
電腦科學中最常用和討論最多的資料結構之一是二元搜尋樹。這通常是引入的第一個具有非線性插入演算法的資料結構。二元搜尋樹類似於雙鍊錶,每個節點包含一些數據,以及兩個指向其他節點的指標;它們在這些節點彼此相關聯的方式上有所不同。二元搜尋樹節點的指標通常被稱為“左”和“右”,用來指示與目前值相關的子樹。這種節點的簡單 JavaScript 實作如下:
var node = {
value: 125,
left: null,
right: null
};從名稱中可以看出,二元搜尋樹被組織成分層的樹狀結構。第一個項目成為根節點,每個附加價值作為該根的祖先添加到樹中。但是,二元搜尋樹節點上的值是唯一的,根據它們包含的值進行排序:作為節點左子樹的值總是小於節點的值,右子樹中的值都是大於節點的值。透過這種方式,在二元搜尋樹中尋找值變得非常簡單,只要你要尋找的值小於正在處理的節點則向左,如果值更大,則向右移動。二元搜尋樹中不能有重複項,因為重複會破壞這種關係。下圖表示一個簡單的二元搜尋樹。
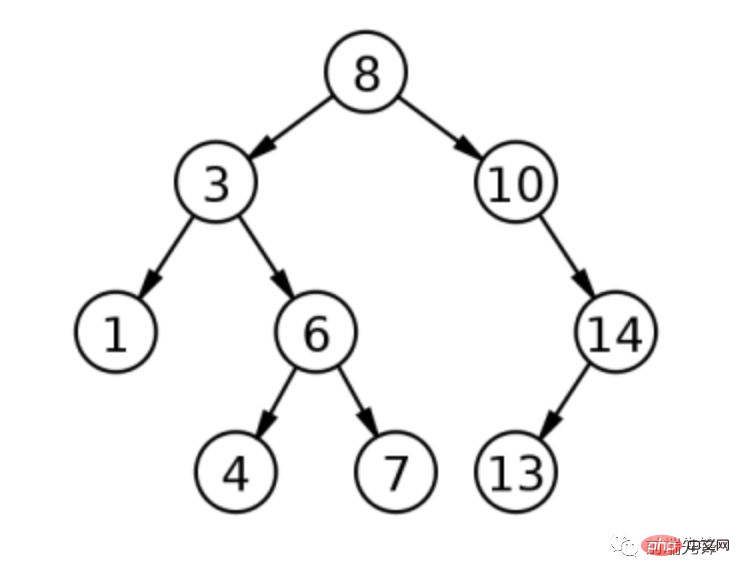
上圖表示一個二元搜尋樹,其根的值為 8。當加值 3 時,它成為根的左子節點,因為 3 小於 8。當增加值 1 時,它變成 3 的左子節點,因為 1 小於 8(所以向左)然後 1 小於3(再向左)。當加值 10 時,它成為跟的右子節點,因為 10 大於 8。不斷用此過程繼續處理值 6,4,7,14 和 13。此二元搜尋樹的深度為 3,表示距離根最遠的節點是三個節點。
二元搜尋樹以自然排序的順序結束,因此可用於快速查找數據,因為你可以立即消除每個步驟的可能性。透過限制需要查找的節點數量,可以更快地進行搜尋。假設你要在上面的樹中找到值 6。從根開始,確定 6 小於 8,因此前往根的左子節點。由於 6 大於 3,因此你將前往右側節點。你就能找到正確的數值。所以你只需訪問三個而不是九個節點來查找這個值。
要在 JavaScript 中實作二元搜尋樹,第一步要先定義基本介面:
function BinarySearchTree() {
this._root = null;
}
BinarySearchTree.prototype = {
//restore constructor
constructor: BinarySearchTree,
add: function (value){
},
contains: function(value){
},
remove: function(value){
},
size: function(){
},
toArray: function(){
},
toString: function(){
}
};基本上接與其他資料結構類似,有新增和刪除值的方法。我還添加了一些方便的方法,size(),toArray()和toString(),它們對 JavaScript 很有用。
要掌握使用二元搜尋樹的方法,最好從 contains() 方法開始。 contains() 方法接受一個值作為參數,如果值存在於樹中則傳回 true,否則傳回 false。此方法遵循基本的二元搜尋演算法來確定該值是否存在:
BinarySearchTree.prototype = {
//more code
contains: function(value){
var found = false,
current = this._root
//make sure there's a node to search
while(!found && current){
//if the value is less than the current node's, go left
if (value < current.value){
current = current.left;
//if the value is greater than the current node's, go right
} else if (value > current.value){
current = current.right;
//values are equal, found it!
