事件原由
(推薦教學:web伺服器安全性)
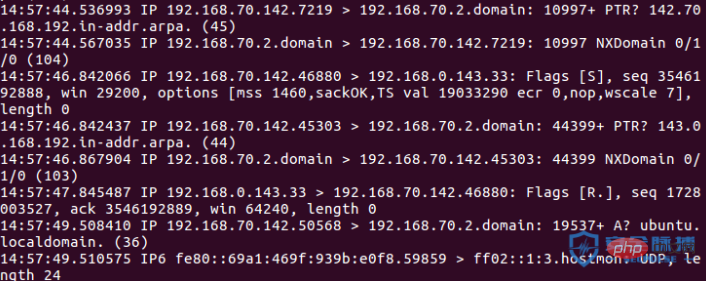
筆者在寫一個小工具,針對滲透測試中需要蒐集的信息,使用腳本自動化採集。而在這個模組中有個很難搞的部分就是端口banner 資訊蒐集,起初我嘗試使用了python nmap 多線程掃描,掃描20 的ip,等的花都謝了。 。 。而筆者目標是掃描200 的ip。下面我就針對連接埠掃描的技術進行分析。
1、nmap探測埠
nmap在掃描多個主機的時候可以設定參數--min-hostgroup ,設定這個參數可以並行掃描多個主機,將這些主機分割成群組,然後一次掃描一個群組。
範例:
--min-hostgroup 50 nmap 以50個主機為一組,在掃描完50個主機之前不會顯示結果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | #coding=utf-8
import nmap
from queue import Queue
from threading import Thread
def portscan(ip):
portlist = []
nm = nmap.PortScannerYield()
for r in nm.scan(ip,ports='1-10000',arguments='-sS --min-hostgroup'):
m = r[1]['scan'][ip]['tcp']
for p in m:
temp = str(p) + "----" +m[p]['state']
portlist.append(temp)
print(portlist)
class Consumer(Thread):
def __init__(self, q):
Thread.__init__(self)
self.q = q
def run(self):
while not self.q.empty():
ip = self.q.get()
try:
portscan(ip)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
continue
def producer(ip_list):
num = 10
threads = []
q = Queue()
for i in ip_list:
print(i)
q.put(i)
threads = [Consumer(q) for i in range(0,int(num))]
for t in threads:
t.start()
for t in threads:
t.join()
ip_list =['120.78.207.76', '120.78.207.231', '120.78.207.18', '120.78.207.233', '120.78.207.165', '120.78.207.48',
'120.78.207.112', '120.78.207.27', '120.78.207.51', '120.78.207.8']
producer(ip_list)
|
登入後複製

