各大公司Java面試題目歸納整理(全)
ThreadLocal(線程變數副本)
Synchronized實作記憶體共享,ThreadLocal為每個執行緒維護一個本地變數。
採用空間換時間,它用於執行緒間的資料隔離,為每一個使用該變數的執行緒提供一個副本,每個執行緒都可以獨立地改變自己的副本,而不會和其他執行緒的副本衝突。
ThreadLocal類別中維護一個Map,用於儲存每個線程的變數副本,Map中元素的鍵為線程對象,而值為對應線程的變數副本。
ThreadLocal在Spring中發揮著巨大的作用,在管理Request作用域中的Bean、事務管理、任務調度、AOP等模組都出現了它的身影。
Spring中絕大部分Bean都可以聲明成Singleton作用域,採用ThreadLocal進行封裝,因此有狀態的Bean就能夠以singleton的方式在多線程中正常工作了。
Java虛擬機器規格中將Java執行時間資料分為六種。
1.程式計數器:是一個資料結構,用來保存目前正常執行的程式的記憶體位址。 Java虛擬機的多執行緒就是透過執行緒輪流切換並分配處理器時間來實現的,為了執行緒切換後能恢復到正確的位置,每個執行緒都需要一個獨立的程式計數器,互不影響,該區域為“線程私有」。
2.Java虛擬機棧:執行緒私有的,與執行緒生命週期相同,用於儲存局部變數表,操作棧,方法傳回值。局部變數表放著基本資料型別,還有物件的參考。
3.本地方法堆疊:跟虛擬機器堆疊很像,不過它是為虛擬機器使用到的Native方法服務。
4.Java堆:所有執行緒共享的一塊記憶體區域,物件實例幾乎都在這裡分配記憶體。
5.方法區:各個執行緒共享的區域,儲存虛擬機器載入的類別信息,常數,靜態變量,編譯後的程式碼。
6.運行時常數池:代表運行時每個class檔案中的常數量表。包括幾種常數:編譯時的數字常數、方法或域的引用。
「你能不能談談,java GC是在什麼時候,對什麼東西,做了什麼事情?」
在什麼時候:
1.新生代有一個Eden區和兩個survivor區,先將物件放入Eden區,如果空間不足就向其中的一個survivor區上放,如果仍然放不下就會引發一次發生在新生代的minor GC,將存活的對象放入另一個survivor區中,然後清空Eden和之前的那個survivor區的記憶體。在某次GC過程中,如果發現仍然又放不下的對象,就將這些對象放入老年代記憶體裡去。
2.大對像以及長期存活的對象直接進入老年區。
3.當每次執行minor GC的時候應該對要晉升到老年代的對象進行分析,如果這些馬上要到老年區的老年對象的大小超過了老年區的剩餘大小,那麼執行一次Full GC以盡可能獲得老年區的空間。
對什麼東西:從GC Roots搜尋不到,而且經過一次標記清理之後仍沒有復活的對象。
做什麼: 新生代:複製清理;老年代:標記-清除和標記-壓縮演算法; 永久代:存放Java中的類別和載入類別的類別載入器本身。
GC Roots都有哪些: 1. 虛擬機棧中的引用的對象2. 方法區中靜態屬性引用的對象,常數引用的對象3. 本地方法棧中JNI(即一般說的Native方法)引用的對象。
Synchronized 與Lock都是可重入鎖,同一個執行緒再次進入同步程式碼的時候.可以使用自己已經取得到的鎖。
Synchronized是悲觀鎖定機制,獨佔鎖。而Locks.ReentrantLock是,每次不加鎖而是假設沒有衝突而去完成某項操作,如果因為衝突失敗就重試,直到成功為止。 ReentrantLock適用場景
某個執行緒在等待一個鎖的控制權的這段時間需要中斷
需要分開處理一些wait-notify ,ReentrantLock裡面的Condition應用,能夠控制notify哪個線程,鎖可以綁定多個條件。
具有公平鎖定功能,每個到來的執行緒都會排隊等候。
StringBuffer是線程安全的,每次操作字串,String會產生一個新的對象,而StringBuffer不會;StringBuilder是非線程安全的
fail- fast:機制是java集合(Collection)中的一種錯誤機制。當多個執行緒對同一個集合的內容進行操作時,就可能會產生fail-fast事件。
例如:當某一個執行緒A透過iterator去遍歷某集合的過程中,若該集合的內容被其他執行緒改變了;那麼執行緒A存取集合時,就會拋出ConcurrentModificationException異常,產生fail-fast事件