} else {
found = true;
}
}
//only proceed if the node was found
return found;
},
//more code
};搜尋從樹的根開始。如果沒有添加數據,則可能沒有根,所以必須進行檢查。遍歷樹遵循前面討論的簡單演算法:如果要尋找的值小於目前節點則向左移動,如果值較大則向右移動。每次都會覆蓋current 指針,直到找到要找的值(在這種情況下found 設定為true)或在那個方向上沒有更多的節點了(在這種情況下,值不在樹上)。
在 contains() 中使用的方法也可用於在樹中插入新值。主要區別在於你要尋找放置新值的位置,而不是在樹中尋找值:
BinarySearchTree.prototype = {
//more code
add: function(value){
//create a new item object, place data in
var node = {
value: value,
left: null,
right: null
},
//used to traverse the structure
current;
//special case: no items in the tree yet
if (this._root === null){
this._root = node;
} else {
current = this._root;
while(true){
//if the new value is less than this node's value, go left
if (value < current.value){
//if there's no left, then the new node belongs there
if (current.left === null){
current.left = node;
break;
} else {
current = current.left;
}
//if the new value is greater than this node's value, go right
} else if (value > current.value){
//if there's no right, then the new node belongs there
if (current.right === null){
current.right = node;
break;
} else {
current = current.right;
}
//if the new value is equal to the current one, just ignore
} else {
break;
}
}
}
},
//more code
};在二元搜尋樹中新增值時,特殊情況是在沒有根的情況。在這種情況下,只需將根設為新值即可輕鬆完成工作。對於其他情況,基本演算法與 contains() 中使用的基本演算法完全相同:新值小於目前節點向左,如果值更大則向右。主要區別在於,當你無法繼續前進時,這就是新值的位置。所以如果你需要向左移動但沒有左側節點,則新值將成為左側節點(與右側節點相同)。由於不存在重複項,因此如果找到具有相同值的節點,則操作將停止。
在继续讨论 size() 方法之前,我想深入讨论树遍历。为了计算二叉搜索树的大小,必须要访问树中的每个节点。二叉搜索树通常会有不同类型的遍历方法,最常用的是有序遍历。通过处理左子树,然后是节点本身,然后是右子树,在每个节点上执行有序遍历。由于二叉搜索树以这种方式排序,从左到右,结果是节点以正确的排序顺序处理。对于 size() 方法,节点遍历的顺序实际上并不重要,但它对 toArray() 方法很重要。由于两种方法都需要执行遍历,我决定添加一个可以通用的 traverse() 方法:
BinarySearchTree.prototype = {
//more code
traverse: function(process){
//helper function
function inOrder(node){
if (node){
//traverse the left subtree
if (node.left !== null){
inOrder(node.left);
}
//call the process method on this node
process.call(this, node);
//traverse the right subtree
if (node.right !== null){
inOrder(node.right);
}
}
}
//start with the root
inOrder(this._root);
},
//more code
};此方法接受一个参数 process,这是一个应该在树中的每个节点上运行的函数。该方法定义了一个名为 inOrder() 的辅助函数用于递归遍历树。注意,如果当前节点存在,则递归仅左右移动(以避免多次处理 null )。然后 traverse() 方法从根节点开始按顺序遍历,process() 函数处理每个节点。然后可以使用此方法实现size()、toArray()、toString():
BinarySearchTree.prototype = {
//more code
size: function(){
var length = 0;
this.traverse(function(node){
length++;
});
return length;
},
toArray: function(){
var result = [];
this.traverse(function(node){
result.push(node.value);
});
return result;
},
toString: function(){
return this.toArray().toString();
},
//more code
};size() 和 toArray() 都调用 traverse() 方法并传入一个函数来在每个节点上运行。在使用 size()的情况下,函数只是递增长度变量,而 toArray() 使用函数将节点的值添加到数组中。 toString()方法在调用 toArray() 之前把返回的数组转换为字符串,并返回 。
删除节点时,你需要确定它是否为根节点。根节点的处理方式与其他节点类似,但明显的例外是根节点需要在结尾处设置为不同的值。为简单起见,这将被视为 JavaScript 代码中的一个特例。
删除节点的第一步是确定节点是否存在:
BinarySearchTree.prototype = {
//more code here
remove: function(value){
var found = false,
parent = null,
current = this._root,
childCount,
replacement,
replacementParent;
//make sure there's a node to search
while(!found && current){
//if the value is less than the current node's, go left
if (value < current.value){
parent = current;
current = current.left;
//if the value is greater than the current node's, go right
} else if (value > current.value){
parent = current;
current = current.right;
//values are equal, found it!
