淺談 Node.js 中間件的工作原理

什麼是 Express 中間件?
- 中間件在字面上的意思是你在軟體的一層和另一層中間放置的任何東西。
- Express 中間件是在 Express 伺服器請求的生命週期內所執行的函數。
- 每個中間件都可以存取其被附加到的所有路由的 HTTP 請求和回應。
- 另外,中間件可以終止 HTTP 請求,也可以用 next 將其傳遞給另一個中間件函數。中間件的這種「鏈」使你可以將程式碼劃分並創建可重複使用的中間件。
寫 Express 中間件的要求
你需要安裝一些東西來建立、使用和測試 Express 中間件。首先需要 Node 和 NPM。為確保已經安裝,可以運行:
npm -v && node -v
你應該會看到已安裝的 Node 和 NPM 版本。如果出現錯誤,則需要安裝 Node。所有範例都應在 Node ver 8 和NPM ver 5 下使用。
本文使用了 Express 4.x 版。這很重要,因為從 3.x 版到 4.x 版有重大的變更。
Express中間件:基礎
首先我們使用 Express 最基本的內建中間件。建立一個新專案並 npm 初始化它…
npm init
npm install express --save
Create server.js and paste the following code:
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.get('/', (req, res, next) => {
res.send('Welcome Home');
});
app.listen(3000);中間件解決什麼問題?為什麼要用它?
假設你在 web 網路伺服器上正在使用 Node.js 和 Express 運行Web應用程式。在這個應用程式中,你需要登入的某些頁面。
當 Web 伺服器收到資料請求時,Express 將為你提供一個請求對象,其中包含有關使用者及其所請求資料的資訊。 Express 還使你可以存取回應對象,可以在Web伺服器回應使用者之前對其進行修改。這些物件通常會縮短為 req,res。
中間件函數是使用相關資訊修改 req 和 res 物件的理想場所。例如使用者登入後,你可以從資料庫中取得其使用者詳細信息,然後將這些詳細資訊儲存在 res.user 中。
中間件函數是什麼樣的?
async function userMiddleware (req, res, next) {
try {
const userData = await getUserData(req.params.id); //see app.get below
if(userData) {
req.user = userData;
next();
}
} catch(error) {
res.status(500).send(error.message); //replace with proper error handling
}
}如果發生錯誤,並且你不想執行其他程式碼,則不要呼叫該函數。請記住在這種情況下要發送回應,否則客戶端將會等待回應直到逾時。
var app = express(); //your normal route Handlers app.get('/user/:id', userMiddleware, userController);
中間件鏈
你可以在中間件數組中或著透過使用多個app.use 呼叫來連結中間件:
app.use(middlewareA); app.use(middlewareB); app.get('/', [middlewareC, middlewareD], handler);
Express 收到請求後,與請求相符的每個中間件都會按照初始化的順序運行,直到有終止操作為止。
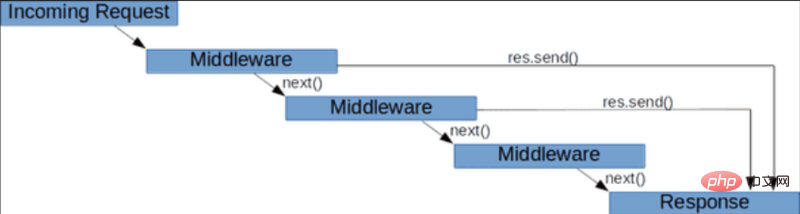
因此,如果發生錯誤,則會依序呼叫所有用於處理錯誤的中間件,直到其中一個不再呼叫next()函數呼叫為止。
Express中間件的型別
- 路由器級中間件,例如:router.use
- 內建中間件,例如:express.static,express.json, express.urlencoded
- 錯誤處理中間件,例如:app.use(err,req,res,next)
- #第三方中間件,例如:bodyparser、cookieparser
- #路由器級中間件
express.Router 使用express.Router 類別建立模組化的、可安裝的路由處理。路由實例是一個完整的中間件和路由系統。
- 你可以用中間件進行日誌記錄、驗證等操作。如下所示,以記錄使用者的最新活動並解析身分驗證標頭,用它來確定目前登入的使用者並將其新增至 Request 物件。
- 該函數在程式每次收到請求時執行。如果有錯誤,它會僅結束回應,而不會呼叫後續的中間件或路由處理。
var router = express.Router()
//Load router-level middleware by using the router.use() and router.METHOD() functions.