happens-before:如果兩個操作之間有happens-before 關係,那麼前一個操作的結果就會對後面一個操作可見。
1.程式順序規則:一個執行緒中的每個操作,happens- before 於該執行緒中的任意後續操作。
2.監視器鎖規則:對一個監視器鎖的解鎖,happens- before 於隨後對這個監視器鎖的加鎖。
3.volatile變數規則:對一個volatile域的寫,happens- before於任意後續對這個volatile域的讀。
4.傳遞性:如果A happens- before B,且B happens- before C,那麼A happens- before C。
5.線程啟動規則:Thread物件的start()方法happens- before於此線程的每一個動作。
Volatile和Synchronized四個不同點:
1 粒度不同,前者針對變量,後者鎖定物件和類別
2 syn阻塞,volatile線程不阻塞
3 syn保證三大特性,volatile不保證原子性
4 syn編譯器優化,volatile不優化volatile具備兩種特性:
1.保證此變數對所有執行緒的可見性,指一條執行緒修改了這個變數的值,新值對於其他執行緒來說是可見的,但並不是多執行緒安全的。
2.禁止指令重新排序最佳化。
Volatile如何保證記憶體可見性:
1.當寫一個volatile變數時,JMM會把該執行緒對應的本地記憶體中的共享變數刷新到主內存。
2.當讀取一個volatile變數時,JMM會把該執行緒對應的本地記憶體置為無效。線程接下來將從主記憶體中讀取共享變數。
同步:就是一個任務的完成需要依賴另一個任務,只有等待被依賴的任務完成後,依賴任務才能完成。
非同步:不需要等待被依賴的任務完成,只是通知被依賴的任務要完成什麼工作,只要自己任務完成了就算完成了,被依賴的任務是否完成會通知回來。 (非同步的特點就是通知)。打電話和發短信來比喻同步和非同步操作。
阻塞:CPU停下來等一個慢的操作完成以後,才會接著完成其他的工作。
非阻塞:非阻塞就是在這個慢的執行時,CPU去做其他工作,等這個慢的完成後,CPU才會接著完成後續的操作。
非阻塞會造成執行緒切換增加,增加CPU的使用時間能不能補償系統的切換成本需要考慮。
CAS(Compare And Swap) 無鎖定演算法: CAS是樂觀鎖技術,當多個執行緒嘗試使用CAS同時更新同一個變數時,只有其中一個執行緒能更新變數的值,而其它線程都失敗,失敗的線程並不會被掛起,而是被告知這次競爭中失敗,並且可以再次嘗試。 CAS有3個運算元,記憶體值V,舊的預期值A,要修改的新值B。當且僅當預期值A和記憶體值V相同時,將記憶體值V修改為B,否則什麼都不做。
執行緒池的作用: 在程式啟動的時候就建立若干執行緒來回應處理,它們稱為執行緒池,裡面的執行緒叫做工作執行緒
第一:降低資源消耗。透過重複利用已建立的執行緒來降低執行緒建立和銷毀造成的消耗。
第二:提高反應速度。當任務到達時,任務可以不需要等到執行緒建立就能立即執行。
第三:提高執行緒的可管理性。
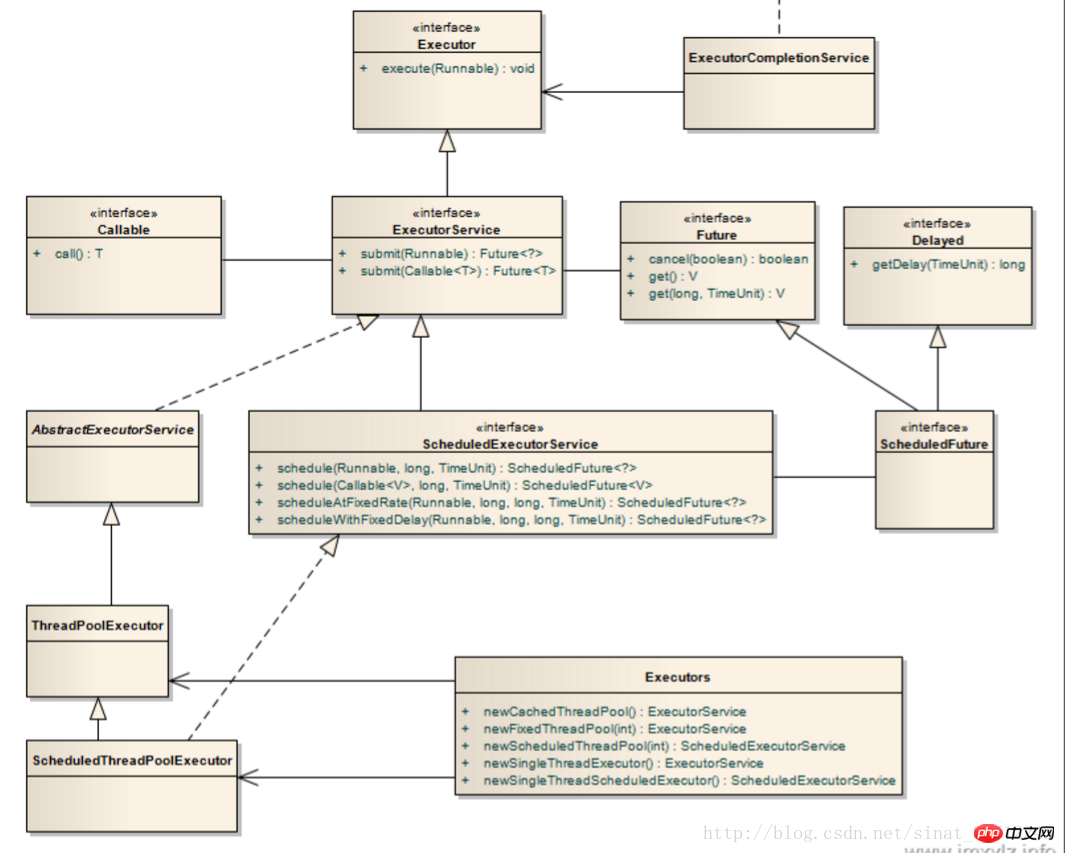
常用執行緒池:ExecutorService 是主要的實作類,其中常用的有 Executors.newSingleThreadPool(),newFixedThreadPool(),newcachedTheadPool(),newScheduledThreadPool()。
類別載入器工作機制:
1.裝載:將Java二進位程式碼匯入jvm中,產生Class檔案。
2.連接:a)校驗:檢查載入Class檔案資料的正確性b)準備:給類別的靜態變數分配儲存空間c)解析:將符號引用轉成直接引用
3:初始化:對類別的靜態變數,靜態方法和靜態程式碼區塊執行初始化工作。
雙親委派模型:類別載入器收到類別載入請求,首先將請求委派給父類別載入器完成使用者自訂載入器->應用程式載入器->擴充類別載入器->啟動類加載器。
一致性雜湊:
Memcahed快取:
資料結構:key,value對
使用方法:get,put等方法
Redis資料結構: String—字串(key-value 類型)
Hash—字典(hashmap) Redis的雜湊結構可以讓你像在資料庫中更新一個屬性一樣只修改某一項屬性值
List —列表實現訊息佇列
Set—集合利用唯一性
Sorted Set—有序集合可以進行排序可以實現資料持久化
java自動裝箱拆箱深入剖析
談談Java反射機制
如何寫一個不可變類別?
