組合模式,將物件組合成樹狀結構以表示「部分-整體」的層次結構,組合模式使得使用者對單一物件和組合物件的使用具有一致性。
它使我們樹型結構的問題中,模糊了簡單元素和複雜元素的概念,客戶程式可以像處理簡單元素一樣來處理複雜元素,從而使得客戶程式與複雜元素的內部結構解耦。它可以幫助開發者對多個具有相似功能物件進行分類, 提高規範化設計
有許多關於分級資料結構的例子,使得組合模式非常有用武之地。關於分級資料結構的一個普遍性的例子是你每次使用電腦時所遇到的:檔案系統。檔案系統由目錄和檔案組成。每個目錄都可以裝內容。目錄的內容可以是文件,也可以是目錄。依照這種方式,電腦的檔案系統就是以遞歸結構來組織的。如果你想要描述這樣的資料結構,那麼你可以使用組合模式Composite。
涉及角色
在組合模式的層次體系中有兩種類型的物件: 葉物件和組合物件, 這是一種遞歸定義, 但者也是其有用的原因所在, 一個組合物件可以由其他組合物件和葉子物件組成, 但葉子物件不再包含子物件, 組合物件用於葉子節點的分類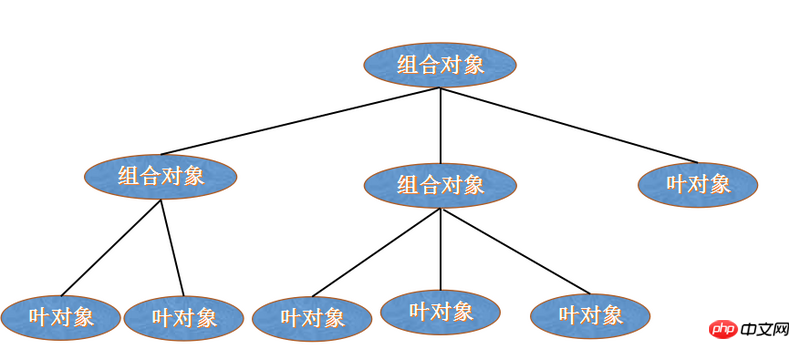
這裡借用javascript設計模式的圖來說明組合模式的設計
Interface 是組合中的物件聲明接口,在適當的情況下,實作所有類別共有介面的預設行為。聲明一個介面用於存取和管理Component子部件。
Field 在組合中表示葉子結點對象,葉子結點沒有子結點, 可以設計成抽象類別, 透過繼承設計出不同類別的葉子對象.
Composite 定義有子節點行為,用來儲存子元件,在Component介面中實作與子元件有關操作,如增加(add)和刪除(remove)等。 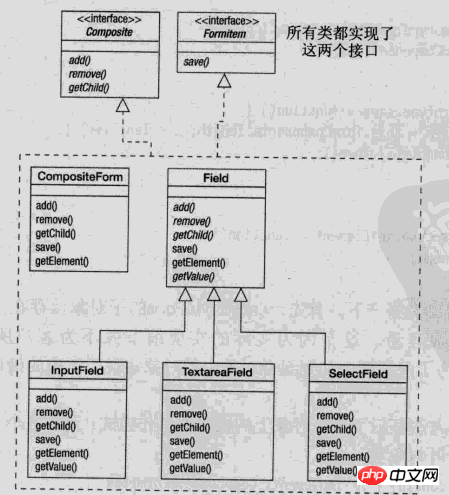
介面
/* Interfaces. */
var Composite = new Interface('Composite', ['add', 'remove', 'getChild']);
var FormItem = new Interface('FormItem', ['save']);組合物件類別
/* CompositeForm class. */
var CompositeForm = function(id, method, action) { // implements Composite, FormItem
this.formComponents = [];
this.element = document.createElement('form');
this.element.id = id;
this.element.method = method || 'POST';
this.element.action = action || '#';
};
CompositeForm.prototype.add = function(child) {
Interface.ensureImplements(child, Composite, FormItem);
this.formComponents.push(child);
this.element.appendChild(child.getElement());
};
CompositeForm.prototype.remove = function(child) {
for(var i = 0, len = this.formComponents.length; i < len; i++) {
if(this.formComponents[i] === child) {
this.formComponents.splice(i, 1); // Remove one element from the array at
// position i.