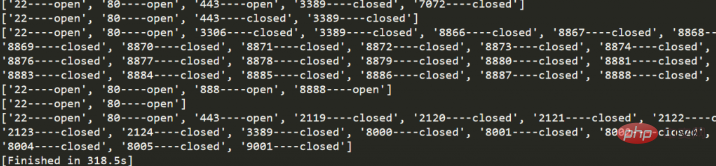
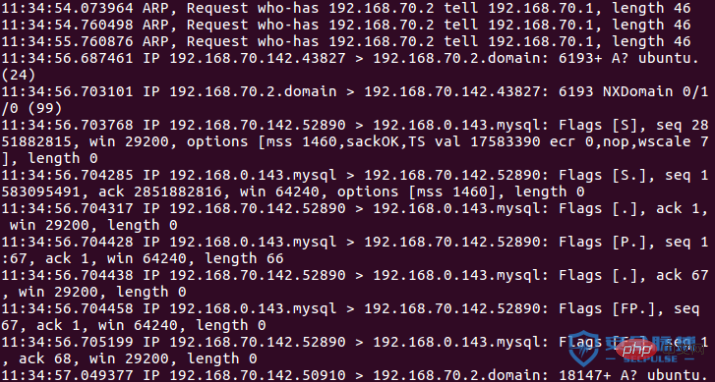
如圖,執行10個ip需要318s。
2、masscan探測埠
(1)呼叫python masscan
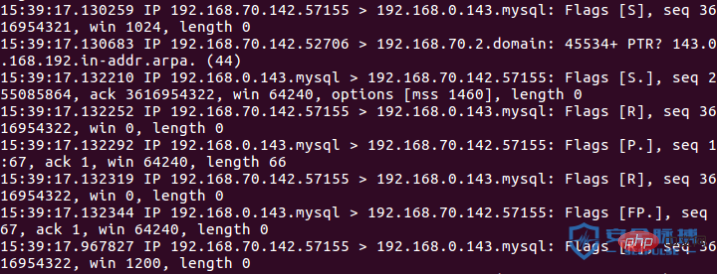
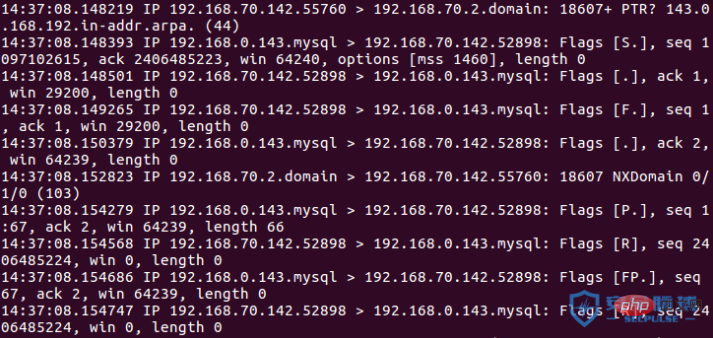
預設情況下,masscan 傳送的是syn封包,如果目標主機回傳ack syn,則說明連接埠開放。具體流程如下
A:192.168.70.142
B:192.168.0.143 開放埠3306
(1)A->B syn
( 2)B->A syn ack
(3)A->B RST

探測未開放的連接埠
# A->B syn
B->A rst

#範例:
1 2 3 4 | def portscan(ip):
mas = masscan.PortScanner()
mas.scan(ip,ports='1-65535')
print(mas.scan_result)
|
登入後複製
使用系統指令探測
#使用方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | 扫描扫描443端口的B类子网
Masscan 10.11.0.0/16 -p443
扫描80或443端口的B类子网
Masscan 10.11.0.0/16 -p80,443
扫描100个常见端口的B类子网,每秒100,000个数据包
Masscan 10.11.0.0/16 --top-ports 100 -rate 100000
结果输出
-oX filename:输出到filename的XML。
-oG filename:输出到filename在的grepable格式。
-oJ filename:输出到filename在JSON格式。
|
登入後複製
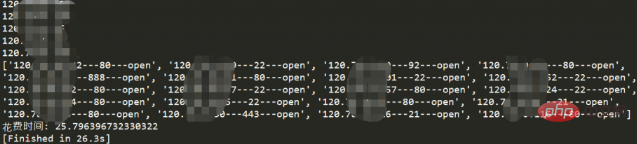
3、socket探測埠
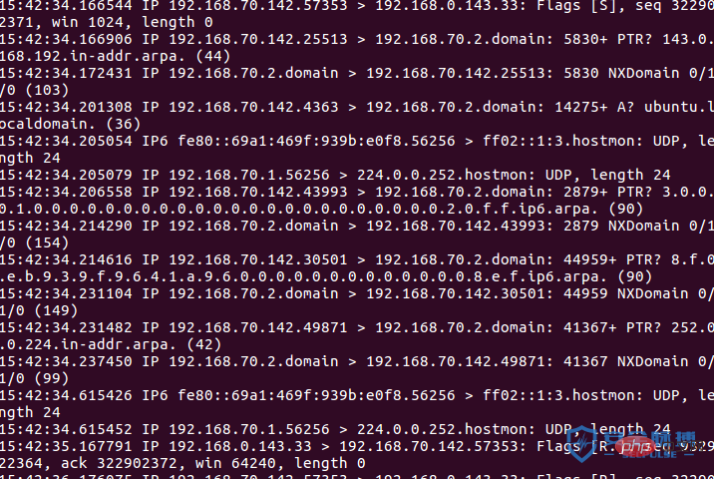
socket 偵測埠發送的不是完整的三次握手包如下,
A:192.168.70.142
B:192.168.0.143 開放埠3306
A接收到B回傳的syn ack封包後,A丟棄資料。

