本文主要記錄了在近期開發中遇到的jQuery dom基本查找方法,然後將各種方法性能做了一個比較,目的是希望自己在以後dom元素查找時,使用最優的方案。文中介紹的非常詳細,需要的朋友可以參考借鑒,下面來一起看看吧。
前言
關於這個問題的產生由於我們前端組每個人的編碼習慣的差異,最主要的還是因為代碼的維護性問題。在此基礎上,我對jQuery源碼(1.11.3)查找dom節點相關的內容進行了仔細的查閱,雖然並不能理解的很深入 。 。同時基於對瀏覽器console物件的了解產生了一系列之後的問題和分析,對jQuery最常用的三種dom查找方式進行了一個查找效率和性能方面的比較分析。
首先我們要用到的是console.time()和console.timeEnd()這兩個成對出現的console物件的方法,該方法的用法是將他們兩者之間的程式碼段執行並輸出所消耗的執行時間,且兩者內傳入的字串命名須統一才能生效,例如:
console.time('Scott');
console.log('seven');
console.timeEnd('Scott');
seven
Scott: 0.256ms程式碼段中三處一致才是正確的用法。
正文
接下來我們來討論我們常用的jQuery查找dom方式:
1.$(‘.parent .child'); 2.$(‘.parent').find(‘.child'); 3.$(‘.child','.parent');
其中方式1和方式3都是基於jQuery的selector和context的查找方式,既我們最常用的jQuery()或$() ,
詳細即為:
jQuery = function( selector, context ) {
// The jQuery object is actually just the init constructor 'enhanced'
// Need init if jQuery is called (just allow error to be thrown if not included)
return new jQuery.fn.init( selector, context );
}基於jQuery(1.11.3)70行處,為該方法的入口,他所做的所有事情就是創建了一個jquery.fn上的init方法的對象,我們再來細看這個對像是什麼:
init = jQuery.fn.init = function( selector, context ) {
var match, elem;
// HANDLE: $(""), $(null), $(undefined), $(false)
if ( !selector ) {
return this;
}
// Handle HTML strings
if ( typeof selector === "string" ) {
if ( selector.charAt(0) === "<" && selector.charAt( selector.length - 1 ) === ">" && selector.length >= 3 ) {
// Assume that strings that start and end with <> are HTML and skip the regex check
match = [ null, selector, null ];
} else {
match = rquickExpr.exec( selector );
}
// Match html or make sure no context is specified for #id
if ( match && (match[1] || !context) ) {
// HANDLE: $(html) -> $(array)
if ( match[1] ) {
context = context instanceof jQuery ? context[0] : context;
// scripts is true for back-compat
// Intentionally let the error be thrown if parseHTML is not present
jQuery.merge( this, jQuery.parseHTML(
match[1],
context && context.nodeType ? context.ownerDocument || context : document,
true
) );
// HANDLE: $(html, props)
if ( rsingleTag.test( match[1] ) && jQuery.isPlainObject( context ) ) {
for ( match in context ) {
// Properties of context are called as methods if possible
if ( jQuery.isFunction( this[ match ] ) ) {
this[ match ]( context[ match ] );
// ...and otherwise set as attributes
} else {
this.attr( match, context[ match ] );
}
}
}
return this;
// HANDLE: $(#id)
} else {
elem = document.getElementById( match[2] );
// Check parentNode to catch when Blackberry 4.6 returns
// nodes that are no longer in the document #6963
if ( elem && elem.parentNode ) {
// Handle the case where IE and Opera return items
// by name instead of ID
if ( elem.id !== match[2] ) {
return rootjQuery.find( selector );
}
// Otherwise, we inject the element directly into the jQuery object
this.length = 1;
this[0] = elem;
}
this.context = document;
this.selector = selector;
return this;
}
// HANDLE: $(expr, $(...))
} else if ( !context || context.jquery ) {
return ( context || rootjQuery ).find( selector );
// HANDLE: $(expr, context)
// (which is just equivalent to: $(context).find(expr)
} else {
return this.constructor( context ).find( selector );
}
// HANDLE: $(DOMElement)
} else if ( selector.nodeType ) {
this.context = this[0] = selector;
this.length = 1;
return this;
// HANDLE: $(function)
// Shortcut for document ready
} else if ( jQuery.isFunction( selector ) ) {
return typeof rootjQuery.ready !== "undefined" ?
