這篇文章帶給大家的內容是關於虛擬dom原理流程的分析與實現,有一定的參考價值,有需要的朋友可以參考一下,希望對你有幫助。
大家都知道,在網頁中瀏覽器資源開銷最大便是DOM節點了,DOM很慢而且非常龐大,網頁效能問題大多數都是有JavaScript修改DOM所引起的。我們使用Javascript來操縱DOM,操作效率往往很低,由於DOM被表示為樹結構,每次DOM中的某些內容都會發生變化,因此對DOM的更改非常快,但更改後的元素,並且它的子項目必須經過Reflow / Layout階段,然後瀏覽器必須重新繪製更改,這很慢的。因此,回流/重繪的次數越多,您的應用程式就越卡頓。但是,Javascript運作速度很快,虛擬DOM是放在JS 和 HTML中間的一個層。它可以透過新舊DOM的對比,來獲得對比之後的差異對象,然後有針對性的把差異部分真正地渲染到頁面上,從而減少實際DOM操作,最終達到性能優化的目的。
簡單概括有三點:
#用JavaScript模擬DOM樹,並且渲染這個DOM樹
比較新舊DOM樹,得到比較的差異物件
把差異物件套用到渲染的DOM樹。
下面是流程圖:
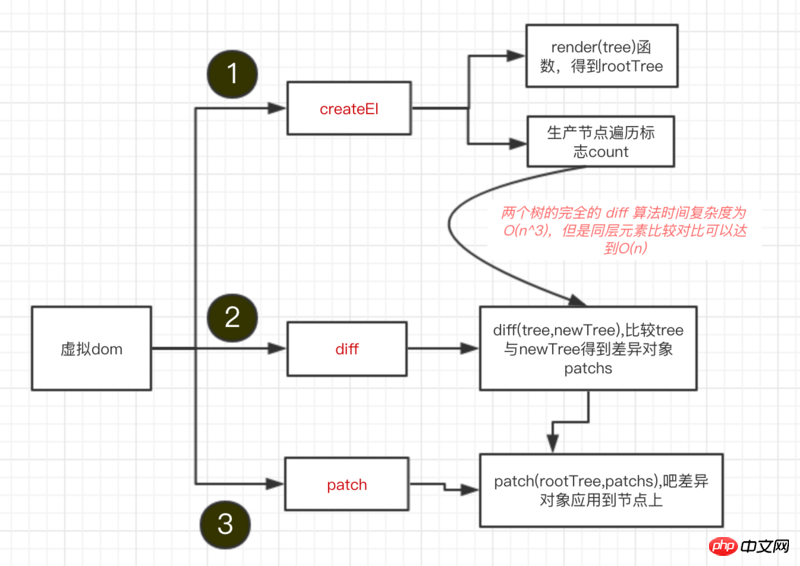
#下面我們用程式碼一步步去實作一個流程圖
其實虛擬DOM,就是用JS物件結構的一種映射,下面我們一步一步實現這個過程。
我們用JS很容易模擬一個DOM樹的結構,例如用這樣的一個函數createEl(tagName, props, children)來建立DOM結構。
tagName標籤名稱、props是屬性的物件、children是子節點。
然後渲染到頁面上,程式碼如下:
const createEl = (tagName, props, children) => new CreactEl(tagName, props, children)
const vdom = createEl('p', { 'id': 'box' }, [
createEl('h1', { style: 'color: pink' }, ['I am H1']),
createEl('ul', {class: 'list'}, [createEl('li', ['#list1']), createEl('li', ['#list2'])]),
createEl('p', ['I am p'])
])
const rootnode = vdom.render()
document.body.appendChild(rootnode)透過上面的函數,呼叫vdom.render()這樣子我們就很好的建構瞭如下所示的一個DOM樹,然後渲染到頁面上
<div id="box">
<h1 style="color: pink;">I am H1</h1>
<ul class="list">
<li>#list1</li>
<li>#list2</li>
</ul>
<p>I am p</p>
</div>下面我們看看CreactEl.js程式碼流程:
import { setAttr } from './utils'
class CreateEl {
constructor (tagName, props, children) {
// 当只有两个参数的时候 例如 celement(el, [123])
if (Array.isArray(props)) {
children = props
props = {}
}
// tagName, props, children数据保存到this对象上
this.tagName = tagName
this.props = props || {}
this.children = children || []
this.key = props ? props.key : undefined
let count = 0
this.children.forEach(child => {
if (child instanceof CreateEl) {
count += child.count
} else {
child = '' + child
}
count++
})
// 给每一个节点设置一个count
this.count = count
}
// 构建一个 dom 树
render () {
// 创建dom
const el = document.createElement(this.tagName)
const props = this.props
// 循环所有属性,然后设置属性
for (let [key, val] of Object.entries(props)) {
setAttr(el, key, val)
}
this.children.forEach(child => {
// 递归循环 构建tree
let childEl = (child instanceof CreateEl) ? child.render() : document.createTextNode(child)
el.appendChild(childEl)
})
return el
}
}上面render函數的功能是把節點創建好,然後設定節點屬性,最後遞歸創建。這樣子我們就得到一個DOM樹,然後插入(appendChild)到頁面上。
上面,我們已經創建了一個DOM樹,然後在創建一個不同的DOM樹,然後做比較,得到比較的差異對象。