} else {
found = true;
}
}
//only proceed if the node was found
if (found){
//continue
}
},
//more code here
};remove()方法的第一部分是用二叉搜索定位要被删除的节点,如果值小于当前节点的话则向左移动,如果值大于当前节点则向右移动。当遍历时还会跟踪 parent 节点,因为你最终需要从其父节点中删除该节点。当 found 等于 true 时,current 的值是要删除的节点。
删除节点时需要注意三个条件:
1、叶子节点
2、只有一个孩子的节点
3、有两个孩子的节点
从二叉搜索树中删除除了叶节点之外的内容意味着必须移动值来对树正确的排序。前两个实现起来相对简单,只删除了一个叶子节点,删除了一个带有一个子节点的节点并用其子节点替换。最后一种情况有点复杂,以便稍后访问。
在了解如何删除节点之前,你需要知道节点上究竟存在多少个子节点。一旦知道了,你必须确定节点是否为根节点,留下一个相当简单的决策树:
BinarySearchTree.prototype = {
//more code here
remove: function(value){
var found = false,
parent = null,
current = this._root,
childCount,
replacement,
replacementParent;
//find the node (removed for space)
//only proceed if the node was found
if (found){
//figure out how many children
childCount = (current.left !== null ? 1 : 0) +
(current.right !== null ? 1 : 0);
//special case: the value is at the root
if (current === this._root){
switch(childCount){
//no children, just erase the root
case 0:
this._root = null;
break;
//one child, use one as the root
case 1:
this._root = (current.right === null ?
current.left : current.right);
break;
//two children, little work to do
case 2:
//TODO
//no default
}
//non-root values
} else {
switch (childCount){
//no children, just remove it from the parent
case 0:
//if the current value is less than its
//parent's, null out the left pointer
if (current.value < parent.value){
parent.left = null;
//if the current value is greater than its
//parent's, null out the right pointer
} else {
parent.right = null;
}
break;
//one child, just reassign to parent
case 1:
//if the current value is less than its
//parent's, reset the left pointer
if (current.value < parent.value){
parent.left = (current.left === null ?
current.right : current.left);
//if the current value is greater than its
//parent's, reset the right pointer
} else {
parent.right = (current.left === null ?
current.right : current.left);
}
break;
//two children, a bit more complicated
case 2:
//TODO
//no default
}
}
}
},
//more code here
};处理根节点时,这是一个覆盖它的简单过程。对于非根节点,必须根据要删除的节点的值设置 parent 上的相应指针:如果删除的值小于父节点,则 left 指针必须重置为 null (对于没有子节点的节点)或删除节点的 left 指针;如果删除的值大于父级,则必须将 right 指针重置为 null 或删除的节点的 right指针。
如前所述,删除具有两个子节点的节点是最复杂的操作。考虑二元搜索树的以下表示。
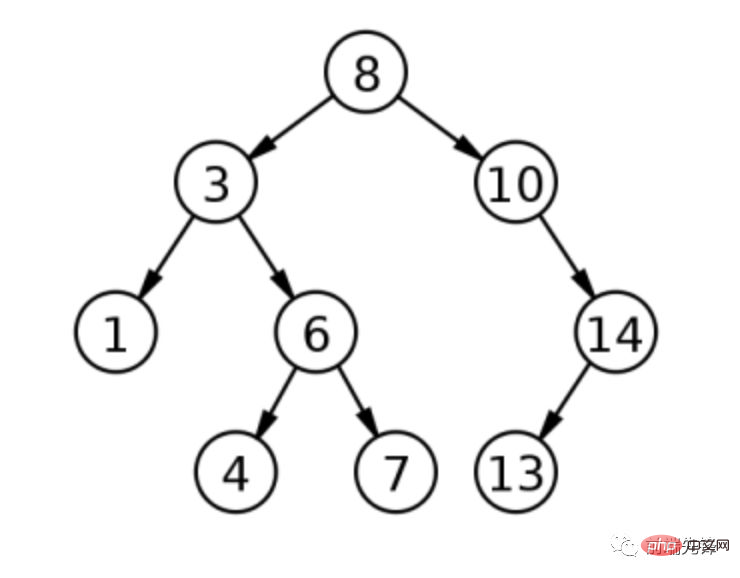
根为 8,左子为 3,如果 3 被删除会发生什么?有两种可能性:1(3 左边的孩子,称为有序前身)或4(右子树的最左边的孩子,称为有序继承者)都可以取代 3。
这两个选项中的任何一个都是合适的。要查找有序前驱,即删除值之前的值,请检查要删除的节点的左子树,并选择最右侧的子节点;找到有序后继,在删除值后立即出现的值,反转进程并检查最左侧的右子树。其中每个都需要另一次遍历树来完成操作:
BinarySearchTree.prototype = {
//more code here
remove: function(value){
var found = false,
parent = null,
current = this._root,
childCount,
replacement,