rootjQuery.ready( selector ) :
// Execute immediately if ready is not present
selector( jQuery );
}
if ( selector.selector !== undefined ) {
this.selector = selector.selector;
this.context = selector.context;
}
return jQuery.makeArray( selector, this );
}基於jQuery(1.11.3) 2776行處,該方法比較長,我就來大概說一下我對這個方法的了解:這裡主要就是做了先對selector的判斷,在判斷完後,查找context如果存在就繼續做對有context存在情況的處理,沒有則進行沒有context情況的處理,而方式1和方式3:
1.$(‘.parent .child'); 3.$(‘.child','.parent');
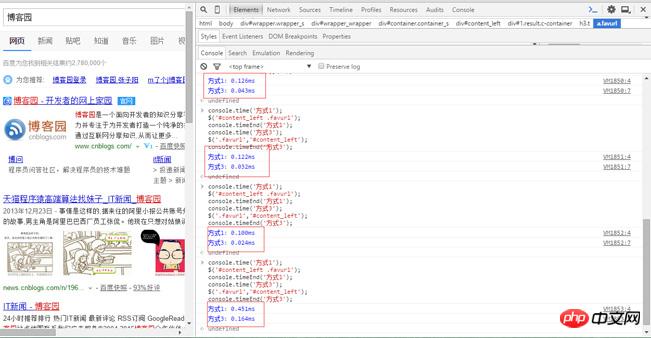
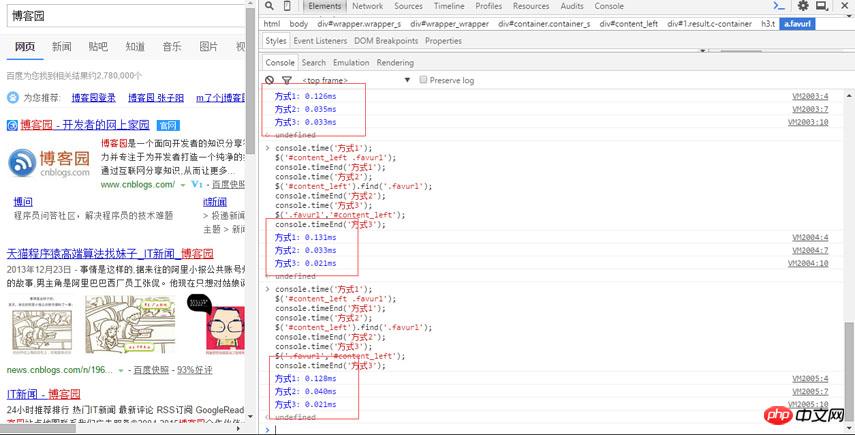
他們都要進入相同的判斷步驟,即上面簡要說明的判斷流程,等到1和3判斷完後所花費的時間基本上差不多,但是1內部的選擇器還需要花時間去進行sizzle相關查找,得出:
方式1. $('.parent .child'); 走完流程花費的時間:a;
方式3. $('.child','.parent'); 走完流程花費的時間:a; 幾乎已經找到dom節點
方式1. $('.parent .child'); sizzle相關查找選擇器.parent .child花費的時間:b;
所以得出初步結論:
方式3. $('.child','.parent');花費的時間:a;
方式1. $('. parent .child');花費的時間:a + b;
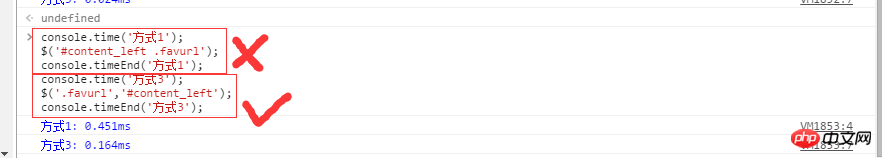
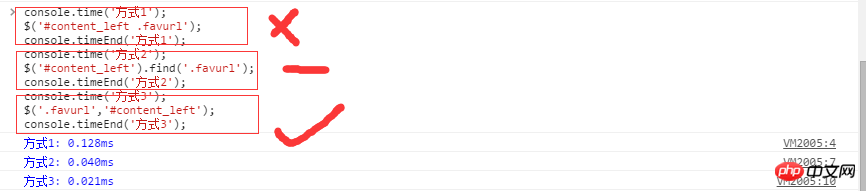
方式3優於方式1
find: function( selector ) {
var i,
ret = [],
self = this,
len = self.length;
if ( typeof selector !== "string" ) {
return this.pushStack( jQuery( selector ).filter(function() {
for ( i = 0; i < len; i++ ) {
if ( jQuery.contains( self[ i ], this ) ) {
return true;
}
}
}) );
}
for ( i = 0; i < len; i++ ) {
jQuery.find( selector, self[ i ], ret );
}
// Needed because $( selector, context ) becomes $( context ).find( selector )
ret = this.pushStack( len > 1 ? jQuery.unique( ret ) : ret );
ret.selector = this.selector ? this.selector + " " + selector : selector;
return ret;
}
相關推薦:
以上是幾種jQuery查找dom的方法的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




