線程同步有幾種方法

執行緒同步的方法有哪些?在linux下,系統提供了很多種方式來實現線程同步,其中最常用的便是互斥鎖、條件變量和信號量這三種方式,可能還有很多夥伴對於這三種方法都不熟悉,下面就給大家詳細介紹下。
Linux下實作執行緒同步的三種方法:
一、互斥鎖(mutex)
#透過鎖機制實現線程間的同步。
1、初始化鎖定。在Linux下,執行緒的互斥資料型別是pthread_mutex_t。在使用前,要對它進行初始化。
靜態分配:pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
動態分配:int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *mutex,const pthread_mutex_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *mutex #2、加鎖。對共享資源的訪問,要對互斥量進行加鎖,如果互斥量已經上了鎖,調用線程會阻塞,直到互斥量被解鎖。
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex *mutex);
int pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
3、解鎖。在完成了共享資源的存取後,要解鎖互斥量。
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
4、銷毀鎖定。鎖在是使用完成後,需要銷毀以釋放資源。
int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex *mutex);
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
int tmp;
void* thread(void *arg)
{
cout << "thread id is " << pthread_self() << endl;
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
tmp = 12;
cout << "Now a is " << tmp << endl;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
pthread_t id;
cout << "main thread id is " << pthread_self() << endl;
tmp = 3;
cout << "In main func tmp = " << tmp << endl;
if (!pthread_create(&id, NULL, thread, NULL))
{
cout << "Create thread success!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Create thread failed!" << endl;
}
pthread_join(id, NULL);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
//编译:g++ -o thread testthread.cpp -lpthread相關推薦:《
PHP入門教學
與互斥鎖不同,條件變數是用來等待而不是用來上鎖的。條件變數用來自動阻塞一個線程,直到某個特殊情況發生為止。通常條件變數和互斥鎖同時使用。條件變數分為兩部分: 條件和變數。條件本身是由互斥量保護的。線程在改變條件狀態前先要鎖住互斥。條件變數使我們可以睡眠等待某種條件出現。條件變數是利用執行緒間共享的全域變數進行同步的一種機制,主要包括兩個動作:一個執行緒等待「條件變數的條件成立」而掛起;另一個執行緒使「條件成立」(給出條件成立訊號).條件的檢測是在互斥鎖的保護下進行的。如果一個條件為假,則一個執行緒自動阻塞,並釋放等待狀態改變的互斥鎖。如果另一個線程改變了條件,它發出訊號給關聯的條件變量,喚醒一個或多個等待它的線程,重新獲得互斥鎖,重新評價條件。如果兩個行程共享可讀寫的內存,條件變數可以用來實現這兩個行程間的執行緒同步。
1、初始化條件變數。
靜態態初始化,pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIER;
動態初始化,int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *cond,pthread_condatt_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *cond,pthread_condatt_t_t *con##r_t); #2、等待條件成立。釋放鎖,同時阻塞等待條件變數為真才行。 timewait()設置等待時間,仍未signal,返回ETIMEOUT(加鎖保證只有一個線程wait)
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
int pthread_cond_timewait(pthread_cond_t *cond,pthread_mutex *mutex,const timespec *abstime);
##int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_tcon
4、清除條件變數。無線程等待,否則返回EBUSY
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);
[cpp] view plain copy
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "unistd.h"