比較兩棵DOM樹的差異,是虛擬DOM的最核心部分,這也是人們常說的虛擬DOM的diff演算法,兩顆完全的樹差異比較一個時間複雜度為O(n^ 3)。但在我們的web中很少用到跨層級DOM樹的比較,所以一個層級跟一個層級對比,這樣演算法複雜度就可以達到 O(n)。如下圖
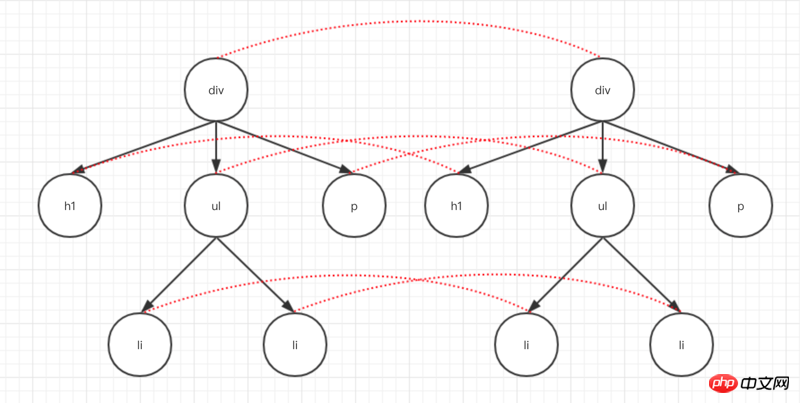
其實在程式碼中,我們會從根節點開始標誌遍歷,遍歷的時候把每個節點的差異(包括文字不同,屬性不同,節點不同)記錄保存起來。如下圖:
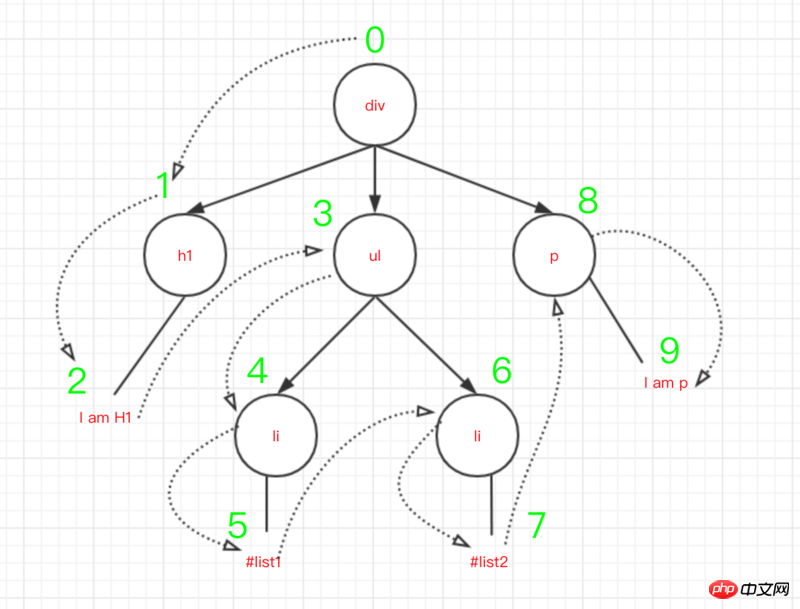
兩個節點之間的差異有總結起來有下面4種
0 直接替换原有节点 1 调整子节点,包括移动、删除等 2 修改节点属性 3 修改节点文本内容
如下列兩棵樹比較,把差異記錄下來。
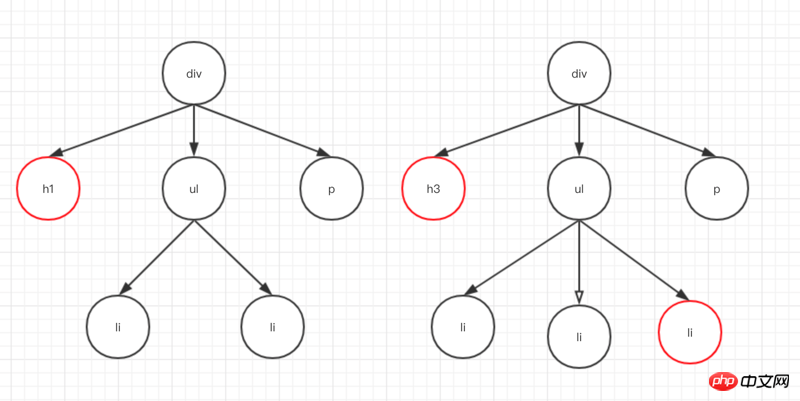
主要是履歷表一個遍歷index(看圖3),然後從根節點開始比較,比較萬之後記錄差異對象,繼續從左子樹比較,記錄差異,一直遍歷下去。主要流程如下
// 这是比较两个树找到最小移动量的算法是Levenshtein距离,即O(n * m)
// 具体请看 https://www.npmjs.com/package/list-diff2
import listDiff from 'list-diff2'
// 比较两棵树
function diff (oldTree, newTree) {
// 节点的遍历顺序
let index = 0
// 在遍历过程中记录节点的差异
let patches = {}
// 深度优先遍历两棵树
deepTraversal(oldTree, newTree, index, patches)
// 得到的差异对象返回出去
return patches
}
function deepTraversal(oldNode, newNode, index, patches) {
let currentPatch = []
// ...中间有很多对patches的处理
// 递归比较子节点是否相同
diffChildren(oldNode.children, newNode.children, index, patches, currentPatch)
if (currentPatch.length) {
// 那个index节点的差异记录下来
patches[index] = currentPatch
}
}
// 子数的diff
function diffChildren (oldChildren, newChildren, index, patches, currentPatch) {
const diffs = listDiff(oldChildren, newChildren)
newChildren = diffs.children
// ...省略记录差异对象
let leftNode = null
let currentNodeIndex = index
oldChildren.forEach((child, i) => {
const newChild = newChildren[i]
// index相加
currentNodeIndex = (leftNode && leftNode.count) ? currentNodeIndex + leftNode.count + 1 : currentNodeIndex + 1
// 深度遍历,递归
deepTraversal(child, newChild, currentNodeIndex, patches)
// 从左树开始
leftNode = child
})
}然後我們調用完diff(tree, newTree)等到最後的差異物件是這樣子的。
{
"1": [
{
"type": 0,
"node": {
"tagName": "h3",
"props": {
"style": "color: green"
},
"children": [
"I am H1"
],
"count": 1
}
}
]
...
}key是代表那個節點,這裡我們是第二個,也就是h1會改成h3,還有省略的兩個差異物件程式碼沒有貼出來~~
然後看diff.js的完整程式碼,如下
import listDiff from 'list-diff2'
// 每个节点有四种变动
export const REPLACE = 0 // 替换原有节点
export const REORDER = 1 // 调整子节点,包括移动、删除等
export const PROPS = 2 // 修改节点属性
export const TEXT = 3 // 修改节点文本内容
export function diff (oldTree, newTree) {
// 节点的遍历顺序
let index = 0
// 在遍历过程中记录节点的差异
let patches = {}
// 深度优先遍历两棵树
deepTraversal(oldTree, newTree, index, patches)
// 得到的差异对象返回出去
return patches
}
function deepTraversal(oldNode, newNode, index, patches) {
let currentPatch = []
if (newNode === null) { // 如果新节点没有的话直接不用比较了
return
}
if (typeof oldNode === 'string' && typeof newNode === 'string') {