break;
}
}
};
CompositeForm.prototype.getChild = function(i) {
return this.formComponents[i];
};
CompositeForm.prototype.save = function() {
for(var i = 0, len = this.formComponents.length; i < len; i++) {
this.formComponents[i].save();
}
};
CompositeForm.prototype.getElement = function() {
return this.element;
};葉子物件類別
葉子物件可以是簡單的一個類別, 也可以設計成抽象類別建構不同類別的葉子, 在此採用抽象類別設計不同類別的葉子
/* Field class, abstract. */
var Field = function(id) { // implements Composite, FormItem
this.id = id;
this.element;
};
Field.prototype.add = function() {};
Field.prototype.remove = function() {};
Field.prototype.getChild = function() {};
Field.prototype.save = function() {
setCookie(this.id, this.getValue);
};
Field.prototype.getElement = function() {
return this.element;
};
Field.prototype.getValue = function() {
throw new Error('Unsupported operation on the class Field.');
};InputField 類別
/* InputField class. */
var InputField = function(id, label) { // implements Composite, FormItem
Field.call(this, id);
this.input = document.createElement('input');
this.input.id = id;
this.label = document.createElement('label');
var labelTextNode = document.createTextNode(label);
this.label.appendChild(labelTextNode);
this.element = document.createElement('p');
this.element.className = 'input-field';
this.element.appendChild(this.label);
this.element.appendChild(this.input);
};
extend(InputField, Field); // Inherit from Field.
InputField.prototype.getValue = function() {
return this.input.value;
};TextareaField 類別
/* TextareaField class. */
var TextareaField = function(id, label) { // implements Composite, FormItem
Field.call(this, id);
this.textarea = document.createElement('textarea');
this.textarea.id = id;
this.label = document.createElement('label');
var labelTextNode = document.createTextNode(label);
this.label.appendChild(labelTextNode);
this.element = document.createElement('p');
this.element.className = 'input-field';
this.element.appendChild(this.label);
this.element.appendChild(this.textarea);
};
extend(TextareaField, Field); // Inherit from Field.
TextareaField.prototype.getValue = function() {
return this.textarea.value;
};SelectField 類別
/* SelectField class. */
var SelectField = function(id, label) { // implements Composite, FormItem
Field.call(this, id);
this.select = document.createElement('select');
this.select.id = id;
this.label = document.createElement('label');
var labelTextNode = document.createTextNode(label);
this.label.appendChild(labelTextNode);
this.element = document.createElement('p');
this.element.className = 'input-field';
this.element.appendChild(this.label);
this.element.appendChild(this.select);
};
extend(SelectField, Field); // Inherit from Field.
SelectField.prototype.getValue = function() {
return this.select.options[this.select.selectedIndex].value;
};/* Usage. */
var contactForm = new CompositeForm('contact-form', 'POST', 'contact.php');
contactForm.add(new InputField('first-name', 'First Name'));
contactForm.add(new InputField('last-name', 'Last Name'));
contactForm.add(new InputField('address', 'Address'));
contactForm.add(new InputField('city', 'City'));
contactForm.add(new SelectField('state', 'State', stateArray));
// var stateArray =[{'al', 'Alabama'}, ...]
contactForm.add(new InputField('zip', 'Zip'));
contactForm.add(new TextareaField('comments', 'Comments'));
addEvent(window, 'unload', contactForm.save);組合模式適合對大批物件進行操作, 且操作物件具有層次關係, 透過對物件的分類操作籍此弱化物件之間的耦合, 這種模式使得程式碼模組化程度更高, 層次更鮮明, 維護性較好
相關推薦:
以上是js組合設計模式詳解的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!