//The following example creates a router as a module, loads a middleware function in it,
// defines some routes, and mounts the router module on a path in the main app.
var express = require(‘express’);
var router = express.Router();
// a middleware function with no mount path. This code is executed for
// every request to the router
// logging
async function logMiddleware (req, res, next) {
try {
console.log(req.user.id, new Date());
next();
} catch() {
res.status(500).send(error.message);
}
}
// authentication
async function checkAuthentication(req, res, next) => {
// check header or url parameters or post parameters for token
const token = req.body.token || req.query.token || req.headers['x-access-token']
|| req.headers['authorization'];
if (token) {
try {
// verifies secret
req.decoded = await jwt.verify(token, config.secret)
let checkUser = await authenticateTokenHelper.getUserDetail(req);
// if everything is good, save to request for use in other routes
if (checkUser) {
req.user = req.decoded
next()
} else {
return res.status(403).json({
message: responseMessage.noAuthorized
})
}
} catch (err) {
return res.status(401).json({ message: responseMessage.invalidToken })
}
} else {
// if there is no token
return res.status(400).json({ message: responseMessage.invalidRequest })
}
}
router.use(logMiddleware);
router.get('/user, checkAuthentication, handler);內建中間件
Express 有以下內建的中間件功能:
express.static提供靜態資源,例如HTML 文件,圖像等。express.json負載解析用 JSON 傳入的請求。express.urlencoded解析傳入的以 URL 編碼的有效載荷請求。
錯誤處理中間件
錯誤處理中間件總是採用四個參數(err,req,res,next)。你必須透過提供四個參數來將其標識為錯誤處理中間件函數。即使你不需要使用 next 對象,也必須指定。否則 next 物件將被解釋為常規中間件,並將無法處理錯誤。基本簽章如下圖:
app.use(function (err, req, res, next) {
console.error(err.stack)
res.status(500).send('Something broke!')
})範例1:
app.get('/users', (req, res, next) => {
next(new Error('I am passing you an error!'));
});
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
console.log(err);
if(!res.headersSent){
res.status(500).send(err.message);
}
});在这种情况下,管道末端的错误处理中间件将会处理该错误。你可能还会注意到,我检查了 res.headersSent 属性。这只是检查响应是否已经将标头发送到客户端。如果还没有,它将向客户端发送 HTTP 500 状态和错误消息。
例2:
你还可以链接错误处理中间件。通常以不同的方式处理不同类型的错误:
app.get('/users, (req, res, next) => {
let err = new Error('I couldn\'t find it.');
err.httpStatusCode = 404;
next(err);
});
app.get('/user, (req, res, next) => {
let err = new Error('I\'m sorry, you can\'t do that, Dave.');
err.httpStatusCode = 304;
next(err);
});
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
// handles not found errors
if (err.httpStatusCode === 404) {
res.status(400).render('NotFound');
}
// handles unauthorized errors
else if(err.httpStatusCode === 304){
res.status(304).render('Unauthorized');
}
// catch all
else if (!res.headersSent) {
res.status(err.httpStatusCode || 500).render('UnknownError');
}
next(err);
});- 在这种情况下,中间件检查是否抛出了 404(not found)错误。如果是,它将渲染 “NotFound” 模板页面,然后将错误传递到中间件中的下一项。
- 下一个中间件检查是否抛出了 304(unauthorized)错误。如果是,它将渲染“Unauthorized”页面,并将错误传递到管道中的下一个中间件。
- 最后,“catch all” 错误处理仅记录错误,如果未发送响应,它将发送错误的 httpStatusCode(如果未提供则发送 HTTP 500 状态)并渲染 “UnknownError” 模板。
第三方级别的中间件
在某些情况下,我们将向后端添加一些额外的功能。先安装 Node.js 模块获取所需的功能,然后在应用级别或路由器级别将其加载到你的应用中。
示例:当 body-parser 处理 Content-Type 请求标头时,所有中间件都将使用解析的正文填充 req.body 属性。
const express = require('express');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const app = express();
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({extended:false}))
app.use(bodyParser.json())
app.post('/save',(req,res)=>{
res.json({
"status":true,
"payload":req.body
})
}
app.listen(3000,(req,res)=>{
console.log('server running on port')
})总结
中间件功能是一种非常好的方式,可以对每个请求或针对特定路由的每个请求运行代码,并对请求或响应数据采取措施。中间件是现代 Web 服务器的重要组成部分,并且非常有用。
英文原文地址:https://www.thirdrocktechkno.com/blog/how-Node-JS-middleware-works/
为了保证的可读性,本文采用意译而非直译。
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程入门!!