// 比较文本节点
if (oldNode !== newNode) {
currentPatch.push({
type: TEXT,
content: newNode
})
}
} else if (oldNode.tagName === newNode.tagName && oldNode.key === newNode.key) {
// 节点类型相同
// 比较节点的属性是否相同
let propasPatches = diffProps(oldNode, newNode)
if (propasPatches) {
currentPatch.push({
type: PROPS,
props: propsPatches
})
}
// 递归比较子节点是否相同
diffChildren(oldNode.children, newNode.children, index, patches, currentPatch)
} else {
// 节点不一样,直接替换
currentPatch.push({ type: REPLACE, node: newNode })
}
if (currentPatch.length) {
// 那个index节点的差异记录下来
patches[index] = currentPatch
}
}
// 子数的diff
function diffChildren (oldChildren, newChildren, index, patches, currentPatch) {
var diffs = listDiff(oldChildren, newChildren)
newChildren = diffs.children
// 如果调整子节点,包括移动、删除等的话
if (diffs.moves.length) {
var reorderPatch = {
type: REORDER,
moves: diffs.moves
}
currentPatch.push(reorderPatch)
}
var leftNode = null
var currentNodeIndex = index
oldChildren.forEach((child, i) => {
var newChild = newChildren[i]
// index相加
currentNodeIndex = (leftNode && leftNode.count) ? currentNodeIndex + leftNode.count + 1 : currentNodeIndex + 1
// 深度遍历,从左树开始
deepTraversal(child, newChild, currentNodeIndex, patches)
// 从左树开始
leftNode = child
})
}
// 记录属性的差异
function diffProps (oldNode, newNode) {
let count = 0 // 声明一个有没没有属性变更的标志
const oldProps = oldNode.props
const newProps = newNode.props
const propsPatches = {}
// 找出不同的属性
for (let [key, val] of Object.entries(oldProps)) {
// 新的不等于旧的
if (newProps[key] !== val) {
count++
propsPatches[key] = newProps[key]
}
}
// 找出新增的属性
for (let [key, val] of Object.entries(newProps)) {
if (!oldProps.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
count++
propsPatches[key] = val
}
}
// 没有新增 也没有不同的属性 直接返回null
if (count === 0) {
return null
}
return propsPatches
}得到差異物件之後,剩下就是把差異物件應用到我們的dom節點上面了。
到了這裡其實簡單多了。我們上面得到的差異對象之後,然後選擇同樣的深度遍歷,如果那個節點有差異的話,判斷是上面4種中的哪一種,根據差異對象直接修改這個節點就可以了。
function patch (node, patches) {
// 也是从0开始
const step = {
index: 0
}
// 深度遍历
deepTraversal(node, step, patches)
}
// 深度优先遍历dom结构
function deepTraversal(node, step, patches) {
// 拿到当前差异对象
const currentPatches = patches[step.index]
const len = node.childNodes ? node.childNodes.length : 0
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const child = node.childNodes[i]
step.index++
deepTraversal(child, step, patches)
}
//如果当前节点存在差异
if (currentPatches) {
// 把差异对象应用到当前节点上