索引:B ,B-,全文索引
Mysql的索引是一個資料結構,旨在使資料庫高效的查找資料。
常用的資料結構是B Tree,每個葉子節點不但存放了索引鍵的相關資訊還增加了指向相鄰葉子節點的指針,這樣就形成了帶有順序訪問指針的B Tree,做這個優化的目的是提高不同區間存取的效能。
什麼時候使用索引:
經常出現在group by,order by和distinc關鍵字後面的欄位
經常與其他表進行連接的表,在連接字段上應該建立索引
經常出現在Where子句中的字段
經常出現用作查詢選擇的欄位
Spring IOC (控制反轉,依賴注入)
Spring支援三種依賴注入方式,分別是屬性(Setter方法)注入,建構注入和介面注入。
在Spring中,那些組成應用的主體及由Spring IOC容器所管理的物件被稱之為Bean。
Spring的IOC容器透過反射的機制實例化Bean並建立Bean之間的依賴關係。
簡單地講,Bean就是由Spring IOC容器初始化、組裝及被管理的物件。
取得Bean物件的過程,先透過Resource載入設定檔並啟動IOC容器,然後透過getBean方法取得bean對象,就可以呼叫他的方法。
Spring Bean的作用域:
Singleton:Spring IOC容器中只有一個共享的Bean實例,一般都是Singleton作用域。
Prototype:每一個請求,都會產生一個新的Bean實例。
Request:每次http請求都會產生一個新的Bean實例。
代理程式的共同優點:業務類別只需要專注於業務邏輯本身,並保證了業務類別的重複使用性。
Java靜態代理:
代理物件和目標物件實作了相同的接口,目標物件作為代理物件的屬性,具體介面實作中,代理物件可以在呼叫目標物件對應方法前後加上其他業務處理邏輯。
缺點:一個代理類別只能代理一個業務類別。如果業務類別增加方法時,對應的代理類別也要增加方法。
Java動態代理:
Java動態代理是寫一個類別實作InvocationHandler接口,重寫Invoke方法,在Invoke方法可以進行增強處理的邏輯的編寫,這個公共代理類別在運行的時候才能明確自己要代理的對象,同時可以實現該被代理類別的方法的實現,然後在實現類別方法的時候可以進行增強處理。
實際上:代理物件的方法= 增強處理被代理物件的方法
JDK和CGLIB產生動態代理類別的區別:
JDK動態代理只能針對實作了介面的類別產生代理(實例化一個類別)。此時代理對象和目標對象實現了相同的接口,目標對像作為代理對象的一個屬性,具體接口實現中,可以在調用目標對象相應方法前後加上其他業務處理邏輯
CGLIB是針對類實現代理,主要是對指定的類別產生一個子類別(沒有實例化一個類別),覆蓋其中的方法。
Spring AOP應用場景
效能偵測,存取控制,日誌管理,交易等。
預設的策略是如果目標類別實作接口,則使用JDK動態代理技術,如果目標物件沒有實作接口,則預設會採用CGLIB代理
SpringMVC運作原理
-
#客戶端請求提交到DispatcherServlet
由DispatcherServlet控制器查詢HandlerMapping,找到並分發到指定的Controller。
Controller呼叫業務邏輯處理後,傳回ModelAndView
#DispatcherServlet查詢一個或多個ViewResoler視圖解析器,找到ModelAndView指定的視圖
視圖負責將結果顯示到客戶端
一個Http請求
DNS網域解析–> 發起TCP的三次握手–> ; 建立TCP連線後發起http請求–> 伺服器回應http請求,瀏覽器得到 html程式碼–>瀏覽器解析html程式碼,並請求html程式碼中的資源(如javascript、css、圖片等) –>瀏覽器對頁面進行渲染呈現給使用者
設計儲存海量資料的儲存系統:設計一個叫做「中間層」的一個邏輯層,在這個層,將資料庫的海量資料抓出來,做成緩存,運行在伺服器的記憶體中,同理,當有新的資料到來,也先做成緩存,再想辦法,持久化到資料庫中,這是一個簡單的思路。主要的步驟是負載平衡,將不同使用者的請求分發到不同的處理節點上,然後先存入緩存,定時向主資料庫更新資料。讀寫的過程採用類似樂觀鎖的機制,可以一直讀(寫資料的時候也可以),但是每次讀的時候會有個版本的標記,如果本次讀的版本低於快取的版本,會重新讀數據,這樣的情況不多,可以忍受。