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
void hander(void *arg)
{
free(arg);
(void)pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
void *thread1(void *arg)
{
pthread_cleanup_push(hander, &mutex);
while(1)
{
printf("thread1 is running\n");
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);
printf("thread1 applied the condition\n");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(4);
}
pthread_cleanup_pop(0);
}
void *thread2(void *arg)
{
while(1)
{
printf("thread2 is running\n");
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);
printf("thread2 applied the condition\n");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t thid1,thid2;
printf("condition variable study!\n");
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL);
pthread_create(&thid1, NULL, thread1, NULL);
pthread_create(&thid2, NULL, thread2, NULL);
sleep(1);
do
{
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
}while(1);
sleep(20);
pthread_exit(0);
return 0;
}#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
static pthread_mutex_t mtx = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
static pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
struct node
{
int n_number;
struct node *n_next;
}*head = NULL;
static void cleanup_handler(void *arg)
{
printf("Cleanup handler of second thread./n");
free(arg);
(void)pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx);
}
static void *thread_func(void *arg)
{
struct node *p = NULL;
pthread_cleanup_push(cleanup_handler, p);
while (1)
{
//这个mutex主要是用来保证pthread_cond_wait的并发性
pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx);
while (head == NULL)
{
//这个while要特别说明一下,单个pthread_cond_wait功能很完善,为何
//这里要有一个while (head == NULL)呢?因为pthread_cond_wait里的线
//程可能会被意外唤醒,如果这个时候head != NULL,则不是我们想要的情况。
//这个时候,应该让线程继续进入pthread_cond_wait
// pthread_cond_wait会先解除之前的pthread_mutex_lock锁定的mtx,
//然后阻塞在等待对列里休眠,直到再次被唤醒(大多数情况下是等待的条件成立
//而被唤醒,唤醒后,该进程会先锁定先pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx);,再读取资源
//用这个流程是比较清楚的
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mtx);
p = head;
head = head->n_next;
printf("Got %d from front of queue/n", p->n_number);
free(p);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx); //临界区数据操作完毕,释放互斥锁
}
pthread_cleanup_pop(0);
return 0;
}
int main(void)
{
pthread_t tid;
int i;
struct node *p;
//子线程会一直等待资源,类似生产者和消费者,但是这里的消费者可以是多个消费者,而
//不仅仅支持普通的单个消费者,这个模型虽然简单,但是很强大
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread_func, NULL);
sleep(1);
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
p = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
p->n_number = i;
pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx); //需要操作head这个临界资源,先加锁,
p->n_next = head;
head = p;
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx); //解锁
sleep(1);
}
printf("thread 1 wanna end the line.So cancel thread 2./n");
//关于pthread_cancel,有一点额外的说明,它是从外部终止子线程,子线程会在最近的取消点,退出
//线程,而在我们的代码里,最近的取消点肯定就是pthread_cond_wait()了。
pthread_cancel(tid);
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
printf("All done -- exiting/n");
return 0;
}
三、信號量(sem)
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define return_if_fail(p) if((p) == 0){printf ("[%s]:func error!/n", __func__);return;}
typedef struct _PrivInfo
{
sem_t s1;
sem_t s2;
time_t end_time;
}PrivInfo;
static void info_init (PrivInfo* thiz);
static void info_destroy (PrivInfo* thiz);
static void* pthread_func_1 (PrivInfo* thiz);
static void* pthread_func_2 (PrivInfo* thiz);
int main (int argc, char** argv)
{
pthread_t pt_1 = 0;
pthread_t pt_2 = 0;
int ret = 0;
PrivInfo* thiz = NULL;
thiz = (PrivInfo* )malloc (sizeof (PrivInfo));
if (thiz == NULL)
{
printf ("[%s]: Failed to malloc priv./n");
return -1;
}
info_init (thiz);
ret = pthread_create (&pt_1, NULL, (void*)pthread_func_1, thiz);
if (ret != 0)
{
perror ("pthread_1_create:");
}
ret = pthread_create (&pt_2, NULL, (void*)pthread_func_2, thiz);
if (ret != 0)
{
perror ("pthread_2_create:");
}
pthread_join (pt_1, NULL);
pthread_join (pt_2, NULL);
info_destroy (thiz);
return 0;
}
static void info_init (PrivInfo* thiz)
{
return_if_fail (thiz != NULL);
thiz->end_time = time(NULL) + 10;
sem_init (&thiz->s1, 0, 1);
sem_init (&thiz->s2, 0, 0);
return;
}
static void info_destroy (PrivInfo* thiz)
{
return_if_fail (thiz != NULL);
sem_destroy (&thiz->s1);
sem_destroy (&thiz->s2);
free (thiz);
thiz = NULL;
return;
}
static void* pthread_func_1 (PrivInfo* thiz)
{
return_if_fail(thiz != NULL);
while (time(NULL) < thiz->end_time)
{
sem_wait (&thiz->s2);
printf ("pthread1: pthread1 get the lock./n");
sem_post (&thiz->s1);
printf ("pthread1: pthread1 unlock/n");
sleep (1);
}
return;
}
static void* pthread_func_2 (PrivInfo* thiz)
{
return_if_fail (thiz != NULL);
while (time (NULL) < thiz->end_time)
{
sem_wait (&thiz->s1);
printf ("pthread2: pthread2 get the unlock./n");
sem_post (&thiz->s2);
printf ("pthread2: pthread2 unlock./n");
sleep (1);
}
return;
}以上是線程同步有幾種方法的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 怎麼刪除微信好友?刪除微信好友的方法
Mar 04, 2024 am 11:10 AM
怎麼刪除微信好友?刪除微信好友的方法
Mar 04, 2024 am 11:10 AM
微信是主流的聊天工具之一,我們可以透過微信認識新的朋友,聯絡老的朋友,維繫朋友之間的友誼。正如天下沒有不散的宴席,人與人之間的相處難免會發生意見不合的時候。當一個人極度影響你的情緒,或是在相處的時候發現三觀不合,沒辦法再繼續溝通,那麼我們可能需要刪除微信好友的方法。怎麼刪除微信好友?刪除微信好友的方法第一步:在微信主介面輕觸【通訊錄】;第二步:點選對應要刪除的好友,進入【詳細資料】;第三步:點選右上角【...】;第四步:點選下方【刪除】即可;第五步:了解後頁面提示後,點選【刪除聯絡人】即可;溫馨