探測不開放端口
A發送syn,B沒有開放33端口,所以返回RST封包。

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | def portscan(ip,port):
try:
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.settimeout(0.2)
status = s.connect_ex((ip,port))
if status == 0:
temp_str = str(ip) + "---" + str(port) + "---open"
port_list.append(temp_str)
else:
pass
except Exception as e:
pass
finally:
s.close()
|
登入後複製

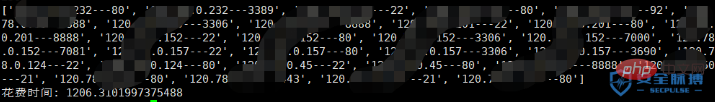
探測10個ip花了26.3s差不多一個2.6s。
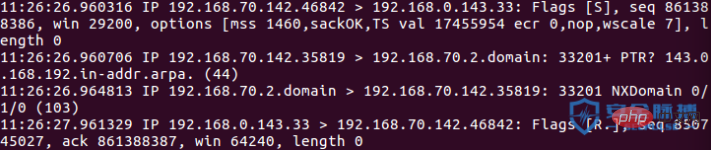
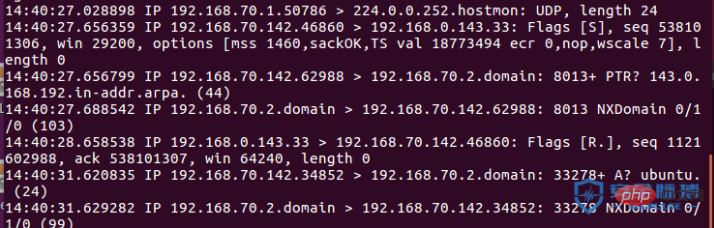
4、telnet探測埠
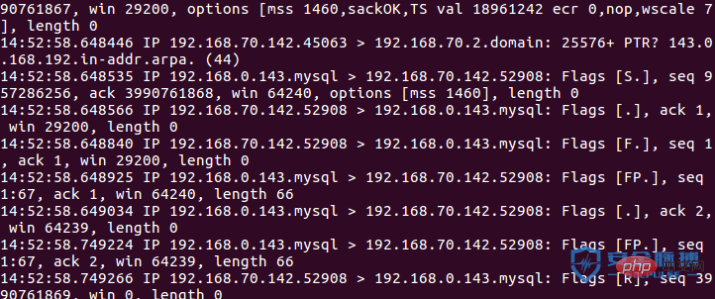
telnet 偵測埠採用完整的三次握手連接,使用指令telnet ip port ,發包流程如下
A:192.168.70.142
B:192.168.0.143 開放端口3306
telnet 192.168.0.143 3306
過程如下:
使用TCP三次握手建立連接: SYN -> SYN ACK ACK

探测不存在端口,发送SYN数据包,然后RST包丢弃。

如果有返回值,则说明端口开放,否则则端口关闭。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | def portscan(ip,port):
try:
t = telnetlib.Telnet(ip,port=port,timeout=0.2)
if t:
temp_str = str(ip) + '---' + str(port)
port_list.append(temp_str)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
pass
|
登入後複製

探测10个ip花费了27.8s差不多一个2.7s。
5、nc探测端口
nc探测端口采用完整的三次握手连接,使用命令 nc -v -w 1 -z ip port,发包过程和telent 探测一样。
探测开放端口的数据包

探测未开放端口的数据包

端口开放,返回值为0,可以依此作为判断依据。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | def portscan(ip,port):
command = 'nc -v -w 1 -z {0} {1}'.format(ip,port)
m = os.system(command)
if m == 0:
temp_str = str(ip) + "---" + str(port)
port_list.append(temp_str)
else:
pass
|
登入後複製

备注:比如你想探测某个指定的端口开放情况,推荐使用nc。
总结
nmap 作为扫描端口的神器,扫描出的结果比其他几种方式要详细。如果追求效率的话,建议采用socket。相比于nmap,socket会存在漏报情况,笔者在测试某主机时,nmap扫出了8888端口,但是socket没有。
以上是連接埠掃描有哪幾種方式的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!