行動端IndexList效果介紹
寫在前面
接著前面的行動端效果講,這次講解的的是行動端IndexList效果介紹的實作原理。效果如下:
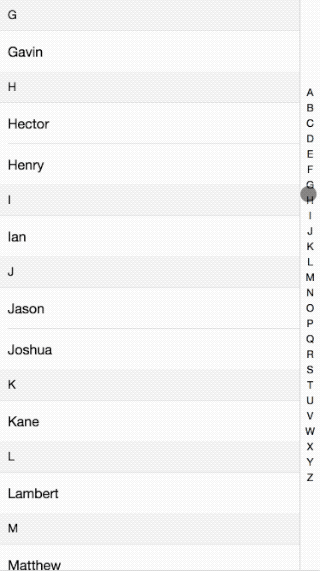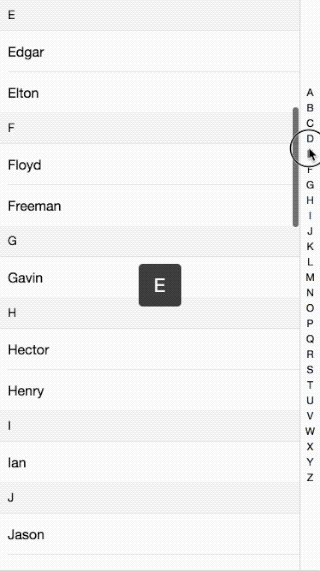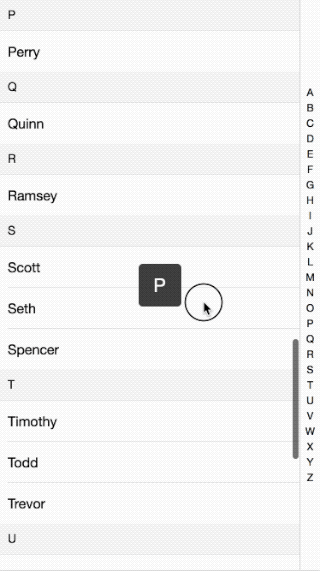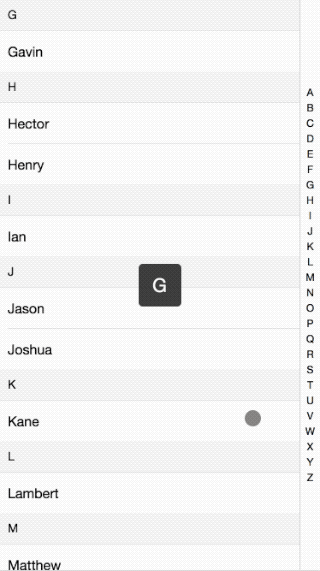
程式碼請看這裡:github
#手機端效果之swiper
行動裝置效果之picker
#手機端效果之cellSwiper
1. 核心解析
整體來說的原理就是當點擊或滑動右邊的索引條時,透過取得點擊的索引值來讓左邊的內容滑動到相應的位置。其中怎麼滑到具體的位置,看下面分解:
1.1 基本html代碼
<p class="indexlist">
<ul class="indexlist-content" id="content">
<!-- 需要生成的内容 -->
</ul>
<p class="indexlist-nav" id="nav">
<ul class="indexlist-navlist" id="navList">
<-- 需要生成的索引条 --> <
/ul>
</p>
<p class="indexlist-indicator" style="display: none;" id="indicator">
</p>
</p>1.2 DOM初始化
##由於餓了麼元件庫中的indexList是採用vue元件產生DOM,我這裡大致使用javascript來模擬產生DOM。
// 内容填充function initialDOM() {
// D.data 获取内容数据
var data = D.data;
var contentHtml = '';
var navHtml = '';
// 初始化内容和NAV
data.forEach(function(d) {
var index = d.index;
var items = d.items;
navHtml += '<li class="indexlist-navitem">'+ index +'</li>';
contentHtml += '<li class="indexsection" data-index="'+ index +'"><p class="indexsection-index">'+ index +'</p><ul>';
items.forEach(function(item) {
contentHtml += '<a class="cell"><p class="cell-wrapper"><p class="cell-title"><span class="cell-text">'+ item +'</span></p></p></a>';
});
contentHtml += '</ul></li>';
});
content.innerHTML = contentHtml;
navList.innerHTML = navHtml;}// 样式初始化if (!currentHeight) {
currentHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight -content.行動端IndexList效果介紹().top;}// 右边索引栏的宽度navWidth = nav.clientWidth;// 左边内容的初始化高度和右边距// 高度为当前页面的高度与内容top的差值content.style.marginRight = navWidth + 'px';content.style.height = currentHeight + 'px';touchstart事件的結尾處,在window上綁定了touchmove與touchend事件,是為了使得滑動得區域更大,只有在開始的時候在索引欄上觸發了touchstart事件時,之後再window上觸發滑動和結束事件,這就意味著我們在滑動的過程中可以在左側的內容區域滑動,同時也能達到index的效果。