 微信刪除的人如何找回(簡單教學告訴你如何恢復被刪除的聯絡人)
May 01, 2024 pm 12:01 PM
微信刪除的人如何找回(簡單教學告訴你如何恢復被刪除的聯絡人)
May 01, 2024 pm 12:01 PM
而後悔莫及、人們常常會因為一些原因不小心刪除某些聯絡人、微信作為一款廣泛使用的社群軟體。幫助用戶解決這個問題,本文將介紹如何透過簡單的方法找回被刪除的聯絡人。 1.了解微信聯絡人刪除機制這為我們找回被刪除的聯絡人提供了可能性、微信中的聯絡人刪除機制是將其從通訊錄中移除,但並未完全刪除。 2.使用微信內建「通訊錄恢復」功能微信提供了「通訊錄恢復」節省時間和精力,使用者可以透過此功能快速找回先前刪除的聯絡人,功能。 3.進入微信設定頁面點選右下角,開啟微信應用程式「我」再點選右上角設定圖示、進入設定頁面,,
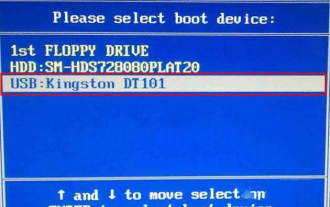 七彩虹主機板怎麼進入bios?教你兩種方法
Mar 13, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
七彩虹主機板怎麼進入bios?教你兩種方法
Mar 13, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
七彩虹主機板在中國國內市場享有較高的知名度和市場佔有率,但是有些七彩虹主機板的用戶還不清楚怎麼進入bios進行設定呢?針對這一情況,小編專門為大家帶來了兩種進入七彩虹主機板bios的方法,快來試試吧!方法一:使用u盤啟動快捷鍵直接進入u盤裝系統七彩虹主機板一鍵啟動u盤的快捷鍵是ESC或F11,首先使用黑鯊裝機大師製作一個黑鯊U盤啟動盤,然後開啟電腦,當看到開機畫面的時候,連續按下鍵盤上的ESC或F11鍵以後將會進入到一個啟動項順序選擇的窗口,將遊標移到顯示“USB”的地方,然
 怎麼在番茄免費小說app中寫小說 分享番茄小說寫小說方法教程
Mar 28, 2024 pm 12:50 PM
怎麼在番茄免費小說app中寫小說 分享番茄小說寫小說方法教程
Mar 28, 2024 pm 12:50 PM
番茄小說是一款非常熱門的小說閱讀軟體,我們在番茄小說中經常會有新的小說和漫畫可以去閱讀,每一本小說和漫畫都很有意思,很多小伙伴也想著要去寫小說來賺取賺取零用錢,在把自己想要寫的小說內容編輯成文字,那麼我們要怎麼樣在這裡面去寫小說呢?小伙伴們都不知道,那就讓我們一起到本站本站中花點時間來看寫小說的方法介紹。分享番茄小說寫小說方法教學 1、先在手機上打開番茄免費小說app,點擊個人中心——作家中心 2、跳到番茄作家助手頁面——點擊創建新書在小說的結
 手機版龍蛋孵化方法大揭密(一步一步教你如何成功孵化手機版龍蛋)
May 04, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
手機版龍蛋孵化方法大揭密(一步一步教你如何成功孵化手機版龍蛋)
May 04, 2024 pm 06:01 PM
手機遊戲成為了人們生活中不可或缺的一部分,隨著科技的發展。它以其可愛的龍蛋形象和有趣的孵化過程吸引了眾多玩家的關注,而其中一款備受矚目的遊戲就是手機版龍蛋。幫助玩家們在遊戲中更好地培養和成長自己的小龍,本文將向大家介紹手機版龍蛋的孵化方法。 1.選擇合適的龍蛋種類玩家需要仔細選擇自己喜歡並且適合自己的龍蛋種類,根據遊戲中提供的不同種類的龍蛋屬性和能力。 2.提升孵化機的等級玩家需要透過完成任務和收集道具來提升孵化機的等級,孵化機的等級決定了孵化速度和孵化成功率。 3.收集孵化所需的資源玩家需要在遊戲中
 Oracle版本查詢方法詳解
Mar 07, 2024 pm 09:21 PM
Oracle版本查詢方法詳解
Mar 07, 2024 pm 09:21 PM
Oracle版本查詢方法詳解Oracle是目前世界上最受歡迎的關聯式資料庫管理系統之一,它提供了豐富的功能和強大的效能,廣泛應用於企業。在進行資料庫管理和開發過程中,了解Oracle資料庫的版本是非常重要的。本文將詳細介紹如何查詢Oracle資料庫的版本信息,並給出具體的程式碼範例。查詢資料庫版本的SQL語句在Oracle資料庫中,可以透過執行簡單的SQL語句
 Win11管理員權限取得方法總計
Mar 09, 2024 am 08:45 AM
Win11管理員權限取得方法總計
Mar 09, 2024 am 08:45 AM
Win11管理員權限取得方法匯總在Windows11作業系統中,管理員權限是非常重要的權限之一,可以讓使用者對系統進行各種操作。有時候,我們可能需要取得管理員權限來完成一些操作,例如安裝軟體、修改系統設定等。下面就為大家總結了一些取得Win11管理員權限的方法,希望能幫助大家。 1.使用快捷鍵在Windows11系統中,可以透過快捷鍵的方式快速開啟命令提
 手機字體大小設定方法(輕鬆調整手機字體大小)
May 07, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
手機字體大小設定方法(輕鬆調整手機字體大小)
May 07, 2024 pm 03:34 PM
字體大小的設定成為了重要的個人化需求,隨著手機成為人們日常生活的重要工具。以滿足不同使用者的需求、本文將介紹如何透過簡單的操作,提升手機使用體驗,調整手機字體大小。為什麼需要調整手機字體大小-調整字體大小可以使文字更清晰易讀-適合不同年齡段用戶的閱讀需求-方便視力不佳的用戶使用手機系統自帶字體大小設置功能-如何進入系統設置界面-在在設定介面中找到並進入"顯示"選項-找到"字體大小"選項並進行調整第三方應用調整字體大小-下載並安裝支援字體大小調整的應用程式-開啟應用程式並進入相關設定介面-根據個人