Session與Cookie:Cookie可以讓服務端追蹤每個客戶端的訪問,但是每次客戶端的訪問都必須傳回這些Cookie,如果Cookie很多,則無形的增加了客戶端與服務端的資料傳輸量,
而Session則很好地解決了這個問題,同一個客戶端每次和服務端交互時,將資料存儲通過Session到服務端,不需要每次都傳回所有的Cookie值,而是傳回一個ID,每個客戶端第一次存取伺服器產生的唯一的ID,客戶端只要傳回這個ID就行了,這個ID通常為NAME為JSESSIONID的一個Cookie。這樣服務端就可以透過這個ID,來將儲存到服務端的KV值取出了。
Session和Cookie的逾時問題,Cookie的安全性問題
分散式Session框架
配置伺服器,Zookeeper叢集管理伺服器可以統一管理所有伺服器的配置檔案
共享這些Session儲存在一個分散式快取中,可以隨時寫入和讀取,而且效能要很好,如Memcache,Tair。
封裝一個類別繼承自HttpSession,將Session存入這個類別然後再存入分散式快取中
由於Cookie不能跨域訪問,要實現Session同步,要同步SessionID寫到不同網域下。
適配器模式:將一個介面適配器到另一個接口,Java I/O中InputStreamReader將Reader類別轉接到InputStream,從而實現了位元組流到字元流的準換。
裝飾者模式:保持原來的接口,增強原來有的功能。
FileInputStream 實作了InputStream的所有接口,BufferedInputStreams繼承自FileInputStream是具體的裝飾器實作者,將InputStream讀取的內容保存在記憶體中,而提高讀取的效能。
Spring事務配置方法:
1.切點信息,用於定位實施事物切面的業務類方法
2.控制事務行為的事務屬性,這些屬性包括事物隔離級別,事務傳播行為,超時時間,回滾規則。
Spring透過aop/tx Schema 命名空間和@Transaction註解技術來進行宣告式事物配置。
Mybatis
每一個Mybatis的應用程式都以一個SqlSessionFactory物件的實例為核心。首先用位元組流透過Resource將設定檔讀入,然後透過SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build方法建立SqlSessionFactory,然後透過SqlSessionFactory.openSession()方法建立一個SqlSession為每個資料庫事務服務。
經歷了Mybatis初始化–>創建SqlSession –>運行SQL語句,返回結果三個過程
Servlet和Filter的區別:
整的流程是:Filter對用戶請求進行預處理,接著將請求交給Servlet進行處理並產生回應,最後Filter再對伺服器回應進行後處理。
Filter有以下幾個用途:
Filter可以進行對特定的url請求和相應做預處理和後處理。
在HttpServletRequest到達Servlet之前,攔截客戶的HttpServletRequest。
根據需要檢查HttpServletRequest,也可以修改HttpServletRequest頭和資料。
在HttpServletResponse到達客戶端之前,攔截HttpServletResponse。
根據需要檢查HttpServletResponse,也可以修改HttpServletResponse頭和資料。
其實Filter和Servlet極為相似,差別只是Filter不能直接對使用者產生回應。實際上Filter裡doFilter()方法裡的程式碼就是從多個Servlet的service()方法裡抽取的通用程式碼,透過使用Filter可以實現更好的複用。
Filter和Servlet的生命週期:
1.Filter在web伺服器啟動時初始化
2.如果某個Servlet配置了1 ,該Servlet也是在Tomcat(Servlet容器)啟動時初始化。
3.如果Servlet沒有配置1 ,則該Servlet不會在Tomcat啟動時初始化,而是在請求到來時初始化。
4.每次請求, Request都會被初始化,回應請求後,請求被銷毀。
5.Servlet初始化後,將不會隨著請求的結束而註銷。
