詳解JavaScript中async/await的使用方法

ES8 引入的 async/await 在 JavaScript 的非同步程式設計中是一個極好的改進。它提供了使用同步樣式程式碼非同步存取 resoruces 的方式,而不會阻塞主執行緒。然而,它們也存在一些坑及問題。在本文中,將從不同的角度探討 async/await,並示範如何正確有效地使用這對兄弟。
前置知識
async 作用是什麼
#從MDN 可以看出:
async函數傳回的是一個Promise 物件。 async 函數(包含函數語句、函數表達式、Lambda表達式)會傳回一個Promise 對象,如果在函數中return 一個直接量,async 會把這個直接量通過Promise.resolve() 封裝成Promise 物件。
如果 async 函數沒有傳回值, 它會傳回 Promise.resolve(undefined)。
await 作用是什麼
從MDN 了解到:
await 等待的是一個表達式,這個表達式的計算結果是Promise 物件或其它值(換句話說,await 可以等任意表達式的結果)。
如果它等到的不是一個 Promise 對象,那麼 await 表達式的運算結果就是它等到的東西。
如果它等到的是一個 Promise 對象,await 就忙起來了,它會阻塞後面的程式碼,等著 Promise 物件 resolve,然後得到 resolve 的值,作為 await 表達式的運算結果。
這就是 await 必須用在 async 函數中的原因。 async 函數呼叫不會造成阻塞,它內部所有的阻塞都被封裝在一個 Promise 物件中非同步執行。
async/await 的優點
async/await 帶給我們的最重要的好處是同步程式設計風格。讓我們來看一個例子:
// async/await
async getBooksByAuthorWithAwait(authorId) {
const books = await bookModel.fetchAll();
return books.filter(b => b.authorId === authorId);
}// promise
getBooksByAuthorWithPromise(authorId) {
return bookModel.fetchAll()
.then(books => books.filter(b => b.authorId === authorId));
}很明顯,async/await 版本比 promise 版本更容易理解。如果忽略 await 關鍵字,程式碼看起來就像任何其他同步語言,例如 Python。
最佳的地方不僅在於可讀性。 async/await 到今天為止,所有主流瀏覽器都完全支援非同步功能。
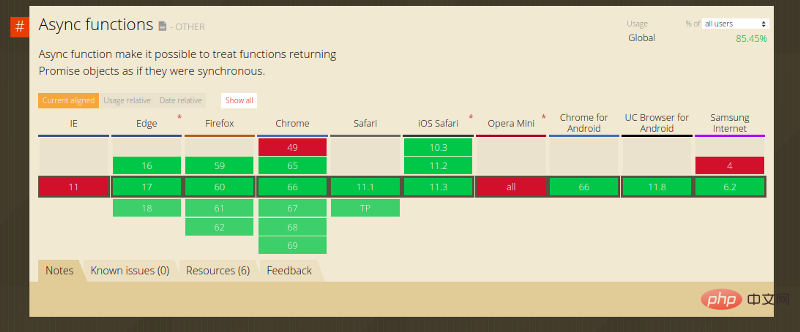
本機瀏覽器的支援意味著你不必轉換程式碼。更重要的是,它便於調試。當在函數入口點設定斷點並跨越await 行時,將看到偵錯器在bookModel.fetchAll() 執行其任務時暫停片刻,然後它將移動到下一個.filter 行,這比promise# 程式碼簡單得多,在promise 中,必須在.filter 行上設定另一個斷點。