function handleTouchstart(e) {
// 如果不是从索引栏开始滑动,则直接return
// 保证了左侧内容区域能够正常滑动
if (e.target.tagName !== 'LI') {
return;
}
// 记录开始的clientX值,这个clientX值将在之后的滑动中持续用到,用于定位
navOffsetX = e.changedTouches[0].clientX;
// 内容滑动到指定区域
scrollList(e.changedTouches[0].clientY);
if (indicatorTime) {
clearTimeout(indicatorTime);
}
moving = true;
// 在window区域注册滑动和结束事件
window.addEventListener('touchmove', handleTouchMove, { passive: false });
window.addEventListener('touchend', handleTouchEnd);}e.changedTouches,這個API可以去MDN查一下。
changedTouches和touches的區別並不是特別大,changedTouches在同一點點擊兩次,第二次將不會有touch值。具體可以看這篇文章
function scrollList(y) {
// 通过当前的y值以及之前记录的clientX值来获得索引栏中的对应item
var currentItem = document.elementFromPoint(navOffsetX, y);
if (!currentItem || !currentItem.classList.contains('indexlist-navitem')) {
return;
}
// 显示指示器
currentIndicator = currentItem.innerText;
indicator.innerText = currentIndicator;
indicator.style.display = '';
// 找到左侧内容的对应section
var targets = [].slice.call(sections).filter(function(section) {
var index = section.getAttribute('data-index');
return index === currentItem.innerText;
});
var targetDOM;
if (targets.length > 0) {
targetDOM = targets[0];
// 通过对比要滑动到的区域的top值与最开始的一个区域的top值
// 两者的差值即为要滚动的距离
content.scrollTop = targetDOM.行動端IndexList效果介紹().top - firstSection.行動端IndexList效果介紹().top;
// 或者使用行動端IndexList效果介紹来达到相同的目的
// 不过存在兼容性的问题
// targetDOM.行動端IndexList效果介紹();
}}elementFromPoint的API#可以看這裡
行動端IndexList效果介紹和行動端IndexList效果介紹的相容性