6.關閉Tomcat時,Servlet、Filter依序被註銷。
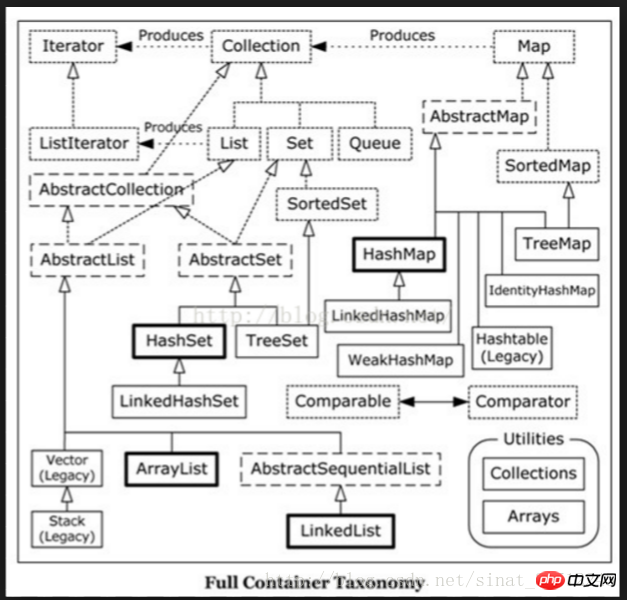
HashMap與HashTable的差異。
1、HashMap是非線程安全的,HashTable是線程安全的。
2、HashMap的鍵和值都允許null值存在,而HashTable則不行。
3、因為執行緒安全的問題,HashMap效率比HashTable的還要高。
HashMap的實作機制:
維護一個每個元素是一個鍊錶的數組,而且鍊錶中的每個節點都是一個Entry[]鍵值對的資料結構。
實現了陣列 鍊錶的特性,查找快,插入刪除也快。
對於每個key,他對應的陣列索引下標是int i = hash(key.hashcode)&(len-1);
-
每個新加入的節點放在鍊錶首,然後該新加入的節點指向原始鍊錶首
HashMap和TreeMap區別
HashMap衝突
HashMap,ConcurrentHashMap與LinkedHashMap的差異
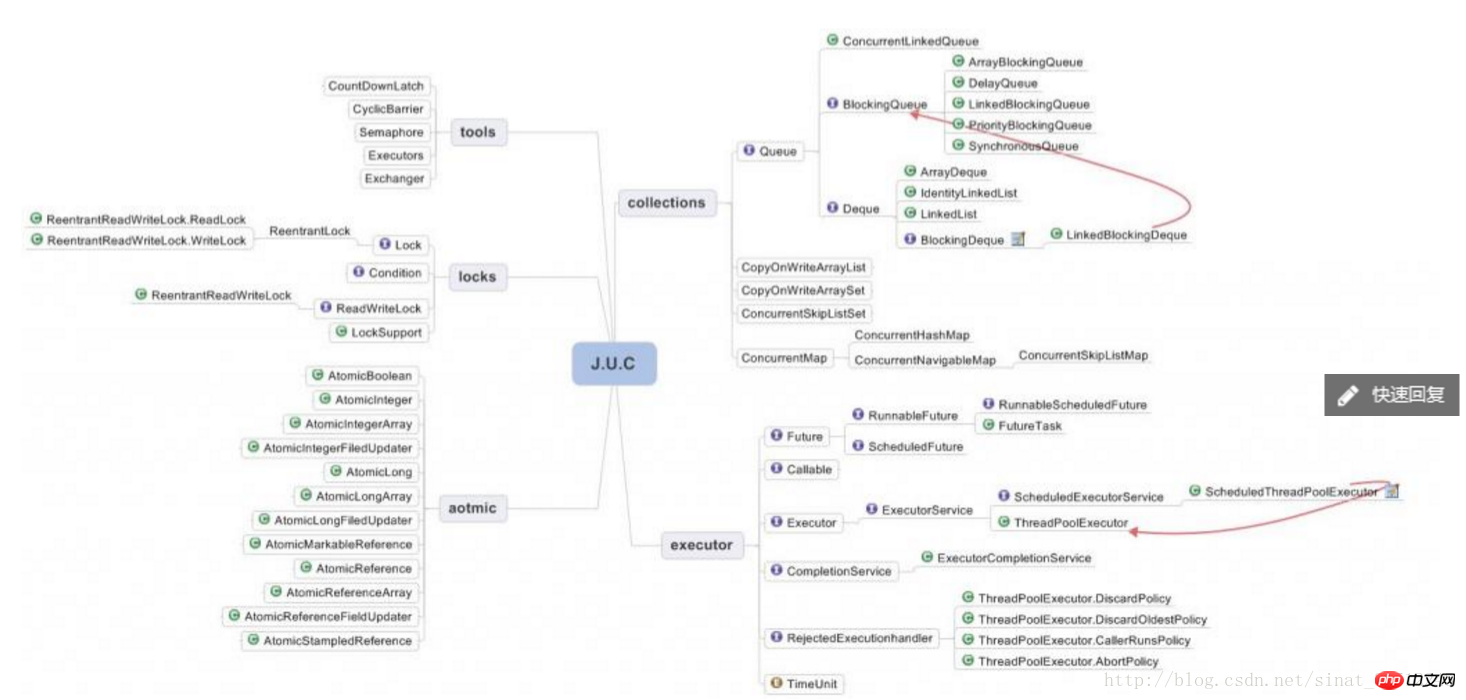
ConcurrentHashMap是使用了鎖分段技術技術來確保線程安全的,鎖分段技術:首先將資料分成一段一段的存儲,然後給每一段資料配一把鎖,當一個當執行緒佔用鎖定存取其中一個段資料的時候,其他段的資料也能被其他執行緒存取
#ConcurrentHashMap 是在每個區段(segment)中執行緒安全的
LinkedHashMap維護一個雙鍊錶,可以將裡面的資料按寫入的順序讀出
ConcurrentHashMap應用場景
1:ConcurrentHashMap的應用場景是高並發,但是並不能保證線程安全,而同步的HashMap和HashMap的是鎖住整個容器,而加鎖之後ConcurrentHashMap不需要鎖住整個容器,只需要鎖住對應的Segment就好了,所以可以保證高並發同步訪問,提升了效率。
2:可以多執行緒寫。
ConcurrentHashMap把HashMap分成若干Segmenet
1.get時,不加鎖,先定位到segment然後在找到頭結點進行讀取操作。而value是volatile變量,所以可以保證在競爭條件時保證讀取最新的值,如果讀到的value是null,則可能正在修改,那麼就調用ReadValueUnderLock函數,加鎖保證讀到的數據是正確的。
2.Put時會加鎖,一律加到hash鏈的頭部。
3.Remove時也會加鎖,由於next是final型別無法改變,所以必須把刪除的節點之前的節點都複製一遍。
4.ConcurrentHashMap允許多個修改操作並發進行,其關鍵在於使用了鎖定分離技術。它使用了多個鎖來控制Hash表的不同Segment進行的修改。
ConcurrentHashMap的應用場景是高並發,但是並不能保證線程安全,而同步的HashMap和HashTable的是鎖住整個容器,而加鎖之後ConcurrentHashMap不需要鎖住整個容器,只需要鎖住對應的segment就好了,所以可以保證高並發同步訪問,提升了效率。
ConcurrentHashMap能夠保證每一次呼叫都是原子操作,但是不保證多次呼叫之間也是原子操作。
Vector和ArrayList的區別
ExecutorService service = Executors…. ExecutorService service = new ThreadPoolExecutor() ExecutorService service = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor();
ecutor();ecutor(); ThreadPoolExecutor原始碼分析
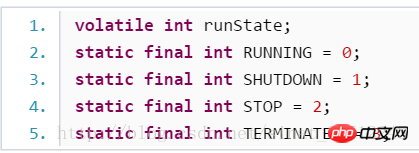
執行緒池本身的狀態:
#等待任務佇列與工作集:

#線程池的主要狀態鎖定:

線程池的存活時間和大小:

1.2 ThreadPoolExecutor 的內部工作原理
有了以上定義好的數據,以下來看看內部是如何實現的。 Doug Lea 的整個思路總結起來就是 5 句話:
如果當前池大小 poolSize 小於 corePoolSize ,則建立新執行緒執行任務。
如果目前池大小poolSize 大於corePoolSize ,且等待佇列未滿,則進入等待佇列