另一個不太明顯的優點是 async 關鍵字。 async宣告getBooksByAuthorWithAwait()函數傳回值可確保是一個promise,因此呼叫者可以安全地使用getBooksByAuthorWithAwait() .then(...) 或await getBooksByAuthorWithAwait()。想想下面的範例(不好的做法!):
getBooksByAuthorWithPromise(authorId) {
if (!authorId) {
return null;
}
return bookModel.fetchAll()
.then(books => books.filter(b => b.authorId === authorId));
}在上述程式碼中,getBooksByAuthorWithPromise 可能回傳promise(正常情況下)或 null 值(異常情況下),在異常情況下,呼叫者不能呼叫.then()。有了async 聲明,這種情況就不會出現了。
async/await 可能會產生誤導
一些文章將async/wait 與Promise 進行了比較,並聲稱它是JavaScript 下一代非同步程式設計風格,對此作者深表異議。 async/await 是一種改進,但它只不過是一種語法糖,不會完全改變我們的程式風格。
本質上來說,async 函數仍然是 promise。在正確使用async 函數之前,你必須先了解 promise,更糟的是,大多數時候你需要在使用promises 的同時使用 async 函數。
考慮上面範例中的 getBooksByAuthorWithAwait() 和getbooksbyauthorwithpromise() 函數。請注意,它們不僅功能相同,而且具有完全相同的介面!
這意味著getbooksbyauthorwithwait() 將傳回一個promise,所以也可以使用.then(...)方式來呼叫它。
嗯,这未必是件坏事。只有 await 的名字给人一种感觉,“哦,太好了,可以把异步函数转换成同步函数了”,这实际上是错误的。
async/await
那么在使用 async/await 时可能会犯什么错误呢?下面是一些常见的例子。
太过串行化
尽管 await 可以使代码看起来像是同步的,但实际它们仍然是异步的,必须小心避免太过串行化。
async getBooksAndAuthor(authorId) {
const books = await bookModel.fetchAll();
const author = await authorModel.fetch(authorId);
return {
author,
books: books.filter(book => book.authorId === authorId),
};
}上述代码在逻辑上看似正确的,然而,这是错误的。
await bookModel.fetchAll()会等待fetchAll()直到fetchAll()返回结果。- 然后
await authorModel.fetch(authorId)被调用。
注意,authorModel.fetch(authorId) 并不依赖于 bookModel.fetchAll() 的结果,实际上它们可以并行调用!然而,用了 await,两个调用变成串行的,总的执行时间将比并行版本要长得多得多。
下面是正确的方式:
async getBooksAndAuthor(authorId) {
const bookPromise = bookModel.fetchAll();
const authorPromise = authorModel.fetch(authorId);
const book = await bookPromise;
const author = await authorPromise;
return {
author,
books: books.filter(book => book.authorId === authorId),
};
}更糟糕的是,如果你想要一个接一个地获取项目列表,你必须依赖使用 promises:
async getAuthors(authorIds) {
// WRONG, this will cause sequential calls
// const authors = _.map(
// authorIds,
// id => await authorModel.fetch(id));// CORRECT
const promises = _.map(authorIds, id => authorModel.fetch(id));
const authors = await Promise.all(promises);
}简而言之,你仍然需要将流程视为异步的,然后使用 await 写出同步的代码。在复杂的流程中,直接使用 promise 可能更方便。
错误处理
在 promise中,异步函数有两个可能的返回值: resolved 和 rejected。我们可以用 .then() 处理正常情况,用 .catch() 处理异常情况。然而,使用 async/await方式的,错误处理可能比较棘手。
try…catch
最标准的(也是作者推荐的)方法是使用 try...catch 语法。在 await 调用时,在调用 await 函数时,如果出现非正常状况就会抛出异常,await 命令后面的 promise 对象,运行结果可能是 rejected,所以最好把await 命令放在 try...catch 代码块中。如下例子:
class BookModel {
fetchAll() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
window.setTimeout(() => { reject({'error': 400}) }, 1000);
});
}
}// async/await
async getBooksByAuthorWithAwait(authorId) {
try {
const books = await bookModel.fetchAll();
} catch (error) {
console.log(error); // { "error": 400 }
}在捕捉到异常之后,有几种方法来处理它:
- 处理异常,并返回一个正常值。(不在
catch块中使用任何return语句相当于使用return undefined,undefined 也是一个正常值。) - 如果你想让调用者处理它,你可以直接抛出普通的错误对象,如
throw errorr,它允许你在 promise 链中使用async getBooksByAuthorWithAwait()函数(也就是说,可以像getBooksByAuthorWithAwait().then(...).catch(error => ...) 处理错误); 或者可以用Error对象将错误封装起来,如throw new Error(error),当这个错误在控制台中显示时,它将给出完整的堆栈跟踪信息。 - 拒绝它,就像
return Promise.reject(error),这相当于throw error,所以不建议这样做。
使用 try...catch 的好处:
- 简单,传统。只要有Java或c++等其他语言的经验,理解这一点就不会有任何困难。
- 如果不需要每步执行错误处理,你仍然可以在一个
try ... catch块中包装多个await调用来处理一个地方的错误。
这种方法也有一个缺陷。由于 try...catch 会捕获代码块中的每个异常,所以通常不会被 promise 捕获的异常也会被捕获到。比如:
class BookModel {
fetchAll() {
cb(); // note `cb` is undefined and will result an exception
return fetch('/books');
}
}try {
bookModel.fetchAll();
} catch(error) {
console.log(error); // This will print "cb is not defined"
}运行此代码,你将得到一个错误 ReferenceError: cb is not defined。这个错误是由console.log()打印出来的的,而不是 JavaScript 本身。有时这可能是致命的:如果 BookModel 被包含在一系列函数调用中,其中一个调用者吞噬了错误,那么就很难找到这样一个未定义的错误。
让函数返回两个值
另一种错误处理方法是受到Go语言的启发。它允许异步函数返回错误和结果。详情请看这篇博客文章:
How to write async await without try-catch blocks in Javascript
简而言之,你可以像这样使用异步函数:
[err, user] = await to(UserModel.findById(1));
作者个人不喜欢这种方法,因为它将 Go 语言的风格带入到了 JavaScript 中,感觉不自然。但在某些情况下,这可能相当有用。
使用 .catch
这里介绍的最后一种方法就是继续使用 .catch()。
回想一下 await 的功能:它将等待 promise 完成它的工作。值得注意的一点是 promise.catch() 也会返回一个 promise ,所以我们可以这样处理错误:
// books === undefined if error happens,
// since nothing returned in the catch statement
let books = await bookModel.fetchAll()
.catch((error) => { console.log(error); });这种方法有两个小问题:
- 它是 promises 和 async 函数的混合体。你仍然需要理解 是promises 如何工作的。
- 错误处理先于正常路径,这是不直观的。
结论
ES7引入的 async/await 关键字无疑是对J avaScrip t异步编程的改进。它可以使代码更容易阅读和调试。然而,为了正确地使用它们,必须完全理解 promise,因为 async/await 只不过是 promise 的语法糖,本质上仍然是 promise。
英文原文地址:https://hackernoon.com/javascript-async-await-the-good-part-pitfalls-and-how-to-use-9b759ca21cda
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程入门!!
以上是詳解JavaScript中async/await的使用方法的詳細內容。更多資訊請關注PHP中文網其他相關文章!