- 行動端IndexList效果介紹
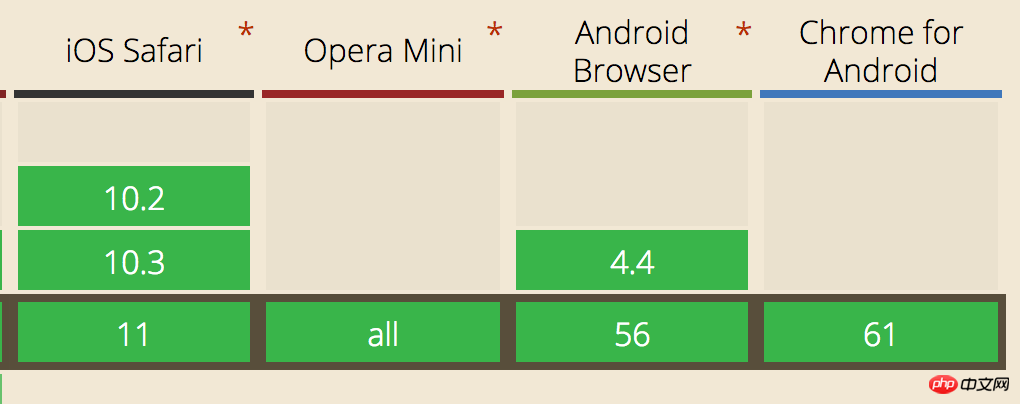
- 行動端IndexList效果介紹
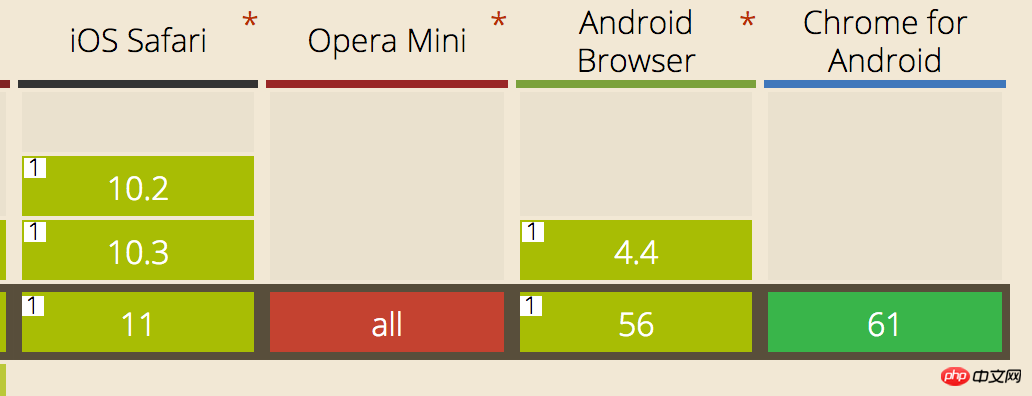
window上的滑動事件
window.removeEventListener('touchmove', handleTouchMove);window.removeEventListener('touchend', handleTouchEnd);
changedTouches以及elementFromPoint等API的學習。
以上是行動端IndexList效果介紹的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 用戶遭遇罕見故障 三星 Watch 智慧手錶突現白螢幕問題
Apr 03, 2024 am 08:13 AM
用戶遭遇罕見故障 三星 Watch 智慧手錶突現白螢幕問題
Apr 03, 2024 am 08:13 AM
你可能遇到過智慧型手機螢幕出現綠色線條的問題,即使沒看過,也一定在網路上看過相關圖片。那麼,智慧手錶螢幕變白的情況你有遇見過嗎? 4月2日,CNMO從外媒了解到,一名Reddit用戶在社群平台上分享了一張圖片,展示了三星Watch系列智慧手錶螢幕變白的情況。該用戶寫道:"我離開時正在充電,回來時就這樣了,我嘗試重啟,但重啟過程中屏幕還是這樣。"三星Watch智能手錶屏幕變白這位Reddit用戶並未指明這款智能手錶的具體型號。不過,從圖片上看,應該是三星Watch5。此前,另一位Reddit用戶也報告
 wapi是什麼東西詳細介紹
Jan 07, 2024 pm 09:14 PM
wapi是什麼東西詳細介紹
Jan 07, 2024 pm 09:14 PM
wapi這個名詞使用者可能在使用網路得時候見過過,但是對於一部分人來說肯定都不知道wapi是什麼,下面就帶來了詳細介紹,幫助不知道小伙伴去了解。 wapi是什麼東西:答:wapi是無線區域網路鑑別和保密的基礎架構。這就像紅外線和藍牙等功能一樣,一般都覆蓋在辦公大樓等地方的附近。基本上都是為一個小部門所有的,所以這個功能涉及的範圍只有幾公里。 wapi相關介紹:1、wapi是無線區域網路裡面的一種傳輸協定。 2.這款技術是可以去避免窄頻帶通訊的問題,可以更好的去進行傳播。 3.只要只需要一個代碼就可以去傳送訊號了
 詳解win11能否運行PUBG遊戲
Jan 06, 2024 pm 07:17 PM
詳解win11能否運行PUBG遊戲
Jan 06, 2024 pm 07:17 PM
pubg又稱絕地求生,是一款非常經典的射擊大逃殺類型遊戲,從2016年火爆以來一直擁有非常多的玩家。在最近的win11系統推出後,就有不少玩家想要在win11上游玩它,下面就跟著小編來看看win11是否可以玩pubg吧。 win11能玩pubg嗎:答:win11可以玩pubg。 1.在win11推出之初,因為win11需要開啟tpm的緣故,所以導致很多玩家被pubg封號處理了。 2.不過後來根據玩家的回饋,藍洞方面已經解決了這個問題,目前已經可以在win11中正常玩pubg了。 3.如果大家遇到了pub
 九州風神阿薩辛 4S 散熱器評測 風冷「刺客大師」範兒
Mar 28, 2024 am 11:11 AM
九州風神阿薩辛 4S 散熱器評測 風冷「刺客大師」範兒
Mar 28, 2024 am 11:11 AM