- ##如果目前池大小poolSize 大於corePoolSize 且小於maximumPoolSize ,且等待佇列已滿,則建立新執行緒執行任務。
- 如果目前池大小 poolSize 大於 corePoolSize 且大於 maximumPoolSize ,且等待佇列已滿,則呼叫拒絕策略來處理該任務。
- 執行緒池裡的每個執行緒執行完任務後不會立刻退出,而是會去檢查下等待佇列裡是否還有執行緒任務需要執行,如果在keepAliveTime 裡等不到新的任務了,那麼執行緒就會退出。
使用場景:CopyOnWriteArrayList適合使用在讀取操作遠大於寫入操作的場景裡,例如快取。
互斥至少有一個資源處於非共享狀態
存在並等待
非搶佔
循環等待
解決死鎖,第一個是死鎖預防,就是不讓上面的四個條件同時成立。二是,合理分配資源。
三是使用銀行家演算法,如果該行程請求的資源作業系統剩餘量可以滿足,那就分配。
進程間的通訊方式
管道( pipe ):管道是一種半雙工的通訊方式,資料只能單向流動,而且只能在具有親緣關係的進程間使用。進程的親緣關係通常是指父子進程關係。
有名管道 (named pipe) : 有名管道也是半雙工的通訊方式,但是它允許無親緣關係進程間的通訊。
信號量( semophore ) : 信號量是一個計數器,可以用來控制多個行程對共享資源的存取。它常作為一種鎖機制,防止某一行程正在存取共享資源時,其他行程也會存取該資源。因此,主要作為進程間以及同一進程內不同執行緒之間的同步手段。
訊息佇列( message queue ) : 訊息佇列是由訊息的鍊錶,存放在核心中並由訊息佇列標識符標識。訊息佇列克服了訊號傳遞訊息少、管道只能承載無格式位元組流以及緩衝區大小受限等缺點。
訊號 ( sinal ) : 訊號是一種比較複雜的通訊方式,用來通知接收程序某個事件已經發生。
共享記憶體( shared memory ) :共享記憶體就是映射一段能被其他進程所存取的內存,這段共享記憶體由一個進程創建,但多個進程都可以存取。共享記憶體是最快的 IPC 方式,它是針對其他進程間通訊方式運作效率低且專門設計的。它往往與其他通訊機制,如信號量,配合使用,來實現進程間的同步和通訊。
套接字( socket ) : 套解口也是一種進程間通訊機制,與其他通訊機制不同的是,它可用於不同機器間的進程通訊。
進程與執行緒的區別和聯繫
作業系統的進程調度演算法
電腦系統的層次儲存結構詳解
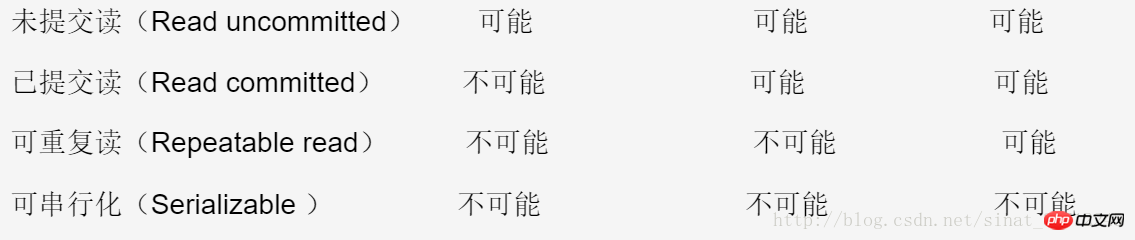
資料庫事務是指作為單個邏輯工作單元執行的一系列操作。
MySQL資料庫最佳化總結
MYSQL 最佳化常用方法
MySQL儲存引擎-MyISAM與InnoDB差異
關於SQL資料庫中的範式
Hibernate的一級快取是由Session提供的,因此它只存在於Session的生命週期中,當程式呼叫save(),update(),saveOrUpdate()等方法及呼叫查詢當介面list,filter,iterate時,如Session快取中還不存在對應的對象,Hibernate會把該對象加入到一級快取中,當Session關閉的時候快取也會消失。
Hibernate的一級快取是Session所內建的,不能被卸載,也不能進行任何配置一級快取採用的是key-value的Map方式來實現的,在快取實體物件時,物件的主關鍵字ID是Map的key,實體物件就是對應的值。
Hibernate二級快取:把獲得的所有資料物件根據ID放入到第二級快取中。 Hibernate二級快取策略,是針對於ID查詢的快取策略,刪除、更新、增加資料的時候,同時更新快取。
進程和執行緒的區別:
進程:每個行程都有獨立的程式碼和資料空間(進程上下文),進程間的切換會有較大的開銷,一個行程包含1–n個線程。
執行緒:同一類別執行緒共享程式碼和資料空間,每個執行緒有獨立的運行堆疊和程式計數器(PC),執行緒切換開銷小。
執行緒和進程一樣分為五個階段:建立、就緒、執行、阻塞、終止。
多進程是指作業系統能同時執行多個任務(程式)。
多執行緒是指在同一程式中有多個順序流在執行。
在java中要想實作多線程,有三種手段,一種是繼續Thread類,另外一種是實作Runable接口,還有就是實作Callable介面。
Switch能否用string做參數?