熱AI工具

Undresser.AI Undress
人工智慧驅動的應用程序,用於創建逼真的裸體照片

AI Clothes Remover
用於從照片中去除衣服的線上人工智慧工具。

Undress AI Tool
免費脫衣圖片

Clothoff.io
AI脫衣器

Video Face Swap
使用我們完全免費的人工智慧換臉工具,輕鬆在任何影片中換臉!

熱門文章

熱工具

記事本++7.3.1
好用且免費的程式碼編輯器

SublimeText3漢化版
中文版,非常好用

禪工作室 13.0.1
強大的PHP整合開發環境

Dreamweaver CS6
視覺化網頁開發工具

SublimeText3 Mac版
神級程式碼編輯軟體(SublimeText3)
 如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript實現線上語音辨識系統
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript實現線上語音辨識系統
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript實現線上語音辨識系統引言:隨著科技的不斷發展,語音辨識技術已成為了人工智慧領域的重要組成部分。而基於WebSocket和JavaScript實現的線上語音辨識系統,具備了低延遲、即時性和跨平台的特點,成為了廣泛應用的解決方案。本文將介紹如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript來實現線上語音辨識系
 WebSocket與JavaScript:實現即時監控系統的關鍵技術
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket與JavaScript:實現即時監控系統的關鍵技術
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket與JavaScript:實現即時監控系統的關鍵技術引言:隨著互聯網技術的快速發展,即時監控系統在各個領域中得到了廣泛的應用。而實現即時監控的關鍵技術之一就是WebSocket與JavaScript的結合使用。本文將介紹WebSocket與JavaScript在即時監控系統中的應用,並給出程式碼範例,詳細解釋其實作原理。一、WebSocket技
 如何利用JavaScript和WebSocket實現即時線上點餐系統
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
如何利用JavaScript和WebSocket實現即時線上點餐系統
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
如何利用JavaScript和WebSocket實現即時線上點餐系統介紹:隨著網路的普及和技術的進步,越來越多的餐廳開始提供線上點餐服務。為了實現即時線上點餐系統,我們可以利用JavaScript和WebSocket技術。 WebSocket是一種基於TCP協定的全雙工通訊協議,可實現客戶端與伺服器的即時雙向通訊。在即時線上點餐系統中,當使用者選擇菜餚並下訂單
 如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript實現線上預約系統
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript實現線上預約系統
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript實現線上預約系統在當今數位化的時代,越來越多的業務和服務都需要提供線上預約功能。而實現一個高效、即時的線上預約系統是至關重要的。本文將介紹如何使用WebSocket和JavaScript來實作一個線上預約系統,並提供具體的程式碼範例。一、什麼是WebSocketWebSocket是一種在單一TCP連線上進行全雙工
 JavaScript與WebSocket:打造高效率的即時天氣預報系統
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript與WebSocket:打造高效率的即時天氣預報系統
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript和WebSocket:打造高效的即時天氣預報系統引言:如今,天氣預報的準確性對於日常生活以及決策制定具有重要意義。隨著技術的發展,我們可以透過即時獲取天氣數據來提供更準確可靠的天氣預報。在本文中,我們將學習如何使用JavaScript和WebSocket技術,來建立一個高效的即時天氣預報系統。本文將透過具體的程式碼範例來展示實現的過程。 We
 簡易JavaScript教學:取得HTTP狀態碼的方法
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
簡易JavaScript教學:取得HTTP狀態碼的方法
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript教學:如何取得HTTP狀態碼,需要具體程式碼範例前言:在Web開發中,經常會涉及到與伺服器進行資料互動的場景。在與伺服器進行通訊時,我們經常需要取得傳回的HTTP狀態碼來判斷操作是否成功,並根據不同的狀態碼來進行對應的處理。本篇文章將教你如何使用JavaScript來取得HTTP狀態碼,並提供一些實用的程式碼範例。使用XMLHttpRequest
 javascript如何使用insertBefore
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
javascript如何使用insertBefore
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
用法:在JavaScript中,insertBefore()方法用於在DOM樹中插入一個新的節點。這個方法需要兩個參數:要插入的新節點和參考節點(即新節點將要插入的位置的節點)。
 JavaScript與WebSocket:打造高效率的即時影像處理系統
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript與WebSocket:打造高效率的即時影像處理系統
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript是一種廣泛應用於Web開發的程式語言,而WebSocket則是一種用於即時通訊的網路協定。結合二者的強大功能,我們可以打造一個高效率的即時影像處理系統。本文將介紹如何利用JavaScript和WebSocket來實作這個系統,並提供具體的程式碼範例。首先,我們需要明確指出即時影像處理系統的需求和目標。假設我們有一個攝影機設備,可以擷取即時的影像數