說起阿薩辛ASSASSIN,相信玩家們一定會想到《刺客信條》中的各位刺客大師,不僅身手了得,而且"躬身於黑暗、服務於光明"的信條,與國內知名機箱/電源/散熱器品牌九州風神(DeepCool)旗下的阿薩辛ASSASSIN系列旗艦級風冷散熱器不謀而合。最近,該系列的最新產品阿薩辛ASSASSIN4S重磅上線,"西裝刺客,再進階"為高級玩家帶來全新的風冷散熱體驗。外觀一覽細節滿滿阿薩辛4S散熱器採用雙塔構造+單風扇內嵌設計,外麵包覆立方體造型的整流罩,整體感極強,並提供白、黑兩種配色可選,滿足不同色系
 輕鬆拿捏 4K 高畫質影像理解!這個多模態大模型自動分析網頁海報內容,打工人簡直不要太方便
Apr 23, 2024 am 08:04 AM
輕鬆拿捏 4K 高畫質影像理解!這個多模態大模型自動分析網頁海報內容,打工人簡直不要太方便
Apr 23, 2024 am 08:04 AM
一個可以自動分析PDF、網頁、海報、Excel圖表內容的大模型,對於打工人來說簡直不要太方便。上海AILab,香港中文大學等研究機構提出的InternLM-XComposer2-4KHD(簡寫為IXC2-4KHD)模型讓這一切成為了現實。相較於其他多模態大模型不超過1500x1500的分辨率限制,該工作將多模態大模型的最大輸入影像提升到超過4K(3840x1600)分辨率,並支援任意長寬比和336像素~4K動態解析度變化。發布三天,模型就登頂HuggingFace視覺問答模型熱度排行榜第一。輕鬆拿捏
 航空嘉 MX750P 全模組電源評測:750W 的白金實力濃縮
Mar 28, 2024 pm 03:20 PM
航空嘉 MX750P 全模組電源評測:750W 的白金實力濃縮
Mar 28, 2024 pm 03:20 PM
ITX平台以小巧的身形吸引了許多追求極致和獨特美感的玩家,隨著製程的提升和技術的進步,英特爾第14代酷睿和RTX40系顯卡都可以在ITX平台中發揮實力,遊戲玩家也對SFX電源有了更高的要求。遊戲愛好者航空嘉推出新的MX系列電源,在滿足高效能需求的ITX平台中,MX750P全模組電源的定額功率高達750W,同時通過了80PLUS白金級認證。以下我們就帶來這款電源的評測。航嘉MX750P全模組電源採用了簡約時尚的設計理念,共有黑白兩款供玩家選擇,均採用磨砂表面處理,搭配銀灰色和紅色的字體有很好的質感,
 春日裡的精緻光影藝術,哈趣 H2 性價比之選
Apr 17, 2024 pm 05:07 PM
春日裡的精緻光影藝術,哈趣 H2 性價比之選
Apr 17, 2024 pm 05:07 PM
隨著春天的到來,萬物復甦,一切都充滿了生命與活力。在這個美好的季節裡,如何為居家生活增添一抹別樣的色彩?哈趣H2投影儀,以其精緻的設計和超高的性價比,成為了這個春天裡不可或缺的一道亮麗風景。這款H2投影機小巧玲瓏卻不失時尚。無論是放在客廳的電視櫃上,或是臥室的床頭櫃旁,都能成為一道明亮的風景線。它的機身採用了奶白色的磨砂質地,這種設計不僅讓投影機的外觀更顯高級,同時也增加了觸感的舒適度。米色仿皮紋材質,更為整體外觀增添了一抹溫馨與雅緻。這種色彩與材質的搭配,既符合現代家居的美感趨勢,又能融入
 七彩虹隱星 P15 24 評測:顏值性能兼具的硬蕊全能遊戲本
Mar 06, 2024 pm 04:40 PM
七彩虹隱星 P15 24 評測:顏值性能兼具的硬蕊全能遊戲本
Mar 06, 2024 pm 04:40 PM
在當下科技快速發展的時代,筆記型電腦已成為人們日常生活和工作中不可或缺的重要工具。對於那些對性能有高要求的玩家而言,擁有配置強大、性能出色的筆記型電腦才能滿足其硬核需求。七彩虹隱星P15筆記型電腦憑藉其卓越性能和令人驚豔的設計,成為了未來的引領者,堪稱硬核筆記本的典範。七彩虹隱星P1524配備了13代英特爾酷睿i7處理器和RTX4060LaptopGPU,外觀採用更時尚的太空船設計風格,同時在細節表現上也有出色表現。讓我們先來了解這款筆記本的特點。至高搭載英特爾酷睿i7-13620H處理






