java中多線程的一些基本方法的使用介紹(附範例)
本篇文章帶給大家的內容是關於java中多線程中的一些基本方法的使用介紹(附示例),有一定的參考價值,有需要的朋友可以參考一下,希望對你有所幫助。
線程睡眠sleep()
Thread.sleep(毫秒);我們可以透過sleep方法設定讓線程睡眠。可以看到sleep是個靜態方法
public static native void sleep(long var0) throws InterruptedException;
try {
System.out.println(new Date().getSeconds());
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println(new Date().getSeconds());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}setDaemon守護線程
非守護線程停止,那麼守護線程自動退出
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i ++) {
System.out.println("非守护线程");
}
}
};
Thread thread2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i < 200; i ++) {
System.out.println("守护线程");
}
}
};
thread2.setDaemon(true);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}可以很明顯的看到thread2本來應該執行200次輸出,但是這裡只輸出了幾行。因為當thread1執行完畢後,thread2作為守護線程就自動停止了。 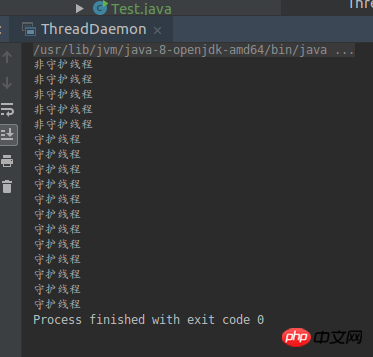
多線程jion
如果執行了jion方法,那麼就停止當前線程,先跑執行了jion()的線程。相當於插隊執行。如下,在執行thread2執行緒的時候,如果i==20的時候,則讓thread1插隊先執行
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Thread thread1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
for(int i = 0; i < 500; i ++) {
System.out.println("thread1---" + i);
}
}
};
Thread thread2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i < 200; i ++) {
if (i == 20) {
try {
//插队执行
thread1.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
};
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}join()方法也可以傳參數long 毫秒join(毫秒)
表示讓執行join的線程,插隊執行XXX毫秒,過了時間後,兩個線程交替執行
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Thread thread1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
for(int i = 0; i < 500; i ++) {
System.out.println("thread1---" + i);
}
}
};
Thread thread2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i < 200; i ++) {
if (i == 20) {
try {
//插队执行1毫秒
thread1.join(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
};
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}yeild 禮讓線程
yeild會讓出cpu,讓其他線程執行
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Thread thread1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
for(int i = 0; i < 500; i ++) {
System.out.println( getName() + "---" + i);
}
}
};
Thread thread2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i < 200; i ++) {
if (i % 5 == 0) {
Thread.yield();
}
System.out.println(getName() + "---" + i);
}
}
};
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}setPriority給執行緒設定優先權
預設優先權是5 最小1,最大10
越大優先權越高
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Thread thread1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
for(int i = 0; i < 500; i ++) {
System.out.println( getName() + "---" + i);
}
}
};
Thread thread2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i < 500; i ++) {
System.out.println(getName() + "---" + i);
}
}
};
//设置最大的线程优先级最大为10
thread1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
//设置最小的线程优先级,最小为1
thread2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}synchronized
同步程式碼區塊
當多執行緒並發,多段程式碼同時執行的時候。希望在執行其中程式碼的時候,cpu不切換執行緒
不用synchronized的情況
我們來看一下不用synchronized的情況會發生什麼
public class ThreadSynchronied {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Say say = new Say();
Thread thread1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i ++) {
say.say();
}
}
};
Thread thread2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i ++) {
say.say1();
}
}
};
//设置最大的线程优先级最大为10
thread1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
//设置最小的线程优先级,最小为1
thread2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
class Say {
void say() {
System.out.print("s ");
System.out.print("a ");
System.out.print("y ");
System.out.print("h ");
System.out.print("e ");
System.out.print("l ");
System.out.print("l ");
System.out.println("o");
}
void say1() {
System.out.print("1 ");
System.out.print("2 ");
System.out.print("3 ");
System.out.print("4 ");
System.out.print("5 ");
System.out.print("6 ");
System.out.print("7 ");
System.out.println("8");
}
}
我們發現有些輸出並沒有印出全,在執行緒thread1的過程中,cpu被thread2搶佔。這種情況下,肯定是不符合我們的業務邏輯的。所以我們要確保執行緒執行了一個完整的方法後,cpu才會被其他執行緒搶佔
使用synchronized
public class ThreadSynchronied {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Say say = new Say();
Thread thread1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i ++) {
say.say();
}
}
};
Thread thread2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i ++) {
say.say1();
}
}
};
//设置最大的线程优先级最大为10
thread1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
//设置最小的线程优先级,最小为1
thread2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
class Say {
String s = "hahaah";
void say() {
synchronized (s) {
System.out.print("s ");
System.out.print("a ");
System.out.print("y ");
System.out.print("h ");
System.out.print("e ");
System.out.print("l ");
System.out.print("l ");
System.out.println("o");
}
}
void say1() {
synchronized (s) {
System.out.print("1 ");
System.out.print("2 ");
System.out.print("3 ");
System.out.print("4 ");
System.out.print("5 ");
System.out.print("6 ");
System.out.print("7 ");
System.out.println("8");
}
}
}
使用synchronized同步程式碼區塊後,就發現不會出現上述情況了
同步方法
public class ThreadSynchroniedMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Say say = new Say();
Thread thread1 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i ++) {
say.say();
}
}
};
Thread thread2 = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i ++) {
say.say1();
}
}
};
//设置最大的线程优先级最大为10
thread1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
//设置最小的线程优先级,最小为1
thread2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
class Say {
//在方法上加锁
static synchronized void say() {
System.out.print("s ");
System.out.print("a ");
System.out.print("y ");
System.out.print("h ");
System.out.print("e ");
System.out.print("l ");
System.out.print("l ");
System.out.println("o");
}
static void say1() {
synchronized (Say.class) {
System.out.print("1 ");
System.out.print("2 ");
System.out.print("3 ");
System.out.print("4 ");
System.out.print("5 ");
System.out.print("6 ");
System.out.print("7 ");
System.out.println("8");
}
}
}同步方法指的就是在方法上加鎖
#靜態同步方法的所物件是該類別的字節碼物件
非靜態的同步方法鎖定物件是this
多個執行緒使用相同資源鎖,容易造成死鎖
什麼是死鎖?