a.在 Java 7 之前, switch 只能支援byte,short,char,int 或其對應的封裝類別以及 Enum 類型。在Java 7中,String 支援被加上了。
Object有哪些公用方法?
a.方法equals測試的是兩個物件是否相等
b.方法clone進行物件拷貝
c.方法getClass傳回和目前物件相關的Class物件
d.方法notify,notifyall,wait都是用來對給定物件進行線程同步的
Java的四種引用,強弱軟弱,以及用到的場景
a. Use soft references and weak references to solve the OOM problem: use a HashMap to save the mapping relationship between the path of the image and the soft reference associated with the corresponding image object. When memory is insufficient, the JVM will automatically recycle these cached image objects. space occupied, thus effectively avoiding the OOM problem.
b. Implement caching of Java objects through soft-accessible object retrieval methods: For example, if we create an Employee class, if we need to query the information of an employee each time. Even if it was queried just a few seconds ago, it needs to rebuild an instance, which takes a lot of time. We can combine soft references and HashMap. First, save the reference: reference an instance of the Employee object in the form of a soft reference and save the reference to the HashMap. The key is the employee's id and the value is the soft reference of this object. , on the other hand, is to take out the reference and see if there is a soft reference to the Employee instance in the cache. If so, get it from the soft reference. If there is no soft reference, or the instance obtained from the soft reference is null, rebuild an instance and save the soft reference to the newly created instance.
c. Strong reference: If an object has a strong reference, it will not be recycled by the garbage collector. Even if the current memory space is insufficient, the JVM will not reclaim it, but will throw an OutOfMemoryError error, causing the program to terminate abnormally. If you want to break the association between a strong reference and an object, you can explicitly assign the reference to null, so that the JVM will recycle the object at the appropriate time.
d. Soft reference: When using soft reference, if there is enough memory space, the soft reference can continue to be used without being recycled by the garbage collector. Only when the memory is insufficient, the soft reference will Recycled by the garbage collector.
e. Weak reference: Objects with weak references have a shorter life cycle. Because when the JVM performs garbage collection, once a weak reference object is found, the weak reference will be recycled regardless of whether the current memory space is sufficient. However, since the garbage collector is a low-priority thread, it may not be able to quickly find weak reference objects.
f. Virtual reference: As the name suggests, it is in name only. If an object only holds a virtual reference, then it is equivalent to having no reference and may be recycled by the garbage collector at any time.
What is the difference between the function of Hashcode and equal?
a. It is also used to identify whether two objects are equal. There are two types of Java collections: list and set. Among them, set does not allow repeated implementation of elements. This method does not allow repeated implementation. If you use equal to For comparison, if there are 1000 elements and you create a new element, you need to call equal 1000 times to compare them one by one to see if they are the same object, which will greatly reduce efficiency. The hashcode actually returns the storage address of the object. If there is no element at this position, the element is stored directly above it. If an element already exists at this position, the equal method is called at this time to compare with the new element. If they are the same, they will not be Save it and hash it to another address.
The meaning and difference between Override and Overload
a.Overload, as the name suggests, is reloading. It can express the polymorphism of the class. It can be that the function can have the same function name but The parameter names, return values, and types cannot be the same; in other words, the parameters, types, and return values can be changed but the function name remains unchanged.
b. It means ride (rewrite). When the subclass inherits the parent class, the subclass can define a method with the same name and parameters as its parent class. When the subclass calls this function, it will be automatically called. Methods of subclasses, while parent classes are equivalent to being overridden (overridden).
For details, you can go to the example analysis of the difference between overloading and rewriting (overwriting) in C
The difference between abstract classes and interfaces
a. A class can only inherit a single class, but Multiple interfaces can be implemented
b. There can be constructors in abstract classes, but there cannot be constructors in interfaces
c. All methods in abstract classes do not have to be abstract, you can Choose to implement some basic methods in abstract classes. The interface requires that all methods must be abstract
d. Abstract classes can contain static methods, but interfaces cannot
e. Abstract classes can have ordinary member variables, and interfaces can Not allowed
The principles and characteristics of several methods of parsing XML: DOM, SAX, PULL
a.DOM: memory consumption: first read all xml documents into memory, and then use DOM API to access the tree structure and get data. This is very simple to write, but it consumes a lot of memory. If the data is too large and the phone is not powerful enough, the phone may crash directly
b.SAX: high parsing efficiency, small memory usage, event-driven: more simply put, it sequentially scans the document. When scanning Notify the event processing function when reaching the start and end of the document (document), the start and end of the element (element), the end of the document (document), etc., and the event processing function will take corresponding actions, and then continue the same scan until the end of the document.
c.PULL: Similar to SAX, it is also event-driven. We can call its next() method to get the next parsing event (that is, start document, end document, start tag, end tag). When at a certain When there is an element, you can call the getAttributte() method of XmlPullParser to get the value of the attribute, or you can call its nextText() to get the value of this node.
