除最少使用的缓存对象)
if (last != null) {
if (last.prev != null)
last.prev.next = null;
else
first = null;
last = last.prev;
}
}
/**
* 移动到链表头,表示这个节点是最新使用过的
*/
private void moveToHead(Entry node) {
if (node == first)
return;
if (node.prev != null)
node.prev.next = node.next;
if (node.next != null)
node.next.prev = node.prev;
if (last == node)
last = node.prev;
if (first != null) {
node.next = first;
first.prev = node;
}
first = node;
node.prev = null;
if (last == null)
last = first;
}
/*
* 清空缓存
*/
public void clear() {
first = null;
last = null;
currentSize = 0;
}
}
class Entry {
Entry prev;//前一节点
Entry next;//后一节点
Object value;//值
Object key;//键
}以上是Java中LRU演算法的使用方法詳解的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