以上是淺談 Node.js 中間件的工作原理的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 tomcat中間件原理是什麼
Dec 27, 2023 pm 04:40 PM
tomcat中間件原理是什麼
Dec 27, 2023 pm 04:40 PM
tomcat中間件原理是基於Java Servlet和Java EE規格來實現的。 Tomcat作為Servlet容器,負責處理HTTP請求和回應,提供Web應用程式的運作環境。 Tomcat中間件的原理主要涉及:1、容器模型;2、元件化架構;3、Servlet處理機制;4、事件監聽和過濾器;5、組態管理;6、安全性;7、叢集和負載平衡; 8、連接器技術;9、嵌入式模式等等。
 如何在Laravel中使用中間件處理表單驗證
Nov 02, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
如何在Laravel中使用中間件處理表單驗證
Nov 02, 2023 pm 03:57 PM
如何在Laravel中使用中間件處理表單驗證,需要具體程式碼範例引言:在Laravel中,表單驗證是非常常見的任務。為了確保使用者輸入的資料的有效性和安全性,我們通常會對表單提交的資料進行驗證。 Laravel提供了一個方便的表單驗證功能,同時也支援使用中間件來處理表單驗證。本文將詳細介紹如何在Laravel中使用中間件處理表單驗證,並提供具體的程式碼範例
 如何在Laravel中使用中間件進行資料加速
Nov 02, 2023 am 09:40 AM
如何在Laravel中使用中間件進行資料加速
Nov 02, 2023 am 09:40 AM
如何在Laravel中使用中間件進行資料加速引言:在使用Laravel框架開發Web應用程式時,資料加速是提高應用程式效能的關鍵。中間件是Laravel提供的重要功能,可以在請求到達控制器之前或回應返回之前對請求進行處理。本文將重點放在如何在Laravel中使用中間件實現資料加速,並提供具體的程式碼範例。一、什麼是中間件中間件是Laravel框架中一種機制,用
 如何在Laravel中使用中間件進行回應轉換
Nov 03, 2023 am 09:57 AM
如何在Laravel中使用中間件進行回應轉換
Nov 03, 2023 am 09:57 AM
如何在Laravel中使用中間件進行回應轉換中間件是Laravel框架中非常強大且實用的功能之一。它允許我們在請求進入控制器之前或回應被發送給客戶端之前,對請求和回應進行處理。在本文中,我將示範如何使用中間件在Laravel中進行回應轉換。在開始之前,確保你已經安裝了Laravel並創建了一個新的專案。現在,我們將按照以下步驟進行操作:建立一個新的中間件打開
 如何在Laravel中使用中間件進行資料恢復
Nov 02, 2023 pm 02:12 PM
如何在Laravel中使用中間件進行資料恢復
Nov 02, 2023 pm 02:12 PM
Laravel是一個流行的PHPWeb應用程式框架,提供了許多快速且簡單的方式來建立高效、安全且可擴展的Web應用程式。在開發Laravel應用程式時,我們經常需要考慮資料恢復的問題,即如何在資料遺失或損壞的情況下恢復資料並保證應用程式的正常運作。在本文中,我們將介紹如何使用Laravel中間件來實現資料復原功能,並提供具體的程式碼範例。一、什麼是Lara
 在Slim框架中使用中間件(Middleware)設定跨域資源共享(CORS)的方法
Jul 30, 2023 pm 08:34 PM
在Slim框架中使用中間件(Middleware)設定跨域資源共享(CORS)的方法
Jul 30, 2023 pm 08:34 PM
在Slim框架中使用中間件(Middleware)設定跨域資源共享(CORS)的方法跨域資源共享(CORS)是一種機制,允許伺服器在HTTP響應頭中設定一些額外的信息,來告知瀏覽器是否允許跨域請求。在一些前後端分離的專案中,使用CORS機制可以實現前端跨域請求後端介面的需求。在使用Slim框架開發RESTAPI時,我們可以使用中間件(Middleware)
 如何在Laravel中使用中間件進行定時任務調度
Nov 02, 2023 pm 02:26 PM
如何在Laravel中使用中間件進行定時任務調度
Nov 02, 2023 pm 02:26 PM
如何在Laravel中使用中間件進行定時任務調度引言:Laravel是一款流行的PHP開源框架,提供了便捷且強大的工具來開發Web應用程式。其中一個重要的特性是定時任務調度,它可以讓開發者在指定的時間間隔內執行特定的任務。在本文中,我們將介紹如何使用中間件來實現Laravel的定時任務調度,並提供具體的程式碼範例。環境準備在開始之前,我們需要確保
 CodeIgniter中間件:提供安全的檔案上傳和下載功能
Aug 01, 2023 pm 03:01 PM
CodeIgniter中間件:提供安全的檔案上傳和下載功能
Aug 01, 2023 pm 03:01 PM
CodeIgniter中間件:提供安全的檔案上傳和下載功能引言:在網路應用程式開發過程中,檔案上傳和下載是非常常見的功能。然而,對於安全性的考慮,處理文件上傳和下載通常需要額外的安全措施。 CodeIgniter是一個流行的PHP框架,提供了豐富的工具和函式庫來支援開發者建立安全可靠的網路應用程式。本文將介紹如何使用CodeIgniter中介軟體來實現安全的文件