replacementParent;
//find the node (removed for space)
//only proceed if the node was found
if (found){
//figure out how many children
childCount = (current.left !== null ? 1 : 0) +
(current.right !== null ? 1 : 0);
//special case: the value is at the root
if (current === this._root){
switch(childCount){
//other cases removed to save space
//two children, little work to do
case 2:
//new root will be the old root's left child
//...maybe
replacement = this._root.left;
//find the right-most leaf node to be
//the real new root
while (replacement.right !== null){
replacementParent = replacement;
replacement = replacement.right;
}
//it's not the first node on the left
if (replacementParent !== null){
//remove the new root from it's
//previous position
replacementParent.right = replacement.left;
//give the new root all of the old
//root's children
replacement.right = this._root.right;
replacement.left = this._root.left;
} else {
//just assign the children
replacement.right = this._root.right;
}
//officially assign new root
this._root = replacement;
//no default
}
//non-root values
} else {
switch (childCount){
//other cases removed to save space
//two children, a bit more complicated
case 2:
//reset pointers for new traversal
replacement = current.left;
replacementParent = current;
//find the right-most node
while(replacement.right !== null){
replacementParent = replacement;
replacement = replacement.right;
}
replacementParent.right = replacement.left;
//assign children to the replacement
replacement.right = current.right;
replacement.left = current.left;
//place the replacement in the right spot
if (current.value < parent.value){
parent.left = replacement;
} else {
parent.right = replacement;
}
//no default
}
}
}
},
//more code here
};具有两个子节点的根节点和非根节点的代码几乎相同。此实现始终通过查看左子树并查找最右侧子节点来查找有序前驱。遍历是使用 while 循环中的 replacement 和 replacementParent 变量完成的。
replacement中的节点最终成为替换 current 的节点,因此通过将其父级的 right 指针设置为替换的 left 指针,将其从当前位置移除。
對於根節點,當replacement 是根節點的直接子節點時,replacementParent 將為null,因此replacement 的right 指標只是設定為root 的right 指標。
最後一步是將替換節點分配到正確的位置。對於根節點,替換設定為新根;對於非根節點,替換被指派到原始 parent 上的適當位置。
關於此實現的說明:始終用有序前驅物替換節點可能導致不平衡樹,其中大多數值會位於樹的一側。不平衡樹意味著搜尋效率較低,因此在實際場景中應該引起關注。在二元搜尋樹實作中,要確定是用有序前驅還是有序後繼以使樹保持適當平衡(通常稱為自平衡二元搜尋樹)。
這個二元搜尋樹實現的完整原始程式碼可以在我的GitHub 中找到。對於替代實現,你也可以查看 Isaac Schlueter 的 GitHub fork。
本文轉載自:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000020044659
英文原文網址:https://humanwhocodes.com/blog/2009/06/09/ computer-science-in-javascript-binary-search-tree-part-1/
作者:Nicholas C. Zakas
推薦教學:《JavaScript影片教學》
以上是一文了解JS實作二元搜尋樹的方法的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!