The difference between wait() and sleep()
sleep comes from the Thread class, and wait comes from the Object class
During the process of calling the sleep() method, the thread will not be released Object lock. The thread that calls the wait method will release the object lock.
Sleep does not give up system resources after sleep. Wait gives up system resources and other threads can occupy the CPU.
sleep(milliseconds) needs to specify a sleep time. It will automatically wake up as soon as it arrives
The difference between heap and stack in JAVA, let’s talk about Java’s memory mechanism
a. Basic data types, variables and object references are all allocated on the stack
b. Heap memory is used to store objects and arrays created by new
c. Class variables (statically modified variables), the program allocates memory for class variables in the heap when it is loaded. , the memory address in the heap is stored in the stack
d. Instance variables: When you use the java keyword new, the system allocates space to variables in the heap that is not necessarily continuous, but is allocated to variables based on scattered The heap memory address is converted into a long string of numbers through a hash algorithm to represent the "physical location" of this variable in the heap. The life cycle of the instance variable – when the reference to the instance variable is lost, it will be GC (garbage collector) Included in the recyclable "list", but the memory in the heap is not released immediately
e. Local variables: from being declared in a certain method or a certain code segment (such as a for loop) to executing it When the memory is allocated on the stack, when the local variable goes out of scope, the memory is released immediately
The implementation principle of JAVA polymorphism
a. Abstractly speaking, polymorphism means the same Messages can behave in many different ways depending on who they are sent to. (Sending a message is a function call)
b. The implementation principle is dynamic binding. The method called by the program is dynamically bound during the runtime. Tracing the source code can be found that the JVM finds the appropriate parameter through automatic transformation. Method.
Related recommendations:
Summary of Java collection interview questions and answers
Analysis of loading order of classes in Java (commonly used in interview questions)
以上是各大公司Java面試題目歸納整理(全)的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 五個常見的Go語言面試問題及解答
Jun 01, 2023 pm 08:10 PM
五個常見的Go語言面試問題及解答
Jun 01, 2023 pm 08:10 PM
作為近年來備受熱捧的程式語言,Go語言已成為許多公司與企業的面試熱點。對於Go語言初學者而言,在面試過程中遇到相關問題時,如何回答是一個值得探討的問題。以下列舉五個常見的Go語言面試題目及解答,供初學者參考。請介紹一下Go語言的垃圾回收機制是如何運作的? Go語言的垃圾回收機制是基於標記-清除演算法和三色標記演算法。當Go程式中的記憶體空間不夠用時,Go垃圾回收器
 2023年前端React面試題大總結(收藏)
Aug 04, 2020 pm 05:33 PM
2023年前端React面試題大總結(收藏)
Aug 04, 2020 pm 05:33 PM
php中文網作為知名程式設計學習網站,為您整理了一些React面試題,幫助前端開發人員準備和清除React面試障礙。
 2023年精選Web前端面試題大全及答案(收藏)
Apr 08, 2021 am 10:11 AM
2023年精選Web前端面試題大全及答案(收藏)
Apr 08, 2021 am 10:11 AM
本篇文章為大家總結一些值得收藏的精選Web前端面試題(附答案)。有一定的參考價值,有需要的朋友可以參考一下,希望對大家有幫助。
 50個你必須掌握的Angular面試題(收藏)
Jul 23, 2021 am 10:12 AM
50個你必須掌握的Angular面試題(收藏)
Jul 23, 2021 am 10:12 AM
這篇文章跟大家分享50個必須掌握的Angular面試題,會從初學者-中級-高級三個部分來解析這50個面試題,帶大家吃透它們!
 面試官:你對高並發了解多少?我:emmm...
Jul 26, 2023 pm 04:07 PM
面試官:你對高並發了解多少?我:emmm...
Jul 26, 2023 pm 04:07 PM
高並發,幾乎是每個程式設計師都想擁有的經驗。原因很簡單:隨著流量變大,會遇到各種各樣的技術問題,例如介面響應逾時、CPU load升高、GC頻繁、死鎖、大數據量儲存等等,這些問題能推動我們在技術深度上不斷精進。
 阿里終面:每天100w次登陸請求, 8G 內存該如何設定JVM參數?
Aug 15, 2023 pm 04:31 PM
阿里終面:每天100w次登陸請求, 8G 內存該如何設定JVM參數?
Aug 15, 2023 pm 04:31 PM
就在上週,一個同學在阿里雲技術面終面的時候被問到這麼一個問題:假設一個每天100w次登陸請求的平台,一個服務節點 8G 內存,該如何設置JVM參數?覺得回答的不太理想,過來找我複盤。
 2023年vue高頻面試題分享(附答案分析)
Aug 01, 2022 pm 08:08 PM
2023年vue高頻面試題分享(附答案分析)
Aug 01, 2022 pm 08:08 PM
本篇文章為大家總結一些值得收藏的2023年精選vue高頻面試題(附答案)。有一定的參考價值,有需要的朋友可以參考一下,希望對大家有幫助。
 看看這些前端面試題,帶你搞定高頻知識點(四)
Feb 20, 2023 pm 07:19 PM
看看這些前端面試題,帶你搞定高頻知識點(四)
Feb 20, 2023 pm 07:19 PM
每天10題,100天后,搞定所有前端面試的高頻知識點,加油! ! ! ,在看文章的同時,希望不要直接看答案,先思考一下自己會不會,如果會,自己的答案是什麼?想過之後再與答案比對,是不是會好一點,當然如果你有比我更好的答案,歡迎留言區留言,一起探討技術之美。