#死鎖是指兩個或兩個以上的進程在執行過程中,由於競爭資源或由於彼此通信而造成的一種阻塞的現象,若無外力作用,它們都將無法推進下去。此時稱系統處於死鎖狀態或系統產生了死鎖,這些永遠在互相等待的進程稱為死鎖進程。
線程安全類別
Vector
StringBuffer
HashTable
線程不安全
ArrayList
StringBuilder
# HashSet
java.util.Collections中有synchronizedList等方法,支援我們把執行緒不安全的集合轉成線程安全的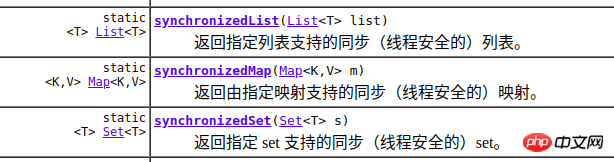
以上是java中多線程的一些基本方法的使用介紹(附範例)的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 PHP和Python:解釋了不同的範例
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP和Python:解釋了不同的範例
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP主要是過程式編程,但也支持面向對象編程(OOP);Python支持多種範式,包括OOP、函數式和過程式編程。 PHP適合web開發,Python適用於多種應用,如數據分析和機器學習。
 在PHP和Python之間進行選擇:指南
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
在PHP和Python之間進行選擇:指南
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP適合網頁開發和快速原型開發,Python適用於數據科學和機器學習。 1.PHP用於動態網頁開發,語法簡單,適合快速開發。 2.Python語法簡潔,適用於多領域,庫生態系統強大。
 PHP和Python:深入了解他們的歷史
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP和Python:深入了解他們的歷史
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP起源於1994年,由RasmusLerdorf開發,最初用於跟踪網站訪問者,逐漸演變為服務器端腳本語言,廣泛應用於網頁開發。 Python由GuidovanRossum於1980年代末開發,1991年首次發布,強調代碼可讀性和簡潔性,適用於科學計算、數據分析等領域。
 Python vs. JavaScript:學習曲線和易用性
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript:學習曲線和易用性
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python更適合初學者,學習曲線平緩,語法簡潔;JavaScript適合前端開發,學習曲線較陡,語法靈活。 1.Python語法直觀,適用於數據科學和後端開發。 2.JavaScript靈活,廣泛用於前端和服務器端編程。
 sublime怎麼運行代碼python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
sublime怎麼運行代碼python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
在 Sublime Text 中運行 Python 代碼,需先安裝 Python 插件,再創建 .py 文件並編寫代碼,最後按 Ctrl B 運行代碼,輸出會在控制台中顯示。
 vs code 可以在 Windows 8 中運行嗎
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
vs code 可以在 Windows 8 中運行嗎
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code可以在Windows 8上運行,但體驗可能不佳。首先確保系統已更新到最新補丁,然後下載與系統架構匹配的VS Code安裝包,按照提示安裝。安裝後,注意某些擴展程序可能與Windows 8不兼容,需要尋找替代擴展或在虛擬機中使用更新的Windows系統。安裝必要的擴展,檢查是否正常工作。儘管VS Code在Windows 8上可行,但建議升級到更新的Windows系統以獲得更好的開發體驗和安全保障。
 visual studio code 可以用於 python 嗎
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
visual studio code 可以用於 python 嗎
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code 可用於編寫 Python,並提供許多功能,使其成為開發 Python 應用程序的理想工具。它允許用戶:安裝 Python 擴展,以獲得代碼補全、語法高亮和調試等功能。使用調試器逐步跟踪代碼,查找和修復錯誤。集成 Git,進行版本控制。使用代碼格式化工具,保持代碼一致性。使用 Linting 工具,提前發現潛在問題。
 vscode在哪寫代碼
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
vscode在哪寫代碼
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
在 Visual Studio Code(VSCode)中編寫代碼簡單易行,只需安裝 VSCode、創建項目、選擇語言、創建文件、編寫代碼、保存並運行即可。 VSCode 的優點包括跨平台、免費開源、強大功能、擴展豐富,以及輕量快速。