applyPatches(node, currentPatches)
}
}這樣子,呼叫patch(rootnode, patches)就直接有針對性的改變有差異的節點了。
path.js完整程式碼如下:
import {REPLACE, REORDER, PROPS, TEXT} from './diff'
import { setAttr } from './utils'
export function patch (node, patches) {
// 也是从0开始
const step = {
index: 0
}
// 深度遍历
deepTraversal(node, step, patches)
}
// 深度优先遍历dom结构
function deepTraversal(node, step, patches) {
// 拿到当前差异对象
const currentPatches = patches[step.index]
const len = node.childNodes ? node.childNodes.length : 0
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const child = node.childNodes[i]
step.index++
deepTraversal(child, step, patches)
}
//如果当前节点存在差异
if (currentPatches) {
// 把差异对象应用到当前节点上
applyPatches(node, currentPatches)
}
}
// 把差异对象应用到当前节点上
function applyPatches(node, currentPatches) {
currentPatches.forEach(currentPatch => {
switch (currentPatch.type) {
// 0: 替换原有节点
case REPLACE:
var newNode = (typeof currentPatch.node === 'string') ? document.createTextNode(currentPatch.node) : currentPatch.node.render()
node.parentNode.replaceChild(newNode, node)
break
// 1: 调整子节点,包括移动、删除等
case REORDER:
moveChildren(node, currentPatch.moves)
break
// 2: 修改节点属性
case PROPS:
for (let [key, val] of Object.entries(currentPatch.props)) {
if (val === undefined) {
node.removeAttribute(key)
} else {
setAttr(node, key, val)
}
}
break;
// 3:修改节点文本内容
case TEXT:
if (node.textContent) {
node.textContent = currentPatch.content
} else {
node.nodeValue = currentPatch.content
}
break;
default:
throw new Error('Unknow patch type ' + currentPatch.type);
}
})
}
// 调整子节点,包括移动、删除等
function moveChildren (node, moves) {
let staticNodelist = Array.from(node.childNodes)
const maps = {}
staticNodelist.forEach(node => {
if (node.nodeType === 1) {
const key = node.getAttribute('key')
if (key) {
maps[key] = node
}
}
})
moves.forEach(move => {
const index = move.index
if (move.type === 0) { // 变动类型为删除的节点
if (staticNodeList[index] === node.childNodes[index]) {
node.removeChild(node.childNodes[index]);
}
staticNodeList.splice(index, 1);
} else {
let insertNode = maps[move.item.key]
? maps[move.item.key] : (typeof move.item === 'object')
? move.item.render() : document.createTextNode(move.item)
staticNodelist.splice(index, 0, insertNode);
node.insertBefore(insertNode, node.childNodes[index] || null)
}
})
}到这里,最基本的虚拟DOM原理已经讲完了,也简单了实现了一个虚拟DOM.
以上是虛擬dom原理流程的分析與實現的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

